Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Denudation, Weathering, Mass Weathering and Erosion
Uploaded by
Amreka Hosein0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views11 pagesOriginal Title
Denudation, weathering, mass weathering and erosion
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views11 pagesDenudation, Weathering, Mass Weathering and Erosion
Uploaded by
Amreka HoseinCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
Denudation, weathering, mass
weathering and erosion
GEOGRAPHY
MISS HOSEIN
Weathering
Weathering is the breakdown,
but not removal, of rocks.
Weathering
• Most rocks are formed beneath the surface and when they are exposed at the
surface, the conditions are very different.
• At the surface, they are exposed to the atmosphere and rainwater. The rocks
begin to break down in situ (in their original position).
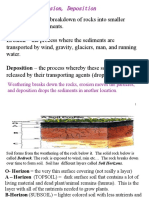
• There are weathered and the layer of weathered, broken and unconsolidated
rock that forms at the Earth’s surface is known as the regolith.
• Where weathering is rapid or material is removed slowly, the regolith is thick.
• Where weathering is slow or material is removed rapidly, the regolith is thin.
• The boundary between the weathered material and unweathered rock is called
the weathering front.
Mass wasting
Mass wasting or mass movement
is the movement downslope of
rock fragments and soil under
the influence of gravity.
Mass wasting
• Most rocks are held together by a structure of solid minerals.
• When rocks are weathered, this structure is weakened and the solid rock is
replaced by a mixture of clay minerals, larger soil and sand particles and
small fragments of rock.
• Weathered material can move downslope under the influence of gravity.
• Movement is faster on steep slopes where the ground is wet.
• This process is known as mass wasting or mass movement.
Erosion
Erosion is the removal of part of
the land surface by wind, water,
gravity or ice.
Erosion
• Weathered material can be removed by running water, by the wind, and in
cold climates, by glaciers.
• In the Caribbean, water is the most important agent of erosion.
• The land may be eroded by rain action, by rivers and streams and by the
sea.
Deposition
Deposition is the dropping of
material which has been picked
up and transported by wind,
water or ice.
Deposition
• When weathered material has been eroded, it is usually transported to
another location by running water, wave action or by wind or glaciers.
• At a later stage, the material is deposited.
• Deposition may occur in many locations, for example: at the base of a
slope, in the lower part of a river valley or on a beach where waves deposit
sand or stones or in the sea.
Denudation
Denudation is the laying bare of
underlying rocks by the
processes of weathering,
transport and erosion.
Denudation
• Weathering, transport and erosion remove rocks and other material from
the surface of the Earth.
• In doing so, they carve out river valleys and create other landforms.
• This process is known as denudation.
• Some landforms are not created by denudation and are called
constructional landforms. Examples include volcanoes and coral reefs.
You might also like
- Weathering Erosion and DepositionDocument33 pagesWeathering Erosion and DepositionFrank DescartesNo ratings yet
- Exogenic Processes 2Document40 pagesExogenic Processes 2petche marie94% (17)
- Erosion, Mass Wasting and DepositionDocument33 pagesErosion, Mass Wasting and DepositionAbu SayeedNo ratings yet
- Erosion and TransportationDocument17 pagesErosion and TransportationbibsNo ratings yet
- Exogenic ProcessesDocument40 pagesExogenic Processesantonio Almiranes100% (1)
- Exogenic ProcessDocument38 pagesExogenic ProcessDuane AlfelorNo ratings yet
- The Geomorphic ProcessDocument10 pagesThe Geomorphic Processrosana f.rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Erosion Mass WastingDocument11 pagesErosion Mass WastingTina YusonNo ratings yet
- Erosion Mass WastingDocument11 pagesErosion Mass WastingCristina YusonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Earth Materials and Processes: Exogenic ProcessDocument67 pagesChapter 4: Earth Materials and Processes: Exogenic ProcessGwen Mara Tanggol100% (4)
