Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Star and Galaxies in The Universe
Uploaded by
g-323477970 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views14 pagesOriginal Title
Star and Galaxies in the Universe
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views14 pagesStar and Galaxies in The Universe
Uploaded by
g-32347797Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
Star and Galaxies in the Universe
Star and Galaxies in the Universe
Galaxies
A setof body consisting of millions of star with
gas and dust particle.
Come in many forms :
spiral galaxies
elliptical galaxies
Irregular galaxies
Types Of Galaxies
Spiral Galaxies Elliptical Galaxies Irregular Galaxies
The Milky Way
The Milky Way
Is a medium large spiral galaxy.
Our solar system is located at the edge of one of
the spiral arms of the Milky Way.
Consists of approximately 200 billion stars and
the Sun is one of it.
Birth of Stars
formed from nebulae.
Nebulae are large clouds consisting of dust particles and gases
such as hydrogen and helium.
The gases and dust particles in a nebula are pulled by a
strong gravitational force
The strong gravitational force causes the globe of gas to
shrink and compress until it becomes very dense and forms
a core.
The core shrinks and becomes dense due to the increasing
strength of the gravitational force.
temperature and pressure in the core become too high, a
nuclear reaction will take place Hydrogen gas turns into
helium. A huge amount of heat energy and light is
released.
The core will shine and a star is formed.
The star that is formed is known as a protostar.
This new star continues to expand and becomes either
an average star like the Sun or a massive star.
Death of Stars
heat is generated which will heat up the outermost layer of the
star.
Hydrogen within this layer starts to burn and cause the star to
expand.
During this stage, the star appears red in colour and is called a red
giant.
If the red giant is not massive, a white dwarf is formed.
Ifthe red giant is big enough, it contracts so quickly that a big
explosion called supernova occurs.
Supernova is extremely bright and can be seen in
the explosion in daylight.
A neutron star is formed if the original star is a
large star.
Ifthe original star is a super-large star, a black
hole is formed.
Itis called a black hole because the light in it
cannot escape.
Relative Size Comparison
between the Earth and
the Universe
There are million of galaxies in the universe
The Milky Way is one of the many gaxies.
In Milky Way, there is a solar system which consists of eight
planets that orbit the Sun, and this includes the Earth where we
live in.
The Earth is smaller than a speck of dust in the universe.
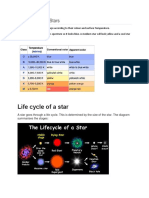
Characteristics of Stars
Characteristics to Classify Stars
Colour Size Distance Brightness Temperature
Classification of stars
based on colour and
temperature
Starshave colours that correspond to its surface
temperature which ranges from a lower to higher
temperature.
Colour Red Orange Yellow Yellowish- White Bluish- Blue
white White
Temperature <3500 3500- 5000- 6000- 7500- 11000- >25000
(K) 5000 6000 7500 11000 25000
Sizes of stars
Stars have different sizes; the really big ones are
called supergiant stars, big stars are called giant
stars while the really small ones are called dwarf
stars.
The brightness of a star depends on its size,
distance and surface temperature.
The brightest stars in the sky are Sirius and
Rigel.
Supergiant Giant Dwarf
You might also like
- Stellar Evolution - The Life Cycle of Stars in 40 CharactersDocument6 pagesStellar Evolution - The Life Cycle of Stars in 40 CharactersMary100% (1)
- Form 2 Chapter 11 Star and GalaxiesDocument26 pagesForm 2 Chapter 11 Star and GalaxiesAmer Malek67% (3)
- Google Meet 2A 21 October 2020: Stars and Galaxies in The UniverseDocument15 pagesGoogle Meet 2A 21 October 2020: Stars and Galaxies in The UniverseAthirah SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Stars and Galaxies in The UniverseDocument13 pagesStars and Galaxies in The UniverseoinyukwongNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of StarsDocument2 pagesCharacteristics of Starsangelie BatallonesNo ratings yet
- Stars: What Is A Star?Document4 pagesStars: What Is A Star?valentineNo ratings yet
- Wish Upon A STAR: Presented By: Daulo, Eunice R. III - Block 3Document17 pagesWish Upon A STAR: Presented By: Daulo, Eunice R. III - Block 3nhyce18No ratings yet
- Classifying Stars and Charting Their Life CyclesDocument6 pagesClassifying Stars and Charting Their Life CyclesAnonymous N3VvjVSTATNo ratings yet
- Stars, Galaxies and the Universe ExplainedDocument23 pagesStars, Galaxies and the Universe ExplainedSyahidah SalehNo ratings yet
- Presentation-WPS Office 081647Document72 pagesPresentation-WPS Office 081647Katherine NicoleNo ratings yet
- Stars and Galaxies in The UniverseDocument5 pagesStars and Galaxies in The UniverseMei Shuen CheamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Lesson 4Document40 pagesChapter 8 Lesson 4Frafti RejekiNo ratings yet
- Astronomy For Kids: StarsDocument2 pagesAstronomy For Kids: StarsOlga Faith BinsonNo ratings yet
- The Formation of The Milky Way and Our Solar System: Lesson3Document36 pagesThe Formation of The Milky Way and Our Solar System: Lesson3Shanen Anica FerancoNo ratings yet
- The Birth and Death of StarsDocument21 pagesThe Birth and Death of Starschrisferolino881No ratings yet
- 27 - Stars and GalaxiesDocument45 pages27 - Stars and GalaxiesNor AdinaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Stars Content NotesDocument2 pagesUnderstanding Stars Content Notesapi-404210114No ratings yet
- Star and Its PropertiesDocument4 pagesStar and Its PropertiesRemond BalabaNo ratings yet
- StarsDocument20 pagesStarsJoshua G. CunananNo ratings yet
- Stellar EvolutionDocument5 pagesStellar EvolutionMayar AzzamNo ratings yet
- Aghhamazing: Everyone!!! Have A Nice and Wonderful DayDocument28 pagesAghhamazing: Everyone!!! Have A Nice and Wonderful DayCALEB DEAREN G. BEMBONo ratings yet
- Name: Yusrinani Ibrahim Form: 2 Tegas 2008 Chapter: Stars and GalaxiesDocument30 pagesName: Yusrinani Ibrahim Form: 2 Tegas 2008 Chapter: Stars and GalaxiesyusrinaniNo ratings yet
- StarDocument2 pagesStarhadji montanoNo ratings yet
- Stars and Galaxies in The UniverseDocument17 pagesStars and Galaxies in The UniverseNur MyraNo ratings yet
- Stars and Galaxies in The UniverseDocument17 pagesStars and Galaxies in The UniverseNur MyraNo ratings yet
- StarDocument50 pagesStarIt's Me ZhinweijinNo ratings yet
- Star Chart PosterDocument2 pagesStar Chart PosterHasrizam86No ratings yet
- Stars and Galaxies in The UniverseDocument29 pagesStars and Galaxies in The UniverseINSYIRAH BINTI M ZAIRURLAIL 105No ratings yet
- Study 3Document16 pagesStudy 3rubisharma198929No ratings yet
- 6.2 Star and the Universe-Handout.docxDocument4 pages6.2 Star and the Universe-Handout.docxMohammad Wajeeh MohsinNo ratings yet
- CONSTELLATIONDocument16 pagesCONSTELLATIONNerissa EstebanNo ratings yet
- 7 Stages Star LifeDocument9 pages7 Stages Star LifeKay LagunaNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Chapter 11 Star and GalaxiesDocument26 pagesForm 2 Chapter 11 Star and GalaxiesNurul HusnaNo ratings yet
- Understanding AstronomyDocument18 pagesUnderstanding AstronomyZafir Ashman100% (1)
- Space Physics 3Document35 pagesSpace Physics 3drake lordNo ratings yet
- UniverseDocument11 pagesUniverseRithamikaNo ratings yet
- Stars PhysicsDocument3 pagesStars PhysicsJane MoralesNo ratings yet
- Beyond Our Solar System: Honors Earth ScienceDocument22 pagesBeyond Our Solar System: Honors Earth Scienceapi-27481415No ratings yet
- Sci8-Q2-W16-L-Heavenly BodiesDocument36 pagesSci8-Q2-W16-L-Heavenly BodiesOliver VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- AP 5 Quarter 4 Week 7Document4 pagesAP 5 Quarter 4 Week 7Parazo LanieNo ratings yet
- Red Dwarf Stars Are The Coolest andDocument3 pagesRed Dwarf Stars Are The Coolest andarkelNo ratings yet
- Stars and Beyond: Teacher GuideDocument29 pagesStars and Beyond: Teacher GuideAjay PesadoNo ratings yet
- Constituents and StructuresDocument18 pagesConstituents and StructuresHassan BareachNo ratings yet
- Stars and GalaxiesDocument10 pagesStars and GalaxiesziNo ratings yet
- G9 Science Q3 Week 8 9 ConstellationDocument87 pagesG9 Science Q3 Week 8 9 ConstellationShyllaNo ratings yet
- Stars and Constellations Characteristics of Stars BrightnessDocument8 pagesStars and Constellations Characteristics of Stars BrightnessRichelle TumambingNo ratings yet
- L 6 UniverseDocument11 pagesL 6 UniverseAbhay NayakNo ratings yet
- The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram: in The Life Cycles of The StarsDocument16 pagesThe Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram: in The Life Cycles of The Starssidharth kashyapNo ratings yet
- StarsDocument38 pagesStarsnozel77No ratings yet
- Fdocuments - in Chemistry Project Space ChemistryDocument22 pagesFdocuments - in Chemistry Project Space ChemistryLip UtNo ratings yet
- The Life Cycle of A Star Begins With The Accretion of Hydrogen and Helium Gas atDocument4 pagesThe Life Cycle of A Star Begins With The Accretion of Hydrogen and Helium Gas ataugustinemc94No ratings yet
- Blue Giant StarsDocument8 pagesBlue Giant Starsgeorge baltasNo ratings yet
- The Stellar Evolution: M (Solar Masses, 0.8-10 Times The Mass of Our Sun) While High Mass Stars Are Around 10-150 MDocument3 pagesThe Stellar Evolution: M (Solar Masses, 0.8-10 Times The Mass of Our Sun) While High Mass Stars Are Around 10-150 MarpithayogaNo ratings yet
- Project Name: Stars World Concept:: Redder LightDocument5 pagesProject Name: Stars World Concept:: Redder LightShruti SabharwalNo ratings yet
- All About Astronomy: The StarsDocument6 pagesAll About Astronomy: The StarspjblkNo ratings yet
- 6.2.2 StarsDocument6 pages6.2.2 StarsIshimwe HabiyakareNo ratings yet
- Stellar EvolutionDocument13 pagesStellar EvolutionJayeeta DasNo ratings yet
- 14 Fun Facts About Stars: A 15-Minute BookFrom Everand14 Fun Facts About Stars: A 15-Minute BookRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Ariane 5 - WikipediaDocument20 pagesAriane 5 - WikipediaMagno JuniorNo ratings yet
- Celestial MechanicsDocument1 pageCelestial MechanicssetyawarnoNo ratings yet
- Sign, Star and Sub Table - KP AstrologyDocument17 pagesSign, Star and Sub Table - KP AstrologyAmiit Luthra100% (2)
- The 21st Century Solar SystemDocument34 pagesThe 21st Century Solar SystemJohanesse GwapaNo ratings yet
- ParallaxDocument4 pagesParallaxapi-278478887No ratings yet
- Brown and Gray Flat Design Auditor Business Commercial ResumeDocument1 pageBrown and Gray Flat Design Auditor Business Commercial ResumeHudzaifah AfifahNo ratings yet
- Chapter S1 (Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation) LEARNING GOALSDocument34 pagesChapter S1 (Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation) LEARNING GOALSМарко Д. СтанковићNo ratings yet
- Aryabhatta Research Institute of Observational Sciences (Aries)Document12 pagesAryabhatta Research Institute of Observational Sciences (Aries)Saurav PatelNo ratings yet
- Solar Eclipses in History and MythologyDocument5 pagesSolar Eclipses in History and MythologyConstantin RoşuNo ratings yet
- Orbital Eccentricity: Problem: What Determines The Shapes of The Planets' Orbits?Document4 pagesOrbital Eccentricity: Problem: What Determines The Shapes of The Planets' Orbits?Indris SianturiNo ratings yet
- Space Exploration: Class: S.Y.B Architecture Sub: Environmental Presented By: Rutuja KandekarDocument21 pagesSpace Exploration: Class: S.Y.B Architecture Sub: Environmental Presented By: Rutuja KandekarAwais SkNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science11 - Q1 - Module 1Document18 pagesEarth and Life Science11 - Q1 - Module 1Kennedy Fieldad VagayNo ratings yet
- STEM SHS Earth Sci. Wk1, Module 1.1Document19 pagesSTEM SHS Earth Sci. Wk1, Module 1.1the witcherNo ratings yet
- Change Job by KP AstrologyDocument2 pagesChange Job by KP AstrologyPt Akaash100% (4)
- 4th Grade Immersion 1Document4 pages4th Grade Immersion 1api-314229616No ratings yet
- Kids Room Decoration Project Proposal by SlidesgoDocument61 pagesKids Room Decoration Project Proposal by SlidesgoTHiNo ratings yet
- Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome Clinical Case by SlidesgoDocument58 pagesEhlers-Danlos Syndrome Clinical Case by SlidesgoIcha AzizahNo ratings yet
- Rendezvous and Proximity Operations Handbook-Part 1Document17 pagesRendezvous and Proximity Operations Handbook-Part 1cezy80No ratings yet
- EC 2045 SyllabusDocument1 pageEC 2045 SyllabusGanesamoorthyNo ratings yet
- KP Astrology-Denial of Child Birth-4Document7 pagesKP Astrology-Denial of Child Birth-4rahul106No ratings yet
- Factors of EarthDocument2 pagesFactors of EarthAnna Dominic De RomaNo ratings yet
- Solar Energy Company Pitch Deck by SlidesgoDocument53 pagesSolar Energy Company Pitch Deck by Slidesgohalima benaliNo ratings yet
- Overview of In-Orbit Radiation Induced Spacecraft Anomalies: R. Ecoffet, Member, IEEEDocument25 pagesOverview of In-Orbit Radiation Induced Spacecraft Anomalies: R. Ecoffet, Member, IEEEalexanderNo ratings yet
- Early Views of The UniverseDocument44 pagesEarly Views of The UniverseAllen KateNo ratings yet
- Astrophysics ExercisesDocument3 pagesAstrophysics ExercisesMax Bastow100% (1)
- Investigating Congressional OrganizationalDocument10 pagesInvestigating Congressional OrganizationalDominique AwisNo ratings yet
- Satillate ProjectDocument3 pagesSatillate Projectapi-391913193No ratings yet
- SRI SAI RAM Satellite Communication Unit TestDocument3 pagesSRI SAI RAM Satellite Communication Unit Testsaravanan100% (1)
- DBSM, DDL, Dan DML: Annisa Salma A.E / 04 / XII RPL ADocument51 pagesDBSM, DDL, Dan DML: Annisa Salma A.E / 04 / XII RPL AMisaka TensaiNo ratings yet
- AstronomyDocument12 pagesAstronomyXeotiicNo ratings yet