Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NSXTICM24 M08 Security
Uploaded by
mmviqtah0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views85 pagesOriginal Title
NSXTICM24_M08_Security
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views85 pagesNSXTICM24 M08 Security
Uploaded by
mmviqtahCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 85
NSX-T Data Center Security
© 2019 VMware, Inc.
Importance
A primary objective of NSX-T Data Center is to provide a secure environment for your IT
operations. To this end, NSX-T Data Center includes features such as micro-segmentation,
distributed firewall, gateway firewall, and service insertion. Thorough understanding and proper
use of these features helps you create a secure environment.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8-2
Module Lessons
Lesson: NSX-T Data Center Micro-Segmentation
Lesson: NSX-T Data Center Distributed Firewall
Lesson: NSX-T Data Center Gateway Firewall
Lesson: NSX-T Data Center Service Insertion
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8-3
NSX-T Data Center Micro-Segmentation
© 2019 VMware Inc. All rights reserved.
Learner Objectives
After completing this lesson, you should be able to meet the following objectives:
• Identify the challenges associated with traditional data center security
• Describe the NSX-T micro-segmentation zero-trust security model
• Recognize micro-segmentation use cases
• Identify benefits of micro-segmentation
• Explain how to enforce the zero-trust model of micro-segmentation
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8-5
Traditional Data Center Security
Traditional data centers face many security
challenges:
• Traditional security policies align with the
environment rather than with applications.
• Shared services can traverse tier boundaries
without being checked.
• Traditional segmentation does not prevent
lateral communication between workloads in
a tier.
• Low-priority systems are often targeted first.
• Attackers can move freely around the data
center and access valuable data.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8-6
Data Center Security Requirements
With built-in zero-trust at the most granular
level:
• Every VM can have:
— Individual firewalls
— Individual security policies
• Security policies can be based on:
— VM attributes
— Network attributes
— Application attributes
• Security controls can be applied to any
application:
— Service insertion and chaining
— Agentless antivirus
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8-7
Micro-Segmentation in NSX-T Data Center
Micro-segmentation performs
several functions:
• Logically divides a data
center into distinct security
segments down to the
individual workload VM level
• Defines distinct controls and
security services
• Attaches the centrally
controlled and operationally
distributed firewalls directly to
each VM
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8-8
Enforcing the Zero-Trust Security Model of Micro-Segmentation (1)
The zero-trust (least privilege) model trusts
nothing and verifies everything.
Micro-segmentation establishes a security
perimeter around each VM or container
workload with a dynamically defined policy.
To build a zero-trust model:
Step 1: Identify applications and their
boundaries.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8-9
Enforcing the Zero-Trust Security Model of Micro-Segmentation (2)
Step 2: Create micro-segments for applications to reduce their exposure to unnecessary network
traffic.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 10
Enforcing the Zero-Trust Security Model of Micro-Segmentation (3)
Step 3: Secure through context.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 11
Micro-Segmentation Use Cases
The main use cases of micro-segmentation in a
data center include:
• Critical application protection with micro-
segmentation
• Secure virtual desktop infrastructures and
mobile devices
• Agentless antivirus with Guest Introspection
• Dynamic security service insertion of third-
party solutions
• Creation of DMZs anywhere
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 12
Micro-Segmentation Benefits
Micro-segmentation operationalizes the zero-trust model for applications in NSX-T Data Center,
using isolation, segmentation, and advanced security services, such as partner service insertion,
service chaining, and traffic steering.
Micro-segmentation offers key business and functional benefits:
• Limits lateral movement within the data center
• Minimizes risks and the impact of security breaches
• Simplifies network traffic flows
• Uses existing infrastructure (network topology agnostic)
• Lowers capital expenditures and operating expenses
• Automates IT service delivery
• Securely enables business agility
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 13
Review Learner Objectives
After completing this lesson, you should be able to meet the following objectives:
• Identify the challenges associated with traditional data center security
• Describe the NSX-T micro-segmentation zero-trust security model
• Recognize micro-segmentation use cases
• Identify benefits of micro-segmentation
• Explain how to enforce the zero-trust model of micro-segmentation
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 14
NSX-T Data Center Distributed Firewall
© 2019 VMware Inc. All rights reserved.
Learner Objectives
After completing this lesson, you should be able to meet the following objectives:
• Identify types of firewalls in NSX-T Data Center
• Describe features of distributed firewalls
• Create firewall policies
• Configure firewall rules for policies
• Configure firewall rule attributes: domains, groups, services, and profiles
• Describe distributed firewall architecture
• Explain how distributed firewalls operate on ESXi and KVM hosts
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 16
NSX-T Data Center Firewalls (1)
NSX-T Data Center includes two types of firewalls: the distributed firewall (east-west) and the
gateway firewall (north-south).
