0% found this document useful (0 votes)
139 views16 pagesAbscess and Boil Types and Treatments
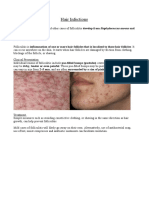
An abscess is a collection of pus in the body that can be caused by bacteria entering through a wound, neighboring structures, lymph vessels, or bloodstream. There are three main types: pyogenic, pyaemic, and cold. Pyogenic abscesses are most common and caused by bacteria, while pyaemic abscesses develop from infected emboli leading to multiple abscesses. Cold abscesses are always a sequel to tuberculosis and form from caseated lymph nodes. Treatment involves drainage of localized pus, taking cultures and antibiotics, and improving overall health.
Uploaded by
Plày GameCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
139 views16 pagesAbscess and Boil Types and Treatments
An abscess is a collection of pus in the body that can be caused by bacteria entering through a wound, neighboring structures, lymph vessels, or bloodstream. There are three main types: pyogenic, pyaemic, and cold. Pyogenic abscesses are most common and caused by bacteria, while pyaemic abscesses develop from infected emboli leading to multiple abscesses. Cold abscesses are always a sequel to tuberculosis and form from caseated lymph nodes. Treatment involves drainage of localized pus, taking cultures and antibiotics, and improving overall health.
Uploaded by
Plày GameCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd