Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ITF Unit 5
Uploaded by
Nandhini Prabakaran0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views13 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views13 pagesITF Unit 5
Uploaded by
Nandhini PrabakaranCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 13
Foreign exchange rate
• An exchange rate is a relative price of one
currency expressed in terms of another
currency (or group of currencies). For
economies like Australia that actively engage
in international trade, the exchange rate is an
important economic variable.
Factors Affecting Exchange Rates
Inflation Rates
• Changes in inflation cause changes in currency exchange
rates. a country with a comparatively lower rate of inflation
will see an appreciation in the value of its currency.
• The price of goods and services increases at a slower rate
when inflation is low.
• Countries with a continually low inflation rate exhibit an
increasing currency value, whereas a country with higher
inflation typically experiences depreciation of its currency
and this is usually accompanied by higher interest rates.
Interest Rates
• Interest rates, inflation and exchange rates are all
correlated. Central banks can influence both
inflation and exchange rates by manipulating
interest rates.
• Higher interest rates offer lenders a higher return
compared to other countries.
• Any increase in a country's interest rate causes its
currency to increase in value as higher interest rates
mean higher rates to lenders,
• thus attracting more foreign capital, which in turn,
creates an increase in exchange rates.
• Recession
In the event a country's economy falls into a
recession, its interest rates will be dropped,
hindering its chances of acquiring foreign
capital. The consequence of this is that its
currency weakens in comparison to that of other
countries, thereby lowering the exchange rate.
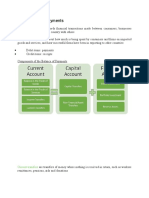
Current Account/Balance of Payments
• A country's current account reflects its balance of trade and
earnings on foreign investment. It comprises of the total
number of transactions including exports, imports and debt.
• A deficit in its current account comes as a result of
spending more of its currency on importing products than
through exports.
• This has the effect of lowering the country's exchange rate
to the point where domestic goods and services become
cheaper than imports, thereby generating domestic sales
and exports as the goods become cheaper on international
markets.
Political Stability and Performance
• A country's political state and economic
performance can affect the strength of its currency.
• A country with a low risk of political unrest is
more attractive to foreign investors, drawing
investment away from other countries perceived to
have more political and economic risk.
• An increase in foreign capital leads to the
appreciation in the value of the country's currency,
but countries prone to political tensions are likely
to see a depreciation in the rate of their currency.
Government Debt
• Government debt is public debt or national debt
owned by the central government. Countries
with large public deficits and debts are less
attractive to foreign investors and are thus less
likely to acquire foreign capital which leading
to inflation.
• Foreign investors will forecast a rise
government debt within a particular country. As
a result, a decrease in the value of this country's
exchange rate will follow.
You might also like
- Summary of David A. Moss's A Concise Guide to Macroeconomics, Second EditionFrom EverandSummary of David A. Moss's A Concise Guide to Macroeconomics, Second EditionNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 The Interntional Flow of Funds and Exchange RatesDocument14 pagesChapter 4 The Interntional Flow of Funds and Exchange RatesRAY NICOLE MALINGI100% (1)
