0% found this document useful (0 votes)
84 views28 pagesLetrature Conclusion
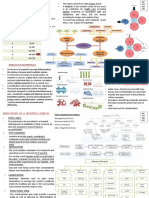
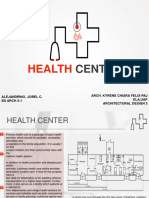
A hospital provides medical treatment using specialized staff and equipment. It consists of several divisions including administration, outpatient care, diagnostic services, inpatient care, and support services. Key areas are arranged by zones - outer, second, inner, deep, and service - based on access and functions. Proper planning of traffic flow, department relationships, and parking is important for efficient hospital operations.
Uploaded by
Wazir Sajid AliCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
84 views28 pagesLetrature Conclusion
A hospital provides medical treatment using specialized staff and equipment. It consists of several divisions including administration, outpatient care, diagnostic services, inpatient care, and support services. Key areas are arranged by zones - outer, second, inner, deep, and service - based on access and functions. Proper planning of traffic flow, department relationships, and parking is important for efficient hospital operations.
Uploaded by
Wazir Sajid AliCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd