Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Prime Movers
Uploaded by
vibhuti0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views7 pagesOriginal Title
3. Prime Movers
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views7 pagesPrime Movers
Uploaded by
vibhutiCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
Prime Movers
© 2006 Weatherford. All rights reserved.
Prime Movers
• Electric motors
• Single-cylinder gas engines
• Multi-cylinder gas engines
© 2006 Weatherford. All rights reserved.
Motor Slip
The difference between motor speed at no loads and the
speed when fully loaded, expressed as a percentage of
no load speed. As torque on the motor increases the
motor slows down (slips) and the motor develops more
torque. Slip goes up as motor torque increases.
© 2006 Weatherford. All rights reserved.
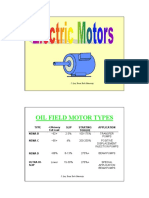
NEMA Motor Classifications
• NEMA B 3% SLIP
• NEMA C 4% SLIP
• NEMA D 5 to 8% SLIP
• NEMA D+ 8 to 13% SLIP
• Special Purpose Greater than 13%
(ultrahigh slip)
Slip = 100 (Synch. RPM-Full load RPM/Synch. RPM)
© 2006 Weatherford. All rights reserved.
Motor Sizing
• HP required = API peak torque rating/3150 x 2.5
• Peak torque is 640,000 in-lb torque
640,000 / (3150 x 2.5) = 81.26
• 1 HP = 0.7457 kW
© 2006 Weatherford. All rights reserved.
Horsepower of Prime Mover
*These values are approximate for high-slip (NEMA D) electric
motors and slow-speed engines.
*HP = BPD x depth
56,000
For normal-slip electric motors and multi-cylinder engines:
*HP = BPD x depth
45,000
Multiply HP by 0.8 for Mark II units.
© 2006 Weatherford. All rights reserved.
Internal Combustion Engines
• Designed to run on natural gas or propane
• Slow-speed engines have a crankshaft speed of 750
RPM or lower.
• High-speed (multi-cylinder) engines have speeds up to
2,000 RPM.
© 2006 Weatherford. All rights reserved.
You might also like
- LS Swaps: How to Swap GM LS Engines into Almost AnythingFrom EverandLS Swaps: How to Swap GM LS Engines into Almost AnythingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Joseph Carraro TransmissionsDocument14 pagesJoseph Carraro TransmissionsHS itNo ratings yet
- MAN V8 V10 V12 Common RailDocument4 pagesMAN V8 V10 V12 Common RailKost KurniaNo ratings yet
- Cat 3512C: Diesel Generator SetsDocument4 pagesCat 3512C: Diesel Generator SetsJavier Delgado Rodríguez100% (1)
- Cat 3512C: Diesel Generator SetsDocument4 pagesCat 3512C: Diesel Generator SetsDavid J SandersNo ratings yet
- Kta38-G5 2Document4 pagesKta38-G5 2Ali AmirNo ratings yet
- Truck Driver Training enDocument33 pagesTruck Driver Training enMUHAMMAD FAUZINo ratings yet
- D2866 PDFDocument4 pagesD2866 PDFMuhammad rizkiNo ratings yet
- 400 Kva DV8Document12 pages400 Kva DV8ravi kumar100% (1)
- Oilproperties.Xls: Γ Api +131 - 5 Ρ Γ R Γ Γ ADocument4 pagesOilproperties.Xls: Γ Api +131 - 5 Ρ Γ R Γ Γ AvibhutiNo ratings yet
- Rod Pump - Failure.analysisDocument109 pagesRod Pump - Failure.analysisvibhutiNo ratings yet
- 4 - Motor Overview and Book Explan - WFD - Rev8Document21 pages4 - Motor Overview and Book Explan - WFD - Rev8josephbenettonNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Roller CamshaftsDocument12 pagesHydraulic Roller Camshaftscrower_scribdNo ratings yet
- HA Series BrochureDocument4 pagesHA Series BrochureAman QureshiNo ratings yet
- Electric Motors How To Read The Nameplate - WorldWide ElectricDocument1 pageElectric Motors How To Read The Nameplate - WorldWide ElectricOsa OsaNo ratings yet
- Cat C32: Diesel Generator SetsDocument6 pagesCat C32: Diesel Generator SetsBilel Ben SlamaNo ratings yet
- Cat 3512B: Diesel Generator SetsDocument9 pagesCat 3512B: Diesel Generator SetsvesadanaNo ratings yet
- 82 - 352 - 6068TF275 - 170 Spec PDFDocument2 pages82 - 352 - 6068TF275 - 170 Spec PDFnay hlaing SoeNo ratings yet
- 3512B - 1500KW - 1875kva - 380V 13800V (2017) (Lehe1250-00)Document9 pages3512B - 1500KW - 1875kva - 380V 13800V (2017) (Lehe1250-00)Darren R. FlorNo ratings yet
- Engine Range en MANDocument24 pagesEngine Range en MANAsik JosNo ratings yet
- GeneratorDocument9 pagesGeneratordinukaeeNo ratings yet
- Motor Divn Presentation 16may20Document55 pagesMotor Divn Presentation 16may20M.Dinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- 106.3 - MotorDocument10 pages106.3 - MotorHassan GDOURANo ratings yet