A distributed firewall is a hypervisor, kernel-embedded stateful firewall:
• It resides outside the VM guest OS.
• It controls the I/O path to and from the vNIC.
• It monitors the state of active connections and uses this information to determine which
packets traverse the VM vNIC.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 17
NSX-T Data Center Firewalls (2)
The gateway firewall, also known as the perimeter firewall, protects traffic to and from physical
environments:
• It is similar to the port-based firewall and applies to Tier-0 and Tier-1 Gateway nodes.
• NSX gateways must be backed by an NSX Edge cluster.
• Destination NAT and source NAT rules are implemented on uplink and back plane interfaces of
the service router (SR).
• The gateway firewall is implemented only on the uplink of Tier-0 and Tier-1 Gateway nodes.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 18
Features of the Distributed Firewall
The distributed firewall provides visibility and
control for virtualized workloads and networks.
Its main features include:
• Centralized configuration through the NSX
Manager simplified UI
• Layer 2 stateless firewall rules
• Layer 3 stateless and stateful firewall rules
• Context-aware (layer 7) firewall rules
• Identity Firewall for virtual desktops and
virtual user sessions
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 19
Distributed Firewall: Key Concepts (1)
Several key concepts apply to distributed firewalls:
• Domain: A logical construct representing a security zone with all rules and groups
• Security policy: A collection of firewall rules and service configurations
• Firewall rule: Set of instructions that determine whether a packet should be allowed or blocked
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 20
Distributed Firewall: Key Concepts (2)
• Group: A construct with multiple objects statically or dynamically pooled together. Groups are
used in firewall rules to specify the source and destination fields.
• Service: Defines a port and protocol combination and is used to specify the type of traffic to be
blocked or allowed in firewall rules.
• Context profile: Inspects the layer 7 application content of packets to allow or deny them.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 21
Creating a Domain
A domain is a collection of workloads and communication rules that are related to each other
through some business criteria:
• The domain defines the scope of security policies.
• The preconfigured default domain represents the entire NSX-T Data Center environment.
• Additional domains can be added as needed.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 22
Security Policy Overview
A security policy is a structure that encompasses various security elements, including firewall
rules and service configurations.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 23
Distributed Firewall Policy
A Distributed Firewall policy is a collection of firewall rules applied to east-west traffic.
The NSX Manager simplified UI enables you to group distributed firewall rules into different
categories.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 24
Configuring Distributed Firewall Policies (1)
A firewall policy is made up of one or more firewall rules, which contain specific instructions for
handling various types of traffic.
A policy can contain stateful or stateless rules for enforcement.
Policies are enforced in top-to-bottom order.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 25
Configuring Distributed Firewall Policies (2)
Firewall rules are processed in top-to-bottom order:
• You can move rules up and down within a policy.
• The first match triggers rule enforcement.
• Nonmatching packets are enforced by the default catch-all rule, which applies to all workloads.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 26
Configuring Distributed Firewall Policy Settings
When creating a new Distributed Firewall policy, you specify settings such as TCP Strict, Stateful,
Locked, and so on.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 27
Creating Distributed Firewall Rules
Rules are a set of criteria used to evaluate traffic flows. They contain instructions that determine
whether a packet should be allowed or blocked.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 28
Configuring Distributed Firewall Rule Parameters
A firewall rule includes parameters such as source, destination, service context profile, logging,
and tag, and defines which action should be taken on a rule match.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 29
Specifying Sources and Destinations for a Rule
When specifying Sources and Destinations for a firewall rule, you can use an IP or MAC
address, or an object (such as a group). If you do not specify these parameters, they match to
Any.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 30
Creating Groups
A group defines a collection of assets on which security policies can be applied.
A group can contain VMs, vNICs, logical segments, logical ports, IP and MAC addresses, AD
user groups, and so on.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 31
Adding Members and Member Criteria for a Group
Groups can be defined by using static or dynamic membership criteria:
• Static group inclusion criteria apply to VMs, logical ports, IP sets, MAC sets, AD user groups,
and nested groups.
• Dynamic group inclusion for VMs can be based on tags, machine names, OS names, or
computer names.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 32
Viewing the Configured Groups
In the NSX Manager simplified UI, you can view the list of groups and their locations.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 33
Specifying Services for a Rule
When configuring distributed firewall rules, you specify one or more services, such as HTTP,
ICMP, SSH, and so on.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 34
Predefined and User-Created Services
The NSX Manager simplified UI
includes an extensive list of
predefined services. You cannot
modify or delete these services.
You can create additional
services to meet your
communication requirements.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 35
Adding a Context Profile to a Rule
You can apply a context profile to a distributed firewall rule to enable a layer 7 firewall.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 36
Predefined and User-Created Context Profiles
NSX Manager includes a list of predefined context profiles.
You can also configure custom context profiles for your firewall rules.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 37
Configuring Context Profile Attributes
When creating a context profile, you configure two attributes: application ID and domain name.
After the context profile is created, you can apply it to your distributed firewall rules.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 38
Setting the Scope of Rule Enforcement
The Applied To attribute optimizes the resource utilization on the ESXi and KVM hosts. It also
helps in defining targeted policies at specific zones or tenants without affecting the policy defined
on other zones or tenants.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 39
Specifying Distributed Firewall Settings
You configure distributed firewall rules settings, such as logging, direction, IP Protocol, tag, and
so on.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 40
Filtering the Display of Firewall Rules
For easier firewall rule management, you can use filters to display a list only of rules of interest.
You can filter rules by policy name, rule name, policy path, rule path, domain, source, destination,
service, and action.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 41
Determining the Default Firewall Behavior
Whitelist and blacklist define the default firewall behavior.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 42
Viewing the Default Firewall Rules
You can view the default firewall behavior (whitelist or blacklist) on the Advanced Network &
Security tab.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 43
Distributed Firewall Architecture
The steps in the high-level distributed firewall workflow:
1. Users configure distributed firewall policies through the NSX
Manager simplified UI.
2. These policies are processed by the policy role.
3. Distributed firewall policies are then pushed to the manager
role.
4. The manager role forwards the distributed firewall rule
configuration to the central control plane (CCP).
5. The CCP stores the distributed firewall configuration in the
transport nodes, which configure the data path accordingly.
6. NSX Manager polls rule statistics and status from the
transport nodes, using the management plane agent (MPA).
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 44
Distributed Firewall Architecture: ESXi
On an ESXi host, the distributed firewall
includes several components:
• nsx-proxy: Retrieves the configuration
changes from the CCP and configures data
path modules
• Data path modules:
– VSIP: Receives firewall rules and
downloads them on each VM’s vNIC
– VDPI: Performs L7 packet inspection
• Stats Exporter: Collects flow records from the
distributed firewall data plane kernel modules
and generates rules statistics
• MPA: Passes rules statistics and real-time
data to the management plane
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 45
Distributed Firewall Architecture: KVM
On a KVM, the distributed firewall includes the
several components:
• nsx-proxy: Retrieves configuration changes
from the CCP and configures data path
modules
• Data path modules:
– OVS: Handles stateless rules
– Conntrack: Tracks established
connections for stateful rules
– VDPI: Performs L7 packet inspection
• Stats Exporter: Collects flow records and
generates rules statistics
• MPA: Passes rules statistics and real-time
data to the management plane
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 46
Lab: Configuring the NSX Distributed Firewall
Create NSX distributed firewall rules to allow or deny application traffic
1. Prepare for the Lab
2. Test the IP Connectivity
3. Create IP Set Objects
4. Create Firewall Rules
5. Create an Intratier Firewall Rule to Allow SSH Traffic
6. Create an Intratier Firewall Rule to Allow MySQL Traffic
7. Prepare for the Next Lab
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 47
Review of Learner Objectives
After completing this lesson, you should be able to meet the following objectives:
• Identify types of firewalls in NSX-T Data Center
• Describe features of distributed firewalls
• Create firewall policies
• Configure firewall rules for policies
• Configure firewall rule attributes: domains, groups, services, and profiles
• Describe distributed firewall architecture
• Explain how distributed firewalls operate on ESXi and KVM hosts
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 48
NSX-T Data Center Gateway Firewall
© 2019 VMware Inc. All rights reserved.
Learner Objectives
After completing this lesson, you should be able to meet the following objectives:
• Describe the functions of the gateway firewall
• Explain the purpose of a gateway policy
• Create gateway firewall policies and rules
• Describe the gateway firewall architecture
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 50
About NSX-T Data Center Gateway Firewall
Characteristics of the gateway firewall:
• A stateful firewall for north-south traffic
• Independent of distributed firewall from policy
configuration and enforcement perspective
• Implemented per NSX gateway node and
supported at both Tier-0 and Tier-1
• Applied to uplinks on Tier-0 or Tier-1
Gateways backed by an NSX Edge cluster
• A centralized service requiring the SR
component of the router
• Supports stateless and stateful firewall rules
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 51
Gateway Firewall on Tier-0 Gateway for Perimeter Protection
The Tier-0 Gateway firewall can be used as a perimeter firewall at the virtual and physical
boundary.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 52
Gateway Firewall Policy
A Gateway Firewall policy is made up of one or more individual firewall rules and is applied to
north-south traffic.
Gateway policies can be applied to Tier-0 and Tier-1 Gateways and their interfaces.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 53
Predefined Gateway Firewall Categories
The gateway firewall includes predefined categories under the ALL SHARED RULES tab, where
rules across all gateways are visible.
You can change the category names by using the API.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 54
Configuring the Gateway Firewall Policy Settings
To create a Gateway Firewall policy, you assign a policy name, specify the domain, and configure
the settings.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 55
Configuring Firewall Rules
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 56
Configuring Gateway Firewall Rules Settings
You can specify the logging, direction, and IP protocol settings for the gateway firewall rule. A
firewall rule must be published for it to take effect.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 57
Gateway Firewall Architecture
You can add gateway firewall rules to Tier-1 or Tier-0 Gateways. The NSX Edge transport node
receives the gateway firewall configuration and enforces the rules on the traffic.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 58
Lab: Configuring the NSX Gateway Firewall
Configure and test the NSX gateway firewall rules to control north-south traffic
1 Prepare for the Lab
2 Test SSH Connectivity
3 Configure an Edge Firewall Rule to Block External SSH Requests
4 Test the Effect of the Configured Gateway Firewall Rule
5 Prepare for the Next Lab
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 59
Review of Learner Objectives
After completing this lesson, you should be able to meet the following objectives:
• Describe the functions of the gateway firewall
• Explain the purpose of a gateway policy
• Create gateway firewall policies and rules
• Describe the gateway firewall architecture
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 60
NSX-T Data Center Service Insertion
© 2019 VMware Inc. All rights reserved.
Learner Objectives
After completing this lesson, you should be able to meet the following objectives:
• Identify types of service insertion
• Explain how north-south service insertion works for Network Introspection
• Explain how east-west service insertion works for Network Introspection
• Describe how Endpoint Protection works
• Recognize use cases for Endpoint Protection
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 62
About Service Insertion
Service Insertion enables users to seamlessly
add third-party network and security services at
various points throughout the network.
Service Insertion includes Network
Introspection and Endpoint Protection:
• Network Introspection examines the network
by offering services such as IDS, IPS, and
next-generation firewall.
• Endpoint Protection examines guest VMs
from inside by offering services such as
antivirus and antimalware solutions.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 63
About Network Introspection
NSX-T Data Center supports both north-south
and east-west service insertion for Network
Introspection.
Network Introspection enables third-party
services to examine north-south or east-west
traffic passing through a gateway and to take
appropriate actions.
Using the provided framework and APIs,
technology partners can integrate their network
and security solutions with NSX-T Data Center.
Partner services typically provide advanced
security features such as IDS, IPS, next-
generation firewall, URL filtering, and so on.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 64
North-South Network Introspection Overview
The north-south partner security service is
typically inserted at the data center perimeter,
between tenant boundaries, or between
containers.
The insertion points are the uplinks of the Tier-0
or Tier-1 Gateway.
The L2 insertion mode of partner services is
supported.
A partner service virtual machine (SVM) is
deployed close to the NSX Edge node.
Policy-based routing redirection is used for
north-south traffic.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 65
Configuring North-South Network Introspection
To set up a service insertion for Network Introspection:
1. Register a partner’s service:
• Service registration makes a service available in the catalog.
• Partners use APIs to register their services with the NSX Manager simplified UI.
2. Deploy a service instance:
• Instances of a registered service can be deployed using the NSX Manager simplified UI.
• Users can select the appropriate Tier-0 or Tier-1 Gateway and host on which to deploy the
SVM.
3. Configure traffic redirection:
• Redirection rules can be configured from the NSX Manager simplified UI or API.
• Classification and redirection occur for traffic entering the uplink interface of the Tier-0 or
Tier-1 Gateway.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 66
Registering a Partner Service
Before a partner security service is available to a security policy, it must be registered with NSX-T
Data Center with an API call or partner CLI.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 67
Deploying a Partner Service Instance
You select the partner service from the catalog and specify instance parameters:
• The service instance must be deployed on a host that is a transport node.
• The service instance is commonly deployed on the same host as the NSX Edge node.
• Each SVM can only be applied to one gateway.
• NSX Manager creates and attaches segments to the gateway and the SVM.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 68
Configuring Traffic Redirection to Partners
After you deploy the partner service instance, you can create a north-south Network Inspection
policy.
The Network Inspection policy determines the type of traffic the gateway redirects to the partner
service.
Redirection rules are stateless.
Reflexive redirection rules are automatically created and applied to the return traffic.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 69
East-West Network Introspection Overview
Partner SVMs for East-West Network Introspection can be deployed either on compute hosts or
in a service cluster.
Common use cases are VM-integrated next-generation firewall and micro-segmentation.
Insertion points are at each guest VM’s vNIC.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 70
Configuring East-West Network Introspection
Steps for configuring east-west Network Introspection:
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 71
Registering Partner Services
Partners must register their services with NSX-T Data Center using the API. Registered services
are listed in the Catalog tab.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 72
Deploying an Instance of a Registered Service
When deploying a partner service, you specify values for several settings, including Service
Deployment Name, Compute Manager, Cluster, Datastore, Networks, Service Segments.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 73
Creating a Service Profile for East-West Network Introspection
A service profile is a specific instantiation of a vendor template.
You can customize attributes of a vendor template to create an instance of the template.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 74
Creating Service Chains
A service chain specifies the sequence of service profiles applied to network traffic.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 75
Configuring Redirection Rules
After a service chain is created, it can be used in a redirection rule.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 76
Endpoint Protection Overview and Use Cases
Endpoint Protection is a process of constantly
looking deep into the OS and file data,
providing visibility into in-guest events.
NSX-T Data Center supports the following
capabilities for Guest Introspection:
• Integration and offloading to third-party
services
• Policy-based agentless antivirus and
antimalware protection
• Protection for Windows VMs running on
vSphere
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 77
Endpoint Protection Process
Steps in the Endpoint Protection process:
1. Modules for Endpoint Protection are installed on hosts as part of host preparation.
2. The partner’s integrated service is deployed as a SVM.
3. The administrator defines Endpoint Protection policies for the VMs.
4. The partner SVM uses the Endpoint Protection API library to introspect and protect guest VMs
from malware.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 78
Automatic Policy Enforcement for New VMs
Endpoint Protection policies are automatically
applied and enforced when a new VM is added.
Automatic policy enforcement follows these
steps:
1. A new ESXi host is added to the cluster.
2. NSX-T Data Center automatically deploys
the Endpoint Protection framework and
SVMs.
3. When a new guest VM comes online on the
host, appropriate security policies are
applied.
4. The security policies follow the VM even
when the VM migrates (vMotion).
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 79
Automated Virus or Malware Quarantine with Tags Example
Endpoint Protection policies and tags can be used to automatically quarantine compromised
workloads.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 80
Creating a Service Profile for Endpoint Protection
Endpoint Protection service profiles define the level of protection for a group of workloads.
Services profiles are created from a template provided by the partner.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 81
Configuring Endpoint Protection Rules
Administrators can create rules to associate a service profile to a specific VM or group of VMs.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 82
Review of Learner Objectives
After completing this lesson, you should be able to meet the following objectives:
• Identify types of service insertion
• Explain how north-south service insertion works for Network Introspection
• Explain how east-west service insertion works for Network Introspection
• Describe how Endpoint Protection works
• Recognize use cases for Endpoint Protection
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 83
Key Points (1)
• Micro-segmentation enables an organization to logically divide its data center into distinct
security segments down to the individual workload level.
• Micro-segmentation defines distinct controls and security services, and attaches the centrally
controlled and operationally distributed firewalls directly to each VM.
• NSX-T Data Center micro-segmentation supports a zero-trust architecture for IT security. It
establishes a security perimeter around each VM or container workload with a dynamically
defined policy.
• The distributed firewall is a hypervisor kernel-embedded stateful firewall.
• The distributed firewall resides outside the VM guest OS, controls the I/O path to and from the
vNIC, and monitors the state of active connections. The distributed firewall uses this
information to determine which packets traverse the VM vNIC.
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 84
Key Points (2)
• The gateway firewall, also known as the perimeter firewall, protects traffic from physical
environments.
• NSX-T Data Center provides the framework and APIs that allow service insertion partners to
integrate their security solutions with NSX-T Data Center.
• Network Introspection examines the network by offering services such as IDS, IPS, and next-
generation firewall.
• Endpoint Protection examines inside guest VMs by offering services such as antivirus and
antimalware solutions, vulnerability management, data security, and data loss prevention
solutions.
Questions?
© 2019 VMware, Inc. VMware NSX-T: Install, Configure, Manage | 8 - 85
You might also like
- Zero Trust Networks with VMware NSX: Build Highly Secure Network Architectures for Your Data CentersFrom EverandZero Trust Networks with VMware NSX: Build Highly Secure Network Architectures for Your Data CentersNo ratings yet
- NSXTD3 M11 Federation 0720Document28 pagesNSXTD3 M11 Federation 0720JacekNo ratings yet
- Module 3: NSX-T Data Center Architecture and Components: © 2020 Vmware, IncDocument32 pagesModule 3: NSX-T Data Center Architecture and Components: © 2020 Vmware, IncDanial TanNo ratings yet
- Vm-Series On Vmware NSX: HighlightsDocument4 pagesVm-Series On Vmware NSX: HighlightsJobs JeddahNo ratings yet
- Module 02 Securing The NetworkDocument52 pagesModule 02 Securing The NetworkAlari AcbNo ratings yet
- Vshield App Design GuideDocument15 pagesVshield App Design GuidenewbeoneNo ratings yet
- New IP Security Principles White PaperDocument6 pagesNew IP Security Principles White PaperwtopwebNo ratings yet
- NSXTICM24 M03 Preparing InfrastructureDocument80 pagesNSXTICM24 M03 Preparing InfrastructuremmviqtahNo ratings yet
- VMware NSX Micro-Segmentation Benchmark Final v1.0Document44 pagesVMware NSX Micro-Segmentation Benchmark Final v1.0Juan Pablo Guerrero CuevaNo ratings yet
- VMware Microsegmentation Solution OverviewDocument2 pagesVMware Microsegmentation Solution Overviewa bNo ratings yet
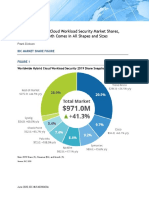
- Worldwide Hybrid Cloud Workload Security Market Shares, 2019: Vendor Growth Comes in All Shapes and SizesDocument21 pagesWorldwide Hybrid Cloud Workload Security Market Shares, 2019: Vendor Growth Comes in All Shapes and SizesCHRISTIAN JERSON HURTADO SAUCEDONo ratings yet
- Vmware NSX DatasheetDocument8 pagesVmware NSX DatasheetДејан СенићNo ratings yet
- Advanced Micro-Segmentation Services With Vmware NSX and Palo Alto NetworksDocument3 pagesAdvanced Micro-Segmentation Services With Vmware NSX and Palo Alto NetworksAmil AkhundzadaNo ratings yet
- VMware Case Studies For Aggregators On NSX ENDocument5 pagesVMware Case Studies For Aggregators On NSX ENSuRiUNo ratings yet
- Architecture Guide For VMware NSX - Rel 2 - Oct 2018Document24 pagesArchitecture Guide For VMware NSX - Rel 2 - Oct 2018Andres Felipe LorzaNo ratings yet
- Virtualization Security and Best PracticesDocument25 pagesVirtualization Security and Best Practicesgenome2014No ratings yet
- Sym WPS PB103Document4 pagesSym WPS PB103husseinNo ratings yet
- Module 13: Network Virtualization: Instructor MaterialsDocument49 pagesModule 13: Network Virtualization: Instructor Materialspatrick gucakeNo ratings yet
- Cisco Prime Infrastructure 3.xDocument5 pagesCisco Prime Infrastructure 3.xC KNo ratings yet
- 21.1 Planning For Security ServicesDocument15 pages21.1 Planning For Security ServicesRaj KaranNo ratings yet
- LogRhythm Microsoft Office 365 Log CollectionDocument3 pagesLogRhythm Microsoft Office 365 Log CollectionCesar AlmadaNo ratings yet
- Devasc Module 6Document93 pagesDevasc Module 6Youssef FatihiNo ratings yet
- Hyperautomated Ai-Based Security Vs Vmware NSX: Manuel NedbalDocument5 pagesHyperautomated Ai-Based Security Vs Vmware NSX: Manuel NedbalVijay MindfireNo ratings yet
- Vm-Series On Vmware: Web App DB Vmware Distributed SwitchDocument5 pagesVm-Series On Vmware: Web App DB Vmware Distributed SwitchoreamunoeNo ratings yet
- ExtremeControl Datasheet Map Extremecontrol For Extremecloud Iq Site Engine Data SheetDocument4 pagesExtremeControl Datasheet Map Extremecontrol For Extremecloud Iq Site Engine Data SheetAna Elisa Quintero CetinaNo ratings yet
- Deploy Your Preferred Security Solution Across Multiple CloudsDocument5 pagesDeploy Your Preferred Security Solution Across Multiple CloudsDuDu DevNo ratings yet
- Benefits of virtualized security over traditional hardware-based securityDocument19 pagesBenefits of virtualized security over traditional hardware-based securityHuma ZaheerNo ratings yet
- NSX With Cisco ACI As UnderlayDocument72 pagesNSX With Cisco ACI As Underlayrohithyd046No ratings yet
