Professional Documents
Culture Documents
of Business Comm.
Uploaded by
kshitijOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
of Business Comm.
Uploaded by
kshitijCopyright:
Available Formats
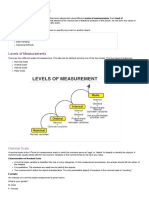
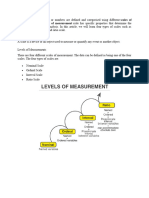
Scales:-
Measurement scales different types:-
Nominal Scale:-
A nominal scale is the 1st level of measurement scale in which the
numbers serve as “tags” or “labels” to classify or identify the objects.
Characteristics of Nominal Scale-
A nominal scale variable is classified into two or more categories. In this
measurement mechanism, the answer should fall into either of the
classes.
It is qualitative. The numbers are used here to identify the objects.
Ordinal Scale:-
The ordinal scale is the 2nd level of measurement that reports the
ordering and ranking of data without establishing the degree of
variation between them.
Characteristics of the Ordinal Scale-
The ordinal scale shows the relative ranking of the variables.
The interval properties are not known.
Interval Scale:-
The interval scale is the 3rd level of measurement scale. It is defined as
a quantitative measurement scale in which the difference between the
two variables is meaningful.
Characteristics of Interval Scale-
The interval scale is quantitative as it can quantify the difference between the
values.
It allows calculating the mean and median of the variables.
Ratio Scale:-
The ratio scale is the 4th level of measurement scale, which is quantitative.
It is a type of variable measurement scale. It allows researchers to
compare the differences or intervals. The ratio scale has a unique feature.
It possesses the character of the origin or zero points.
Characteristics of Ratio Scale-
Ratio scale has a feature of absolute zero.
It doesn’t have negative numbers, because of its zero-point feature.
Various Scales:-
Nominal Scale:-
Used for labelling variables or recognition of a group or
individual, without any quantitative value .
“Nominal” “Name”
“Nominal scale” “labels” “Names”
All these scales are mutually exclusive (NO OVERLAP)
Example:- male or female groups ,religious preferences,
name of states etc.
None of them have any numerical significance.
A subtype of nominal scale with only two categories is called
“Dichotomous”.
Example:- Male Female, Yes No, etc.
Ordinal Scale:-
Ordinal scale are typically measures of nonnumeric concepts
like satisfaction, happiness, discomfort, etc.
“ Ordinal” “Order”
Example:- Socioeconomic status Poor, Middle, Rich
Interval scale:-
Interval scales are numerical scales in which we know not
only the order but, also exact difference between the values.
“Interval scales” “Interval”
“Equal space in between”
Example :- Celsius temperature “the differences between 90
and 70 degrees a 20 degrees, as is the difference between 40
and 60 degrees
Limitations :- They don’t have “true zeros” but may have an
arbitrary zeros.
Without “true zeros” , it is impossible to compute ratios.
Only addition and subtraction are possible
Ratios Scales:-
In Ratio scale we have Name and can be divided
into categories such as Order and they can tell us the
exact values between the unit
They also have absolute zeros
Example :- Height and Weight
The values under ratio scales can be Added,
subtracted, multiplied and divided.