- International financial forces impacting businessDocument29 pagesInternational financial forces impacting businessY.h. TariqNo ratings yet
- International Flow of FundsDocument18 pagesInternational Flow of FundsKazi Abdullah Al FarhadNo ratings yet
- Exchange RateDocument10 pagesExchange RateSteeeeeeeephNo ratings yet
- Exchange RateDocument10 pagesExchange RateSteeeeeeeephNo ratings yet
- EnglishDocument7 pagesEnglisharibahamjad8129No ratings yet
- Exchange Rates Foreign-Exchange Rate, Forex Rate or FX Rate)Document5 pagesExchange Rates Foreign-Exchange Rate, Forex Rate or FX Rate)SaadRasheedNo ratings yet
- Determinants of Exchange RateDocument2 pagesDeterminants of Exchange RateSajid Ali BhuttaNo ratings yet
- How Inflation, Interest Rates, Debt, and More Impact Currency ExchangeDocument2 pagesHow Inflation, Interest Rates, Debt, and More Impact Currency ExchangeTikitaka TitiNo ratings yet
- Currency War - Reasons and RepercussionsDocument15 pagesCurrency War - Reasons and RepercussionsRaja Raja91% (11)
- Global Financial System: International InstitutionsDocument21 pagesGlobal Financial System: International Institutionsapi-265248190% (1)
- IfDocument3 pagesIfAman MalviyaNo ratings yet
- 8 Key Factors That Affect Foreign Exchange RatesDocument2 pages8 Key Factors That Affect Foreign Exchange RatesdhitalkhushiNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Exchange RatesDocument2 pagesFactors Affecting Exchange Ratesanish-kc-8151No ratings yet
- Week 6 IMS, BoPDocument18 pagesWeek 6 IMS, BoPMustafa KhanNo ratings yet
- Basics of Exchange RatesDocument6 pagesBasics of Exchange RatesSushant MalveNo ratings yet
- IB Economics SL14 - Exchange Rates and Balance of PaymentsDocument6 pagesIB Economics SL14 - Exchange Rates and Balance of PaymentsTerran100% (6)
- Factors Affecting Exchange RatesDocument12 pagesFactors Affecting Exchange RatesHaritha JayanNo ratings yet
- Foreign ExchangeDocument9 pagesForeign ExchangeTopuNo ratings yet
- DownloadDocument4 pagesDownloadmanirajpoot45No ratings yet
- 2020 International Fin Syst PrintDocument31 pages2020 International Fin Syst PrintAndrea RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Exchange RateDocument3 pagesExchange RateSaugat PantNo ratings yet
- IT Final Ch.6.2023Document12 pagesIT Final Ch.6.2023Amgad ElshamyNo ratings yet
- Factors Determining Foreign Exchange RatesDocument1 pageFactors Determining Foreign Exchange Ratesshibashish PandaNo ratings yet
- L2 Exchange Rate DeterminationDocument25 pagesL2 Exchange Rate DeterminationKent ChinNo ratings yet
- The Impact of The Devaluation of CurencyDocument25 pagesThe Impact of The Devaluation of CurencycooldudeakhilNo ratings yet
- Module No. 4: International Parity Relationships & Forecasting Foreign Exchange rateDocument24 pagesModule No. 4: International Parity Relationships & Forecasting Foreign Exchange rateManjunath BVNo ratings yet
- Exchange Rates: Factors Affecting Exchange RateDocument3 pagesExchange Rates: Factors Affecting Exchange RateTheOnlyNamelessNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document3 pagesUnit 2sahooabhijit637No ratings yet
- Bop 2018Document7 pagesBop 2018mba departmentNo ratings yet
- Differentials in Inflation: Cost-Push Inflation Versus Demand-Pull InflationDocument2 pagesDifferentials in Inflation: Cost-Push Inflation Versus Demand-Pull InflationKirat GillNo ratings yet
- Global Financial System: International InstitutionsDocument15 pagesGlobal Financial System: International Institutionsapi-26524819No ratings yet
- The Balance of Payments, ExchangeDocument16 pagesThe Balance of Payments, ExchangeMoazzam AzadNo ratings yet
- ShresthaDocument4 pagesShresthaShubham SaxenaNo ratings yet
- IF.UNIT 1Document10 pagesIF.UNIT 1Rk BainsNo ratings yet