- VSP 1Document4 pagesVSP 1Quangvinh HPNo ratings yet
- Vmware NSX-T Data Center: Design: © 2019 Vmware Inc. All Rights ReservedDocument13 pagesVmware NSX-T Data Center: Design: © 2019 Vmware Inc. All Rights ReservedDanial TanNo ratings yet
- ENSA Module 13Document35 pagesENSA Module 13Hanifi ElabidiNo ratings yet
- VMware NSX Security Review: Micro-segmentation, Distributed Firewall & Partner IntegrationDocument7 pagesVMware NSX Security Review: Micro-segmentation, Distributed Firewall & Partner IntegrationEduardo Ramírez De LamaNo ratings yet
- NSX T Deployment GuideDocument81 pagesNSX T Deployment Guideninodjukic100% (3)
- Palo Alto Networks Cybersecurity AcademyDocument5 pagesPalo Alto Networks Cybersecurity AcademyCarlos GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Network VirtualizationDocument105 pagesNetwork VirtualizationCharlie MonterreyNo ratings yet
- Cloud SecurityDocument13 pagesCloud SecurityVaishnavi ChockalingamNo ratings yet
- Abc of MerakiDocument80 pagesAbc of Merakileo123No ratings yet
- DMZ Virtualization Vsphere4 Nexus1000VDocument20 pagesDMZ Virtualization Vsphere4 Nexus1000Vhulikul22No ratings yet
- DEVASC Module 6Document93 pagesDEVASC Module 6JUAN MAURICIO QUEZADA JAMASMIENo ratings yet
- Module 6 - Application Deployment and SecurityDocument86 pagesModule 6 - Application Deployment and SecurityDaniilNo ratings yet
- NSX Microsegmentation Part 1Document13 pagesNSX Microsegmentation Part 1Sudeep MishraNo ratings yet
- Vmware Vcloud Networking Security DatasheetDocument2 pagesVmware Vcloud Networking Security DatasheetrachamreddyrNo ratings yet
- Work Virtualization Design & Deploy SOW R2.0 - NVDocument13 pagesWork Virtualization Design & Deploy SOW R2.0 - NVDavid GuzmanNo ratings yet
- WP SDN Security Framework UpdatedDocument5 pagesWP SDN Security Framework UpdatedJayesh NowbuthNo ratings yet
- VMware Vshield Presentation PP en Dec10Document34 pagesVMware Vshield Presentation PP en Dec10Daividdi MoraisNo ratings yet
- Vmware NSX Data Center: Networking in SoftwareDocument6 pagesVmware NSX Data Center: Networking in Softwarealdozp1No ratings yet
- Ebook Securing Digital AccelerationDocument19 pagesEbook Securing Digital AccelerationGokhan GULENNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Technologies 5Document7 pagesCloud Computing Technologies 5serdal bilginNo ratings yet
- Dell Technologies Trusted Hybrid CloudDocument2 pagesDell Technologies Trusted Hybrid Cloudmiguex_reloadedNo ratings yet
- Top-Down Network Design: Chapter SixDocument50 pagesTop-Down Network Design: Chapter SixyogaNo ratings yet
- VM Series For Microsoft AzureDocument7 pagesVM Series For Microsoft AzureRobinson Garcia GarciaNo ratings yet
- Module 12: Network Security Infrastructure: Cyberops Associate V1.0Document30 pagesModule 12: Network Security Infrastructure: Cyberops Associate V1.0Mihai MarinNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Security Planning Guide2Document26 pagesCloud Computing Security Planning Guide2Sukanya ChakravartyNo ratings yet
- Network Security v1.0 - Module 9Document17 pagesNetwork Security v1.0 - Module 9Ernesto Silverio FloresNo ratings yet
- EUD SecurityDocument20 pagesEUD SecurityDJMASSNo ratings yet
- NCE-T HCIA LectureDocument95 pagesNCE-T HCIA LectureSayed Rahim NaderiNo ratings yet
- W9-10 - CLO3 - Cloud Computing SecurityDocument39 pagesW9-10 - CLO3 - Cloud Computing Securitymaryam saeedNo ratings yet
- AutomationDocument30 pagesAutomationTrần Tuấn PhongNo ratings yet
- Vmware NSX: Install, Configure, Manage (V6.2) H6D08S: AudienceDocument3 pagesVmware NSX: Install, Configure, Manage (V6.2) H6D08S: AudienceHarshal TapadiyaNo ratings yet
- Top 10 Best Practices For Cloud Security Posture Management - Ebook - 1601397167067001lASODocument13 pagesTop 10 Best Practices For Cloud Security Posture Management - Ebook - 1601397167067001lASOjomasoNo ratings yet
- 178 - 7 - Fun For Flyers. Progress Tests - 2017, 4th - 91p.pdf Foods NatureDocument1 page178 - 7 - Fun For Flyers. Progress Tests - 2017, 4th - 91p.pdf Foods NatureYu KoNo ratings yet