Which allows for a wide range of both descriptive
and inferential statistics to be applied
References:-
www.google.com
www.youtube.com
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Social_semi
otics
You might also like
- Multivariate Analysis – The Simplest Guide in the Universe: Bite-Size Stats, #6From EverandMultivariate Analysis – The Simplest Guide in the Universe: Bite-Size Stats, #6No ratings yet
- Statistics: Notes: NamedDocument5 pagesStatistics: Notes: NamedSecondel BorresNo ratings yet
- Level of MeasurementDocument4 pagesLevel of Measurementpegtimaryjoy091No ratings yet
- Scales of Measurement - Nominal, Ordinal, Interval and RatioDocument2 pagesScales of Measurement - Nominal, Ordinal, Interval and RatioDESHRAJ MEENANo ratings yet
- Types of Data & Measurement Scales: Ordinal ScaleDocument2 pagesTypes of Data & Measurement Scales: Ordinal ScaleTanmay MaityNo ratings yet
- ScalesDocument16 pagesScalesOwais PanditNo ratings yet
- Scaling TechniquesDocument29 pagesScaling TechniquesAnshika AroraNo ratings yet
- Measurement ToolDocument30 pagesMeasurement ToolLekhnath SubediNo ratings yet
- Measurement ScaleDocument24 pagesMeasurement ScalesoniNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document25 pagesUnit 3Yash SonkarNo ratings yet
- Name Kamga Nzoh 2Document1 pageName Kamga Nzoh 2mohammadou awaluNo ratings yet
- Nominal Ordinal Interval RatioDocument7 pagesNominal Ordinal Interval RatioDaniel Laoaten100% (1)
- Submission of Assignment 3Document2 pagesSubmission of Assignment 3raj kNo ratings yet
- Types of Data & Measurement Scales: Nominal, Ordinal, Interval and RatioDocument4 pagesTypes of Data & Measurement Scales: Nominal, Ordinal, Interval and RatioRochelle PrieteNo ratings yet
- Statistic S: Mhel Alexis P. Murillo 8-AristotleDocument54 pagesStatistic S: Mhel Alexis P. Murillo 8-AristotleMhel Alexis MurilloNo ratings yet
- Measurement and Scaling ConceptDocument20 pagesMeasurement and Scaling ConceptVãńšh WädhwåNo ratings yet
- Types of Data & Measurement Scales: Nominal, Ordinal, Interval and RatioDocument5 pagesTypes of Data & Measurement Scales: Nominal, Ordinal, Interval and RatioMaia Traje PamolinoNo ratings yet
- Types of DataDocument9 pagesTypes of DataIqbal TaufiqurrochmanNo ratings yet
- Stats - GC MaterialDocument7 pagesStats - GC MaterialHazel SmithNo ratings yet
- Types of DataDocument21 pagesTypes of DataAdarsh MohantyNo ratings yet
- Scales of MeasurementDocument12 pagesScales of MeasurementXyrene Keith MedranoNo ratings yet
- Types of Data & Measurement Scales: Nominal, Ordinal, Interval and RatioDocument5 pagesTypes of Data & Measurement Scales: Nominal, Ordinal, Interval and RatioJannahJoyCatamioNo ratings yet
- BRM Unit 3&4 Complete1Document69 pagesBRM Unit 3&4 Complete114122001riya2001No ratings yet
- Scale of MeasurementDocument5 pagesScale of MeasurementashishNo ratings yet
- 1.measurement and ScalingDocument44 pages1.measurement and ScalingGaganNo ratings yet
- Scales of Measurement: By-Yukti SharmaDocument15 pagesScales of Measurement: By-Yukti SharmaYukti SharmaNo ratings yet
- Levels of Measurement FinalDocument41 pagesLevels of Measurement FinalMary SutingcoNo ratings yet
- Scales of MeasurementDocument6 pagesScales of MeasurementArslan ZaibNo ratings yet
- Measurement Scales in StatisticsDocument3 pagesMeasurement Scales in Statisticsتابندہ نعیمNo ratings yet
- Measurement and ScalingDocument12 pagesMeasurement and ScalingShafak MahajanNo ratings yet
- BA - Scales of MeasurementDocument11 pagesBA - Scales of Measurementnaveen_b_rNo ratings yet
- Subject: Probability and Random Variables Submitted To: Sir Tauseef Ahmed Submitted By: Amina Nadeem Roll No: 090317 Section: BEE-4-BDocument4 pagesSubject: Probability and Random Variables Submitted To: Sir Tauseef Ahmed Submitted By: Amina Nadeem Roll No: 090317 Section: BEE-4-BaminanadeemNo ratings yet