- Lesson-5 of Earth and Life ScienceDocument53 pagesLesson-5 of Earth and Life ScienceAJ PAMISANo ratings yet
- Earth Science Week 5Document47 pagesEarth Science Week 5Brenan BaltazarNo ratings yet
- ESci Finals - Lesson 1 Exogenic ProcessesDocument54 pagesESci Finals - Lesson 1 Exogenic ProcessesZACKIENo ratings yet
- Earth's Processes: Exogenic and EndogenicDocument73 pagesEarth's Processes: Exogenic and EndogenicJgwenneth Aljhane Pintor100% (1)
- Earth's Processes: Jerome A. Bigael, Leyte Progressive High SchoolDocument37 pagesEarth's Processes: Jerome A. Bigael, Leyte Progressive High SchoolJenica PatzNo ratings yet
- Earth Science: WeatheringDocument85 pagesEarth Science: WeatheringElijah Raphael YasaNo ratings yet
- Earth Science - Group 1Document19 pagesEarth Science - Group 1HerwienNo ratings yet
- Earth's Processe SDocument37 pagesEarth's Processe SReizexen GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Eksogen - PPTX (Recovered)Document38 pagesEksogen - PPTX (Recovered)Gagas Tri LaksonoNo ratings yet
- Exogenic Processeses 1Document7 pagesExogenic Processeses 1Teacher MelNo ratings yet
- Exogenic ProcessesDocument39 pagesExogenic Processesbangtansonyeondan100% (1)
- Week 2Document34 pagesWeek 2Tessalonika WongkarNo ratings yet
- Weathering and ErosionDocument53 pagesWeathering and ErosionKesev KeshavNo ratings yet
- Exogenic ProcessesDocument76 pagesExogenic ProcessesNok NokNo ratings yet
- Exogenic ProcessDocument6 pagesExogenic ProcessCharis Ann Limotan MataNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Unit 7Document46 pagesEarth and Life Science Unit 7Sherna BaitingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Lesson 1 The Erosion-Deposition ProcessDocument21 pagesChapter 3 Lesson 1 The Erosion-Deposition ProcessHana LimNo ratings yet
- Lecture6-Erosion and DepositionDocument28 pagesLecture6-Erosion and DepositionALBERT MALIRONo ratings yet
- Earth ScienceDocument6 pagesEarth ScienceKarylle PingolNo ratings yet
- Exogenic ProcessDocument25 pagesExogenic Processjeon's bae100% (1)
- Describe Erosion and Deposition Features of Wind and WaveDocument80 pagesDescribe Erosion and Deposition Features of Wind and WaveKOWAK TVNo ratings yet
- Exo Genic ProcessesDocument19 pagesExo Genic ProcessesJan Francis AlmoniaNo ratings yet
- Erosion Mass Wasting and SedimentationDocument37 pagesErosion Mass Wasting and SedimentationrikrikNo ratings yet
- Cor 008 Reviewer 2nd Quarter 3Document9 pagesCor 008 Reviewer 2nd Quarter 3Armhay Loraine DuavezNo ratings yet
- Earth Life Notes - Week 10Document2 pagesEarth Life Notes - Week 10Ian IglesiaNo ratings yet
- WEEK2Document19 pagesWEEK2Cristina YusonNo ratings yet
- Weathering and Erosion NewDocument33 pagesWeathering and Erosion NewJoyce Catherine Buquing UysecoNo ratings yet
- Erosion and Deposition Power PointDocument29 pagesErosion and Deposition Power PointAadil ShakulNo ratings yet
- Geologic ProcessesDocument37 pagesGeologic ProcessesMaricar Vecinal Magnaye100% (1)
- 5.1. Weathering: Chapter 5: Surface and Earth ProcessesDocument15 pages5.1. Weathering: Chapter 5: Surface and Earth ProcessesdaniNo ratings yet
- Exogenic ProcessesDocument28 pagesExogenic ProcessesShannel Kate NuñezNo ratings yet
- WeatheringDocument40 pagesWeatheringtjeremyalleneNo ratings yet
- Presentation 085135Document22 pagesPresentation 085135SultanNo ratings yet
- Exogenic ProcessesDocument17 pagesExogenic ProcessesAngelica SeñaNo ratings yet
- Exogenic ProcessesDocument32 pagesExogenic ProcesseskarmelasaydeefdelatoreeNo ratings yet
- Deposition and Depositional Landforms - Formation and Various Types of Depositional Landforms.-1Document1 pageDeposition and Depositional Landforms - Formation and Various Types of Depositional Landforms.-1Lucia BontilaoNo ratings yet
- Exogenic ProcessesDocument7 pagesExogenic ProcessesMj YuNo ratings yet
- Applied Hydrology Lecture 5aDocument11 pagesApplied Hydrology Lecture 5aMsigwapetro0No ratings yet
- External Forces Shaping The EarthDocument11 pagesExternal Forces Shaping The EarthJesse RamroopNo ratings yet
- 2 Week 2 Origin of SoilDocument12 pages2 Week 2 Origin of SoilBrylle JamenNo ratings yet
- Geology ReportDocument76 pagesGeology ReportPrime Rose CutaonNo ratings yet
