Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Muscle Relaxant
Uploaded by
RadyanPramono0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views8 pagesAtracurium is extensively metabolized by two processes, ester hydrolysis catalyzed by nonspecific esterases and spontaneous Hofmann elimination at physiological pH. Less than 10% is excreted unchanged. It can cause dose-dependent histamine release and cardiovascular side effects above 0.5 mg/kg. Laudanosine, a breakdown product of the Hofmann elimination, has been associated with central nervous system excitation. Rocuronium undergoes no metabolism and is eliminated primarily by the liver, with its duration modestly prolonged by liver failure, pregnancy, or decreased liver function in elderly patients.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAtracurium is extensively metabolized by two processes, ester hydrolysis catalyzed by nonspecific esterases and spontaneous Hofmann elimination at physiological pH. Less than 10% is excreted unchanged. It can cause dose-dependent histamine release and cardiovascular side effects above 0.5 mg/kg. Laudanosine, a breakdown product of the Hofmann elimination, has been associated with central nervous system excitation. Rocuronium undergoes no metabolism and is eliminated primarily by the liver, with its duration modestly prolonged by liver failure, pregnancy, or decreased liver function in elderly patients.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views8 pagesMuscle Relaxant
Uploaded by
RadyanPramonoAtracurium is extensively metabolized by two processes, ester hydrolysis catalyzed by nonspecific esterases and spontaneous Hofmann elimination at physiological pH. Less than 10% is excreted unchanged. It can cause dose-dependent histamine release and cardiovascular side effects above 0.5 mg/kg. Laudanosine, a breakdown product of the Hofmann elimination, has been associated with central nervous system excitation. Rocuronium undergoes no metabolism and is eliminated primarily by the liver, with its duration modestly prolonged by liver failure, pregnancy, or decreased liver function in elderly patients.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
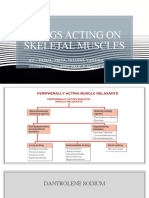
MUSCLE RELAXANT
ATRACURIUM
Metabolism & Excretion
Atracurium is so extensively metabolized that its pharmacokinetics are independent of
renal and
hepatic function, and less than 10% is excreted unchanged by renal and biliary routes.
Two separate processes are responsible for metabolism.
A. Ester Hydrolysis
This action is catalyzed by nonspecific esterases, not by acetylcholinesterase or
pseudocholinesterase.
B. Hofmann Elimination
A spontaneous nonenzymatic chemical breakdown occurs at physiological pH and
temperature.
ATRACURIUM
Side Effects & Clinical Considerations
Atracurium triggers dose-dependent histamine release that becomes significant at doses above 0.5
mg/kg.
Hypotension and Tachycardia
Cardiovascular side effects are unusual unless doses in excess of 0.5 mg/kg are administered. Atracurium
may also cause a transient drop in systemic vascular resistance and an increase in cardiac index
independent of any histamine release. A slow rate of injection minimizes these effects.
Bronchospasm
Atracurium should be avoided in asthmatic patients. Severe bronchospasm is occasionally seen in
patients without a history of asthma.
Laudanosine Toxicity
Laudanosine, a tertiary amine, is a breakdown product of atracurium’s Hofmann elimination and has
been associated with central nervous system excitation, resulting in elevation of the minimum alveolar
concentration and even precipitation of seizures
ROCURONIUM
Metabolism & Excretion
Rocuronium undergoes no metabolism and is eliminated primarily by the liver and
slightly by the kidneys.
Its duration of action is not significantly affected by renal disease, but it is modestly
prolonged by severe liver failure and pregnancy.
Elderly patients may experience a prolonged duration of action due to decreased liver
mass
TERIMA KASIH
You might also like
- Anticholinergic DrugsDocument19 pagesAnticholinergic DrugseashshankarNo ratings yet
- FINAL Drug StudyDocument9 pagesFINAL Drug StudyKristen Leigh MarianoNo ratings yet
- Skeletal Muscle RelaxantsDocument34 pagesSkeletal Muscle RelaxantsLohithNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System-2Document8 pagesAutonomic Nervous System-2محمد علي حميدNo ratings yet
- Suggamadex Remifentanyl PalonosetronDocument28 pagesSuggamadex Remifentanyl PalonosetronSai TejeswiNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of The Gastrointestinal Drugs (I)Document12 pagesPharmacology of The Gastrointestinal Drugs (I)anaNo ratings yet
- ParacetamolDocument10 pagesParacetamolANa AntonioNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in CcuDocument169 pagesDrugs Used in CcuAnusha Verghese100% (3)
- Current Management Guidline in Organophosphors Poisoning: DR - Surendra Khosya Guided by Dr. S.R Meena Dr. Meenaxi ShardaDocument28 pagesCurrent Management Guidline in Organophosphors Poisoning: DR - Surendra Khosya Guided by Dr. S.R Meena Dr. Meenaxi ShardasurendrakhosyaNo ratings yet
- OrganophosphateDocument21 pagesOrganophosphatehendra_darmawan_4No ratings yet
- Neuromuscular Blocking DrugsDocument5 pagesNeuromuscular Blocking DrugsTherese Jane TiradorNo ratings yet
- Asthalin InhalerDocument7 pagesAsthalin InhalerINDAH WIDYANING TYASNo ratings yet
- AtropineDocument13 pagesAtropineMostafa HassanNo ratings yet
- Suxamethonium Chloride Injection Bp-PiDocument8 pagesSuxamethonium Chloride Injection Bp-PinanaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Act2 MidtermDocument3 pagesPharmacology Act2 MidtermJhjhasNo ratings yet
- Poisoning: Clinical Biochemistry: Metabolic and Clinical Aspects (Third Edition)Document2 pagesPoisoning: Clinical Biochemistry: Metabolic and Clinical Aspects (Third Edition)lia lykimNo ratings yet
- AnticholinergicDocument44 pagesAnticholinergicLucas JelmarNo ratings yet
- Acetazolamide (Uramox)Document5 pagesAcetazolamide (Uramox)ddandan_2No ratings yet
- Acute Poisoning of Therapeutic Agents: by Alemayehu TomaDocument42 pagesAcute Poisoning of Therapeutic Agents: by Alemayehu TomaYohannis AsefaNo ratings yet
- Obat Asma: Irme Adhitya 21804101051 Pembimbing: Andri Tilaqza, S.Farm, M.Farm, AptDocument85 pagesObat Asma: Irme Adhitya 21804101051 Pembimbing: Andri Tilaqza, S.Farm, M.Farm, AptIrme AdhityaNo ratings yet
- 1.for Many YearsDocument41 pages1.for Many YearsAbdelouahed Elle AlaouiNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic SyndromeDocument3 pagesCholinergic SyndromeEmman AguilarNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive AgentsDocument33 pagesAntihypertensive AgentsJuwairia tariqNo ratings yet
- CholinergicDocument11 pagesCholinergicmadeha goharNo ratings yet
- Atropine Sulfate InjectionDocument4 pagesAtropine Sulfate InjectionIrawanMarlyNo ratings yet
- HaemaccelinfDocument9 pagesHaemaccelinfSisca YulistianaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyGail SantosNo ratings yet
- Leaflet MaxflowDocument1 pageLeaflet MaxflowKamran IjazNo ratings yet
- Drug OrnDocument25 pagesDrug OrnOrnwadee Jit-owatNo ratings yet
- Acetazolamide-Acetazolamide Injection, Powder, Lyophilized, For Solution Xgen Pharmaceuticals DJB, IncDocument9 pagesAcetazolamide-Acetazolamide Injection, Powder, Lyophilized, For Solution Xgen Pharmaceuticals DJB, Incandi hasri ainunNo ratings yet
- (BMI) of 30 kg/m2 or GreaterDocument3 pages(BMI) of 30 kg/m2 or GreaterRackyNo ratings yet
- Summary of Product CharacteristicDocument5 pagesSummary of Product Characteristicresearch universalNo ratings yet
- DuaventDocument9 pagesDuaventAjurs UrsabiaNo ratings yet
- Anti AritmiaDocument27 pagesAnti AritmiadoraemonmayaNo ratings yet
- PHARMACOLOGYDocument69 pagesPHARMACOLOGYKiran ShahNo ratings yet
- Acetazolamide-Acetazolamide Injection, Powder, Lyophilized, For Solution Xgen Pharmaceuticals DJB, IncDocument13 pagesAcetazolamide-Acetazolamide Injection, Powder, Lyophilized, For Solution Xgen Pharmaceuticals DJB, Incandi hasri ainunNo ratings yet
- Amiodarone Hydrochloride in JDocument18 pagesAmiodarone Hydrochloride in JChrizzna HaryantoNo ratings yet
- 36-Organophosphorus PoisoningDocument28 pages36-Organophosphorus PoisoningSumaiyyaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyChickz HunterNo ratings yet
- NAME OF DRUG NozinanDocument3 pagesNAME OF DRUG NozinanMill Jan CruzNo ratings yet
- Paracetamol OverdoseDocument6 pagesParacetamol OverdoseAhmad KamaluddinNo ratings yet
- Neuropharma AntidementiaDocument29 pagesNeuropharma AntidementiaKeanne Paula AmamanglonNo ratings yet
- VernakalantDocument15 pagesVernakalantAkif AhamadNo ratings yet
- Clinical Toxicology TreatmentDocument22 pagesClinical Toxicology TreatmentRatheesh KumarNo ratings yet
- RoculaxDocument4 pagesRoculaxvannyanoyNo ratings yet
- IV Induction Agents Slides For Podcast UpdatedDocument59 pagesIV Induction Agents Slides For Podcast UpdateddsfdsfNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetics of Oxicam Nonsteroidal AntiDocument3 pagesPharmacokinetics of Oxicam Nonsteroidal AntiIir Irma SuryaniNo ratings yet
- Alda Risma CaseDocument13 pagesAlda Risma CasealdiraNo ratings yet
- Agonis Dan Antagonis MuskarinikDocument21 pagesAgonis Dan Antagonis MuskarinikKartikaNo ratings yet
- (Printed) Pass Medicine Notes - Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology (Edited)Document53 pages(Printed) Pass Medicine Notes - Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology (Edited)Joanne HoNo ratings yet
- AmbroxolDocument1 pageAmbroxolPrecious CarmelaNo ratings yet
- Verapamil PDFDocument13 pagesVerapamil PDFddandan_2No ratings yet
- Management of Overdose and Poisoning: Paula Jerrard-DunneDocument44 pagesManagement of Overdose and Poisoning: Paula Jerrard-DunneAziz EzoNo ratings yet
- Drug RationaleDocument77 pagesDrug RationaleYolanda WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Antigout PDFDocument21 pagesAntigout PDFshaifNo ratings yet
- Furosemide Tables:: Pharmacokinetics Bioavailability Peak Plasma Level Plasma Half-Life Active Metabolites EliminationDocument4 pagesFurosemide Tables:: Pharmacokinetics Bioavailability Peak Plasma Level Plasma Half-Life Active Metabolites Eliminationmole_fkNo ratings yet
- Icu ProtocolDocument4 pagesIcu Protocolmehal guptaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology NMB Ds and Anti Cholinesterase S FinalDocument8 pagesPharmacology NMB Ds and Anti Cholinesterase S FinalPamella Kusuma WerdanieNo ratings yet