- SBDnotes BFIA1BDocument4 pagesSBDnotes BFIA1BChetan SinghNo ratings yet
- Classification of Variables and Types of ScalesDocument4 pagesClassification of Variables and Types of ScalesNika BautistaNo ratings yet
- Q.1 Describe Level of Measurement. Give Five Examples of Each Level and Explain The Role of Level of Measurement in Decision Making. Ans. Levels of MeasurementDocument27 pagesQ.1 Describe Level of Measurement. Give Five Examples of Each Level and Explain The Role of Level of Measurement in Decision Making. Ans. Levels of MeasurementashaNo ratings yet
- Ch3 - Measurement in ResearchDocument34 pagesCh3 - Measurement in Researchshagun.2224mba1003No ratings yet
- Measurement and Scale Construction TechniquesDocument61 pagesMeasurement and Scale Construction TechniquesAbhishek kumarNo ratings yet
- Measurement and ScalingDocument4 pagesMeasurement and ScalingPrakriti DuttaNo ratings yet
- Principle Measurement Scales Social Science by Assoc Prof DR Caroline Geetha AP B ArokiadasanDocument29 pagesPrinciple Measurement Scales Social Science by Assoc Prof DR Caroline Geetha AP B ArokiadasanGirmaw YeshanbelNo ratings yet
- Measurement in ResearchDocument4 pagesMeasurement in ResearchGideon K. Mutai100% (1)
- Ch13 Zikmund Measurement and ScaleDocument31 pagesCh13 Zikmund Measurement and Scalerohitoberoi1175% (4)
- Measurement and ScalingDocument70 pagesMeasurement and ScalingRitik ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Measurement ScalesDocument13 pagesMeasurement ScalesVeena VaishyNo ratings yet
- Measurement ScalesDocument14 pagesMeasurement ScalesKaran KumarNo ratings yet
- Measurement and ScalingDocument14 pagesMeasurement and ScalingabcdNo ratings yet
- Four Levels of Measurement in StatsDocument7 pagesFour Levels of Measurement in StatsGowther DesuNo ratings yet
- Types of Data & The Scales of Measurement: Data at The Highest Level: Qualitative and QuantitativeDocument7 pagesTypes of Data & The Scales of Measurement: Data at The Highest Level: Qualitative and QuantitativeSanthosh K SNo ratings yet
- Measurement and Scaling Techniques: Scales of Measurement, Sources of Error in MeasurementDocument12 pagesMeasurement and Scaling Techniques: Scales of Measurement, Sources of Error in MeasurementwickedramanNo ratings yet
- Type of DataDocument18 pagesType of DatarameshNo ratings yet
- Data and AttributesDocument5 pagesData and AttributesAishwarya JagtapNo ratings yet
- Scales or Level of MeasurementsDocument2 pagesScales or Level of Measurementshytii gamesNo ratings yet
- Measurement ScalesDocument2 pagesMeasurement ScalesMary Rose Alfie DabalosNo ratings yet
- BA Group-4 .Document16 pagesBA Group-4 .Khan FaizanNo ratings yet
- 3 Observations Measurement and VariablesDocument9 pages3 Observations Measurement and Variablesncarab15No ratings yet
- Measurement ScalesDocument14 pagesMeasurement ScalesAnitha PurushothamanNo ratings yet
- Statistics Is Mainly Divided Into The Following Two CategoriesDocument6 pagesStatistics Is Mainly Divided Into The Following Two CategoriesPalleti RenukaNo ratings yet
- Types of ScalesDocument8 pagesTypes of ScalesBahrouniNo ratings yet
- STATISTICSDocument2 pagesSTATISTICSChristine TutorNo ratings yet
- Scaling ConceptDocument35 pagesScaling ConceptKoteswaraRaoBNo ratings yet
- Statistics IsDocument3 pagesStatistics IsArvz Vash ArcadioNo ratings yet
- Strategic Planning and Corporate Social ResponsibilityDocument2 pagesStrategic Planning and Corporate Social ResponsibilitykshitijNo ratings yet
- Trade Theory 1Document9 pagesTrade Theory 1kshitijNo ratings yet
- BBDU PhDRegulations2023Document13 pagesBBDU PhDRegulations2023kshitijNo ratings yet
- Business EnvironmentDocument7 pagesBusiness EnvironmentkshitijNo ratings yet