- CIVE 1002: - WeatheringDocument40 pagesCIVE 1002: - WeatheringMadav BalgobinNo ratings yet
- 1.niseroo 2.flatedion 3.rasionab 4.toosedinip 5.nudes 6. ScaalpendDocument32 pages1.niseroo 2.flatedion 3.rasionab 4.toosedinip 5.nudes 6. ScaalpendEllen May GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Els Week 6Document3 pagesEls Week 6Jessica BorromeoNo ratings yet
- 5 Erosion LectureDocument52 pages5 Erosion LectureKhalid YousafNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 11 WEEK 6B - Weathering and ErosionDocument37 pagesSCIENCE 11 WEEK 6B - Weathering and ErosionChristine CayosaNo ratings yet
- Geologic Processes On Earth 2Document68 pagesGeologic Processes On Earth 2naning1113No ratings yet
- Cor 008 - Module 15-20Document11 pagesCor 008 - Module 15-20Armhay Loraine DuavezNo ratings yet
- Exogenic ProcessesDocument12 pagesExogenic ProcessesFelicity Hermionne Aspiras GatchalianNo ratings yet
- Kid’s Guide to Types of Landforms - Children's Science & NatureFrom EverandKid’s Guide to Types of Landforms - Children's Science & NatureNo ratings yet
- YoditDocument170 pagesYoditgezahegnNo ratings yet
- GeographyDocument8 pagesGeographyOzan EffendiNo ratings yet
- Exogenic ProcessesDocument61 pagesExogenic ProcessesQueen PajulasNo ratings yet
- Geography Notes Form 3Document138 pagesGeography Notes Form 3hussain korirNo ratings yet
- Geo Chapter15questionsanswers PDFDocument2 pagesGeo Chapter15questionsanswers PDFIesha ClarkNo ratings yet
- Endogenic Exogenic ProcessesDocument3 pagesEndogenic Exogenic ProcessesMaria Janelle BlanzaNo ratings yet
- Mass WastingDocument10 pagesMass WastingAbhinav RajeevanNo ratings yet
- ELS Final Module - 5-08082020 - 023002Document26 pagesELS Final Module - 5-08082020 - 023002CelerinaRusianaLonodNo ratings yet
- Engineering GeologyDocument110 pagesEngineering GeologyEdgarGarciaNo ratings yet
- DRRR - Q2 - Week 1Document14 pagesDRRR - Q2 - Week 1Nylinam67% (3)
- Exogenic Forceslong QuizDocument7 pagesExogenic Forceslong QuizMr Shn MrcdNo ratings yet
- 2 DLL Mbregalado Earth ScienceDocument27 pages2 DLL Mbregalado Earth ScienceMarjorie Brondo100% (1)
- Rocks and WeatheringDocument17 pagesRocks and WeatheringKabeloNo ratings yet
- The Landslide Threats in Maharashtra: Lessons To Be Learnt From The Malin LandslideDocument4 pagesThe Landslide Threats in Maharashtra: Lessons To Be Learnt From The Malin LandslideShatakshi HulgundeNo ratings yet
- IATG 05.30 Barricades v.2Document21 pagesIATG 05.30 Barricades v.2DOC LABNo ratings yet
- Slope Protection - DTP1Document75 pagesSlope Protection - DTP1Dominador O. MatbaganNo ratings yet
- Exogenic Processes NotesDocument6 pagesExogenic Processes NotesCNo ratings yet
- I. Definition - The Bulk Movement of Weathered and Broken RockDocument7 pagesI. Definition - The Bulk Movement of Weathered and Broken RockMbiko SabeyoNo ratings yet
- III. Earth Materials and Processes (Endogenic Processes)Document5 pagesIII. Earth Materials and Processes (Endogenic Processes)Jenalyn JavierNo ratings yet
- Draft SNC Geography (6-8) PDFDocument48 pagesDraft SNC Geography (6-8) PDFabidishaq5558No ratings yet
- InferenceDocument7 pagesInferenceMajaNo ratings yet
- Review Pardeshi SPlus PDFDocument11 pagesReview Pardeshi SPlus PDFParag Jyoti DuttaNo ratings yet
- Exogeneous Processes and The Rock Cycle: Ii. Lesson ObjectivesDocument9 pagesExogeneous Processes and The Rock Cycle: Ii. Lesson ObjectivesRiguel Jameson AllejeNo ratings yet
- Slope SubsystemDocument51 pagesSlope SubsystemPavnitKiranAmoghJainNo ratings yet
- Mass Wasting in East AfricaDocument9 pagesMass Wasting in East Africakalule elvisNo ratings yet
- 8.4 How Is The Physical Landscape of Hong Kong Shaped by External Processes StudentDocument36 pages8.4 How Is The Physical Landscape of Hong Kong Shaped by External Processes Students200196No ratings yet
- Geography Form 2 AssessmentDocument2 pagesGeography Form 2 AssessmentAriel Lakatoo MingNo ratings yet
- Iloilo Geohazard ReportDocument150 pagesIloilo Geohazard ReportZairah Ann Borja0% (1)
- Exogenous ProcessDocument19 pagesExogenous ProcessLoralyn LlanderNo ratings yet
- 07 Chapter 1Document16 pages07 Chapter 1roshansm1978No ratings yet