- Investigation of Nursing Students Knowledge of and Attitudes About Problem Based LearningDocument4 pagesInvestigation of Nursing Students Knowledge of and Attitudes About Problem Based LearningasdasdasdasNo ratings yet
- F5 GTM Concepts Guide v11Document209 pagesF5 GTM Concepts Guide v11Majnu SmNo ratings yet
- Australian Institute For Teaching and School Leadership - AITSLDocument5 pagesAustralian Institute For Teaching and School Leadership - AITSLYu LiNo ratings yet
- Educ 580 - Edpuzzle PD HandoutDocument3 pagesEduc 580 - Edpuzzle PD Handoutapi-548868233No ratings yet
- Main Body Recruitment Process of Human Resource Division in Brac BankDocument55 pagesMain Body Recruitment Process of Human Resource Division in Brac BankAsfia PrantyNo ratings yet
- Max-OT For Dummies - Bodybuilding - Com ForumsDocument21 pagesMax-OT For Dummies - Bodybuilding - Com ForumsPhong QuachNo ratings yet
- From Birth Till Palatoplasty Prosthetic.20Document5 pagesFrom Birth Till Palatoplasty Prosthetic.20Maria FernandaNo ratings yet
- Analgesia SystemDocument7 pagesAnalgesia SystemMudassar Roomi100% (1)
- Certified Islamic Professional Accountant (Cipa) ProgramDocument13 pagesCertified Islamic Professional Accountant (Cipa) ProgramTijjani Ridwanulah AdewaleNo ratings yet
- Sajid Bhuiya CVDocument3 pagesSajid Bhuiya CVapi-612088476No ratings yet
- Fault ModelingDocument21 pagesFault ModelingRamarao ChNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Security Issues in Web Applications Through Penetration TestingDocument7 pagesAnalysis of Security Issues in Web Applications Through Penetration Testingabdel_lakNo ratings yet
- Self-test on the COSO ERM frameworkDocument6 pagesSelf-test on the COSO ERM frameworkLady BirdNo ratings yet
- New Age Int. Publication Civil EngineeringDocument28 pagesNew Age Int. Publication Civil EngineeringLove SharmaNo ratings yet
- Sunday School Lesson Activity 219 Moses Builds A Tablernacle in The Wilderness - Printable 3D Model KitDocument17 pagesSunday School Lesson Activity 219 Moses Builds A Tablernacle in The Wilderness - Printable 3D Model Kitmcontrerasseitz3193No ratings yet
- Bizagi Licensing Explained ENGDocument7 pagesBizagi Licensing Explained ENGGuidoNo ratings yet
- Probability Tree Diagrams Solutions Mathsupgrade Co UkDocument10 pagesProbability Tree Diagrams Solutions Mathsupgrade Co UknatsNo ratings yet
- MdmedichaoiceDocument324 pagesMdmedichaoicelancastd54No ratings yet
- Large Generators WEBDocument16 pagesLarge Generators WEBMaycon MaranNo ratings yet
- Breaugh Starke PDFDocument30 pagesBreaugh Starke PDFRichard YeongNo ratings yet
- 32 Productivity Increase in A PeirceSmith Convert 153013Document14 pages32 Productivity Increase in A PeirceSmith Convert 153013amirlpNo ratings yet
- Neil Strauss - The Annihilation Method - Style's Archives - Volume 1 - The Origin of Style - How To Transform From Chump To Champ in No TimeDocument132 pagesNeil Strauss - The Annihilation Method - Style's Archives - Volume 1 - The Origin of Style - How To Transform From Chump To Champ in No TimeDaniel Nii Armah Tetteh100% (2)
- Exercise 1: Chọn đáp án đúng:: Buổi 9: Động từ khuyết thiếu (Modal verb)Document6 pagesExercise 1: Chọn đáp án đúng:: Buổi 9: Động từ khuyết thiếu (Modal verb)Huyền HồNo ratings yet
- Forum Ex 2 2Document5 pagesForum Ex 2 2Didan EnricoNo ratings yet
- Quickguide Students For CopyrightsDocument2 pagesQuickguide Students For Copyrightslordvorldomort100% (1)
- English Assignment Team:: Devia Annisa E. E44190045 2. TB. Aditia Rizki E44190027 3. Tedi Irfan Jelata E44190028Document3 pagesEnglish Assignment Team:: Devia Annisa E. E44190045 2. TB. Aditia Rizki E44190027 3. Tedi Irfan Jelata E4419002856TB. Aditia RizkiNo ratings yet
- Customer Satisfaction in Maruti SuzukiDocument31 pagesCustomer Satisfaction in Maruti Suzukirajesh laddha100% (1)
- Serv Manual SM 100 FREEDocument75 pagesServ Manual SM 100 FREEGustavo Vargas Ruiz100% (1)