- ETHICAL and Legal ISSUES IN SALES AND DISTRIBUTION MANAGEMENTDocument1 pageETHICAL and Legal ISSUES IN SALES AND DISTRIBUTION MANAGEMENTkshitijNo ratings yet
- Theories of Personal SellingDocument6 pagesTheories of Personal SellingkshitijNo ratings yet
- Unit1 Technology ManagementDocument8 pagesUnit1 Technology ManagementkshitijNo ratings yet
- A Study On Mrketing Strategy at K.B Products (Nakoda) Pvt. LTDDocument5 pagesA Study On Mrketing Strategy at K.B Products (Nakoda) Pvt. LTDkshitijNo ratings yet
- Research PaperDocument5 pagesResearch PaperkshitijNo ratings yet
- Creating NC FilesDocument8 pagesCreating NC FilesStelian ConstantinescuNo ratings yet
- Classification of ComputersDocument2 pagesClassification of Computerseduardo acuniaNo ratings yet
- Jchps 6 (4) 15 Page 286-292 MsreddyDocument7 pagesJchps 6 (4) 15 Page 286-292 MsreddydwahyusafriNo ratings yet
- Western Underground - HV and Ehv Cables-CmeDocument38 pagesWestern Underground - HV and Ehv Cables-CmeA. Hassan100% (2)
- QSV 2 Product Release Procedure EN 01 PDFDocument6 pagesQSV 2 Product Release Procedure EN 01 PDFprashanthNo ratings yet
- Midas Manual PDFDocument49 pagesMidas Manual PDFNishad Kulkarni100% (1)
- Books For GATE Mechanical EngineeringDocument9 pagesBooks For GATE Mechanical EngineeringNikhilChauhanNo ratings yet
- Graduate Enlistment: DAF 202 - Economics & Social Aspect of DevelopmentDocument43 pagesGraduate Enlistment: DAF 202 - Economics & Social Aspect of DevelopmentJames Ray HjPotter MendajeNo ratings yet
- Tech Bull 3 - Free Fall of ConcreteDocument4 pagesTech Bull 3 - Free Fall of ConcreteJoel TorcuatorNo ratings yet
- Autodesk Navisworks 2012 - Guia Do UsuárioDocument820 pagesAutodesk Navisworks 2012 - Guia Do UsuárioericfgNo ratings yet
- Kursus Literasi MaklumatDocument5 pagesKursus Literasi MaklumatDanTanNo ratings yet
- Strategic Planning ModelDocument55 pagesStrategic Planning ModelShamkant KomarpantNo ratings yet
- History of AAMI BIT StoryDocument11 pagesHistory of AAMI BIT StoryManojNo ratings yet
- Gender Theory SummaryDocument10 pagesGender Theory SummaryDanar CristantoNo ratings yet
- Applied Thermodynamics IIDocument124 pagesApplied Thermodynamics IIHimanshu1712100% (2)
- Group 1 Nondigital Instructional MaterialsDocument22 pagesGroup 1 Nondigital Instructional MaterialsJhon Paul Esplanada Soriano100% (1)
- IPT and DepressionDocument14 pagesIPT and DepressionReanna WaughNo ratings yet
- Titan OrionDocument7 pagesTitan Orionajwad7No ratings yet
- Sustainable Architecture WikiDocument9 pagesSustainable Architecture WikisiddiqueaquibNo ratings yet
- 05 AccelerationDownIncline-2Document4 pages05 AccelerationDownIncline-2PeterNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment in Shipping CompaniesDocument18 pagesRisk Assessment in Shipping Companiesleopradeep100% (4)
- Chapter 3 - Basic Statistical ConceptsDocument16 pagesChapter 3 - Basic Statistical ConceptsChristian Alfred VillenaNo ratings yet
- 2009 S+S BrochureDocument45 pages2009 S+S BrochureSMITH+SMITHNo ratings yet
- Fallacy - Philosophy Grade 11Document17 pagesFallacy - Philosophy Grade 11leila vesagasNo ratings yet
- Iso 14520 5 2019Document9 pagesIso 14520 5 2019salazarafael0% (1)
- Happy FinalDocument32 pagesHappy FinalRaju MehtaNo ratings yet
- GEK 63383d Turbine Generator FoundationDocument61 pagesGEK 63383d Turbine Generator Foundationbong2rm100% (6)
- Practical Research 1 Qualitative 2Document112 pagesPractical Research 1 Qualitative 2ZleCerboAtienza100% (3)
- Railway Fatalities in South West MumbaiDocument12 pagesRailway Fatalities in South West MumbaiAwpan SabaleNo ratings yet
- Leadership in Innovation 1194529453608858 3Document22 pagesLeadership in Innovation 1194529453608858 3shashi4u.kumar5817No ratings yet