- Related Notes On Financial ForcesDocument3 pagesRelated Notes On Financial ForcesJesilin ManjulaNo ratings yet
- Factors That Influence Exchange RatesDocument2 pagesFactors That Influence Exchange RatesJoelene ChewNo ratings yet
- Quiz AnswerDocument11 pagesQuiz Answercharlie tunaNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting The Forex: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleDocument13 pagesFactors Affecting The Forex: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleShivangi MathurNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of Exchange Rate MechanismsDocument34 pagesThe Evolution of Exchange Rate MechanismsSimoNo ratings yet
- Factors Influencing Exchange RatesDocument2 pagesFactors Influencing Exchange RatesPravin Kumar PNo ratings yet
- Macro Group ProjectDocument6 pagesMacro Group ProjectNEETU AHUJANo ratings yet
- International Trade and Balance of PaymentsDocument18 pagesInternational Trade and Balance of PaymentsWALTER simsokweNo ratings yet
- Foreign Exchange RateDocument18 pagesForeign Exchange RateShehroz UsmanNo ratings yet
- Unit SDocument42 pagesUnit Ssprayzza tvNo ratings yet
- International Trade of Goods and Services And: Key Factors That Affect Foreign Exchange Rates 1. Inflation RatesDocument5 pagesInternational Trade of Goods and Services And: Key Factors That Affect Foreign Exchange Rates 1. Inflation RatesUtkarsh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Factors That Influence Foreign Exchange RatesDocument3 pagesFactors That Influence Foreign Exchange RatesChahil BapnaNo ratings yet
- What Is The Balance of PaymentsDocument11 pagesWhat Is The Balance of PaymentslordspatulaquotesNo ratings yet
- Sec B B.6. International Finance: Cma Athul KrishnaDocument28 pagesSec B B.6. International Finance: Cma Athul KrishnaAjay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- 6 Key Factors That Influence Exchange RatesDocument9 pages6 Key Factors That Influence Exchange RatesRizwan BashirNo ratings yet
- Determinants of Exchange RateswordDocument2 pagesDeterminants of Exchange RateswordHamid RehmanNo ratings yet
- 8 Key Factors Affecting Forex RatesDocument3 pages8 Key Factors Affecting Forex RatesyzaNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument6 pagesDocumentLesego Geraldine KgoeleNo ratings yet
- Exchange ControlDocument28 pagesExchange Controljaved iqbalNo ratings yet
- 01 Global Financial System: 1.1 International InstitutionsDocument25 pages01 Global Financial System: 1.1 International Institutionsapi-26524819No ratings yet
- Exchange Rate - TheoryDocument10 pagesExchange Rate - TheoryHieptaNo ratings yet
- Key Currencies:: Share of National Currencies in Total Identified Official Holdings of Foreign Exchange, 1998Document12 pagesKey Currencies:: Share of National Currencies in Total Identified Official Holdings of Foreign Exchange, 1998KaranPatilNo ratings yet
- BOP and BOTDocument18 pagesBOP and BOTmohanraokp2279No ratings yet
- FIM AssignmentDocument5 pagesFIM AssignmentNoor AliNo ratings yet
- ITF Unit 1Document25 pagesITF Unit 1Nandhini PrabakaranNo ratings yet
- FemaDocument5 pagesFemaNandhini PrabakaranNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument8 pagesCase StudyNandhini PrabakaranNo ratings yet
- ITF Unit 1Document25 pagesITF Unit 1Nandhini PrabakaranNo ratings yet
- 2nd Unit - SAPMDocument21 pages2nd Unit - SAPMNandhini PrabakaranNo ratings yet
- Primary Market - Definition, Types & Functions of Primary MarketDocument10 pagesPrimary Market - Definition, Types & Functions of Primary MarketNandhini PrabakaranNo ratings yet
- Over The Counter Exchange of India (OTCEI) - Definition, Features & BenefitDocument8 pagesOver The Counter Exchange of India (OTCEI) - Definition, Features & BenefitNandhini PrabakaranNo ratings yet
- Security AnalysisDocument9 pagesSecurity AnalysisNandhini PrabakaranNo ratings yet
- Investment Analysis & Portfolio Security GuideDocument16 pagesInvestment Analysis & Portfolio Security GuideNandhini PrabakaranNo ratings yet
- Cfi Gte BrochureDocument20 pagesCfi Gte Brochuresilesh gizachewNo ratings yet
- Trading Options BlueprintDocument12 pagesTrading Options BlueprintBujji Bangaru100% (2)
- IPO StatsDocument75 pagesIPO StatsprasannakumarNo ratings yet
- Generate Monthly Cash Flow by Selling OptionsDocument23 pagesGenerate Monthly Cash Flow by Selling OptionsCHAIMA CHICHA100% (2)
- Forex Mart IndiaDocument20 pagesForex Mart IndiaGaming FfNo ratings yet
- Order in The Matter of Kalpesh K ChawallaDocument20 pagesOrder in The Matter of Kalpesh K ChawallaShyam SunderNo ratings yet
- The Capital Market Represents The Market of The Financial Long-Term TitlesDocument9 pagesThe Capital Market Represents The Market of The Financial Long-Term TitlesDaiva ValienėNo ratings yet
- Selamat Sempurna's 2016 Performance and Commitment to GrowthDocument290 pagesSelamat Sempurna's 2016 Performance and Commitment to GrowthDimas32No ratings yet
- Spinoff Splitoff Splitup CarveoutDocument2 pagesSpinoff Splitoff Splitup CarveouttransitxyzNo ratings yet
- Valuation: Packet 2 Relative Valuation, Asset-Based Valuation and Private Company ValuationDocument170 pagesValuation: Packet 2 Relative Valuation, Asset-Based Valuation and Private Company Valuationluvie melatiNo ratings yet
- Norway's GPFG Model for Endowment InvestingDocument15 pagesNorway's GPFG Model for Endowment Investingrutty7No ratings yet
- Generic Convertible NoteDocument8 pagesGeneric Convertible Noteg4nz0100% (1)
- FINA3070 Lecture Notes v6Document215 pagesFINA3070 Lecture Notes v6aduiduiduio.oNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals July 2019 PDFDocument84 pagesFundamentals July 2019 PDFPRAGYAN PANDANo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Pub - Options Trading Made Simple How To Buy Calls Amp Puts and Achieve Financial Freedom in Only 5 Years Passive Stock Options Trading Book 1Document159 pagesDokumen - Pub - Options Trading Made Simple How To Buy Calls Amp Puts and Achieve Financial Freedom in Only 5 Years Passive Stock Options Trading Book 1ritu.dhakaNo ratings yet
- Airline Accounting Guideline No. 1Document24 pagesAirline Accounting Guideline No. 1hhap411No ratings yet
- Q4 Principles of Marketing 12 - Module 5 (W2)Document18 pagesQ4 Principles of Marketing 12 - Module 5 (W2)Oreo McflurryNo ratings yet
- Fee Based ServicesDocument2 pagesFee Based ServicesGurwinder SinghNo ratings yet
- FIN-310 Report PDFDocument15 pagesFIN-310 Report PDFHusen AliNo ratings yet
- Initial Public Offering Investment: The General Investors' PerspectiveDocument12 pagesInitial Public Offering Investment: The General Investors' PerspectiveBickramNo ratings yet
- SFRS For SE Statement of Applicability (2017)Document6 pagesSFRS For SE Statement of Applicability (2017)dgajudoNo ratings yet
- Resume 2Document1 pageResume 2Quek HJNo ratings yet
- Investment Assign 2 - QuestionsDocument7 pagesInvestment Assign 2 - QuestionsYuhan KENo ratings yet
- Technical Analysis Curriculum UpdatesDocument14 pagesTechnical Analysis Curriculum UpdatesJamesMc114433% (3)
- Risk Aversion and Capital Allocation To Risky AssetsDocument16 pagesRisk Aversion and Capital Allocation To Risky Assets777priyankaNo ratings yet
- K-Ratio - Gold Timing by KaeppelDocument4 pagesK-Ratio - Gold Timing by Kaeppelstummel6636No ratings yet
- How To Make Money in The Stock MarketDocument3 pagesHow To Make Money in The Stock MarketGilner PomarNo ratings yet
- Q.No. Options AnswerDocument3 pagesQ.No. Options AnswerRishiraj SinghNo ratings yet
- Stoxx Index GuideDocument370 pagesStoxx Index GuideThierry de PortzamparcNo ratings yet
- VP and USPDocument34 pagesVP and USPJoycee Mae JabinesNo ratings yet