- Cat C32: Diesel Generator SetsDocument6 pagesCat C32: Diesel Generator Setsavinash_1229No ratings yet
- CM20180319 12475 41483Document5 pagesCM20180319 12475 41483Recep KayaNo ratings yet
- Placa de Caracteristicas Motor IngDocument25 pagesPlaca de Caracteristicas Motor IngJorge ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Cat C32: Diesel Generator SetsDocument6 pagesCat C32: Diesel Generator SetsJean Claude EidNo ratings yet
- Cat C32: Diesel Generator SetsDocument6 pagesCat C32: Diesel Generator SetsIlung MarpaungNo ratings yet
- Powertech 6125H Diesel EngineDocument2 pagesPowertech 6125H Diesel EngineErman IndragiriNo ratings yet
- Nema A, B, C and D DesignDocument3 pagesNema A, B, C and D Designsteve_y100% (1)
- Engine DataSheetDocument4 pagesEngine DataSheetLinda ApriyantiNo ratings yet
- Folder 924KDocument4 pagesFolder 924KDelgado FelipeNo ratings yet
- 3516B - 2000kVA - LV - Spec SheetDocument9 pages3516B - 2000kVA - LV - Spec Sheetavinash_1229No ratings yet
- Lehe1514 02Document5 pagesLehe1514 02Jean Claude EidNo ratings yet
- Cat C32 SubmittalDocument68 pagesCat C32 SubmittalAnh VuNo ratings yet
- KP D50PDocument5 pagesKP D50PDerek ChenNo ratings yet
- Motor Terminology and Electrical Performance CharacteristicsDocument37 pagesMotor Terminology and Electrical Performance CharacteristicsErick Yael Alcantar MaresNo ratings yet
- C32 - 1000KW - 1250kva - 220V 600V (2018) (Lehe1626-01)Document4 pagesC32 - 1000KW - 1250kva - 220V 600V (2018) (Lehe1626-01)Darren R. FlorNo ratings yet
- Cat 3512B: Diesel Generator SetsDocument6 pagesCat 3512B: Diesel Generator SetsMohiuddin totulNo ratings yet
- Cat C175-16: Diesel Generator SetsDocument4 pagesCat C175-16: Diesel Generator SetsMiriam GaboNo ratings yet
- 4bt g3Document4 pages4bt g3acere18No ratings yet
- Electric Motors How To Read The NameplateDocument1 pageElectric Motors How To Read The NameplateSaurabh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Planta Elect. Cat 3512Document5 pagesPlanta Elect. Cat 3512MauricioNo ratings yet
- 3512 - 1100KW 1250KW - 1375kva 1563kva - 380V 13800V (2018) (Lehe1246-01)Document5 pages3512 - 1100KW 1250KW - 1375kva 1563kva - 380V 13800V (2018) (Lehe1246-01)Darren R. FlorNo ratings yet
- WEG Soft StartersDocument38 pagesWEG Soft StartersCyrix.OneNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet QSK38Document4 pagesData Sheet QSK38acere18No ratings yet
- Kta19 G2Document4 pagesKta19 G2Victor Ortega SamNo ratings yet
- Kta38 g6 PDFDocument4 pagesKta38 g6 PDFM Arshad Iqbal HarralNo ratings yet
- CM20180320 16121 49538Document5 pagesCM20180320 16121 49538Ignacio LucasNo ratings yet
- Perkins 750KVA-825KVADocument4 pagesPerkins 750KVA-825KVAHải Nguyễn HồngNo ratings yet
- CM20170815-12040-00839 - C27 Diesel GeneratorDocument4 pagesCM20170815-12040-00839 - C27 Diesel GeneratorAlfredoNo ratings yet
- V8 900 Marine LightDocument4 pagesV8 900 Marine LightNoui BouzidNo ratings yet
- Mta11 g2Document4 pagesMta11 g2Yè WințNo ratings yet
- Diesel Generator Sets: Standard FeaturesDocument4 pagesDiesel Generator Sets: Standard FeaturesMuhammad Ary safartaNo ratings yet
- Funk 28000 Triple Pump DriveDocument1 pageFunk 28000 Triple Pump Driverakhikishore143No ratings yet
- Cat C175-16: Diesel Generator SetsDocument5 pagesCat C175-16: Diesel Generator SetsMiriam GaboNo ratings yet
- Diesel Generator Sets: FeaturesDocument5 pagesDiesel Generator Sets: FeaturesFarrukh SharfiNo ratings yet
- Power To Get Your Yacht Up To Speed.: MAN Nutzfahrzeuge GroupDocument4 pagesPower To Get Your Yacht Up To Speed.: MAN Nutzfahrzeuge GroupFlo MarineNo ratings yet
- Cat C27: Diesel Generator SetsDocument4 pagesCat C27: Diesel Generator SetsJose LibrerosNo ratings yet
- Best Practice Guide Book: Operation, Maintenance and Rewinding of Induction Motors in SME IndustriesDocument21 pagesBest Practice Guide Book: Operation, Maintenance and Rewinding of Induction Motors in SME Industriesdedi sanatraNo ratings yet
- SS 7227603 18331146 000Document8 pagesSS 7227603 18331146 000heniNo ratings yet
- Sucker RodsDocument61 pagesSucker RodsvibhutiNo ratings yet
- Fluid Level Using Dynamometer CardDocument8 pagesFluid Level Using Dynamometer CardvibhutiNo ratings yet