Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Module 4 - Information Security
Uploaded by
cq4cx4zf6qCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Module 4 - Information Security
Uploaded by
cq4cx4zf6qCopyright:
Available Formats
COMPUTING SKILLS (FPCS0001)
Semester 2, AY 2022-2023
Module 4 – Information Security
02/15/2024 MODULE 4 - INFORMATION SECURITY 1
Learning Outcomes:
Upon completion of the course, students should be able to:
1. Identify the benefits and risks of network computing.
2. Identify the security issues with electronic mails.
3. Identify risks to personal and organizational data.
4. Describe the protected web sites, use of digital certificates, encryption-decryption, and
uses of firewall and how to get protected from hackers etc.
5. Explain different types of viruses (including worms, Trojans etc) and clean viruses and
worm-infected system with appropriate software.
6. Explain privacy issues, good passwords and access right.
7. Describe the concept of backup and its importance to data recovery.
8. Explain the provisions under the Omani Data Protection Legislation.
02/15/2024 MODULE 4 - INFORMATION SECURITY 2
Information Security
Information security is the protection of information and information systems
from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or
destruction in order to achieve confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
Computer network security risks
Computer security risk is a concept that indicates actions or events
that could cause a loss of or damage to computer hardware, software,
information, data or processing capability and signifies the
likelihood of a hazard or dangerous threat.
02/15/2024 MODULE 4 - INFORMATION SECURITY 3
Network security threats
Risks to personal and organizational data
Information privacy refers to the right of individuals and companies to
deny or restrict the collection and use of information about them.
02/15/2024 MODULE 4 - INFORMATION SECURITY 4
Computer Malware
Malware is malicious software designed specifically to damage
computers without the user’s consent.
02/15/2024 MODULE 4 - INFORMATION SECURITY 5
Virus
Virus is malicious software that is designed to take control of system
operations and destroy some or all files stored on the computer or even
the computer itself.
Viruses can easily copy themselves and spread throughout the
computer system once activated by the user.
Computer viruses can be transferred through downloaded files or
programs, email attachments, CDs, and flash drives.
02/15/2024 MODULE 4 - INFORMATION SECURITY 6
Worm
Worm is a self-replicating program that usually consumes system and
network resources.
It makes copies of itself repeatedly and infects additional computers.
Trojan Horse
This causes damage or compromises the security of the computer.
It can enter a computer as a virus or hide within or even looks like a
legitimate program.
02/15/2024 MODULE 4 - INFORMATION SECURITY 7
Spyware
Spyware is a program placed on a computer without user
consent that can capture information like Web browsing habits,
e-mail messages, usernames and passwords, and credit card
information.
02/15/2024 MODULE 4 - INFORMATION SECURITY 8
Security issues with electronic mails
Phishing email is a type of email-based social engineering in which an attacker
sends an official-looking email from a source, such as a bank, and attempts to
obtain personal and financial information from the victim.
02/15/2024 MODULE 4 - INFORMATION SECURITY 9
Safeguards against Computer Malware
1. Strong password protects your account
A password is a private combination of characters associated with the
username that allows access to certain computer resources.
02/15/2024 MODULE 4 - INFORMATION SECURITY 10
Safeguards against Computer Malware
2. Create the password with adequate length
They should never be less than eight characters and preferably longer.
Short passwords can easily be determined by a brute-force password cracker.
3. Adequate character mix
A good policy is to use a meaningless combination of letters and numbers
that is seven or eight characters long.
02/15/2024 MODULE 4 - INFORMATION SECURITY 11
Safeguards against Computer Malware
4. Avoid using directly identifiable information
They should not be the names of family members or pets or anything
else that would be easy for a hacker.
02/15/2024 MODULE 4 - INFORMATION SECURITY 12
Backup and Recovery
Backup is a way to copy selected
files or an entire hard disk to another
storage medium such as another hard
disk, optical disc, or USB / flash
drive.
Recovery is a special tool that
contains some system files capable of
restarting a computer when the computer
cannot boot from its hard disk due to
system failure.
02/15/2024 MODULE 4 - INFORMATION SECURITY 13
Regular updating software
No computer software is perfect, just as no human is
perfect
1. Security update
2. Updating applications
3. Update operating system applications
02/15/2024 MODULE 4 - INFORMATION SECURITY 14
Regular updating software
Security update
Designed to protect your software (and computer) from harmful programs, viruses, and exploits
Updating applications
Additions to software that can help prevent or fix problems, or enhance and improve how your
computer works.
Update operating system applications
Enhanced overall performance of the software and the computer is also often a good reason to
keep up-to-date with updates to your PC programs
02/15/2024 MODULE 4 - INFORMATION SECURITY 15
Digital Certificates
Digital Certificate
A digital certificate is a notice that guarantees a user or a Web
site is legitimate.
Web browsers, such as Internet Explorer, often display a warning
message if a Web site does not have a valid digital certificate.
02/15/2024 MODULE 4 - INFORMATION SECURITY 16
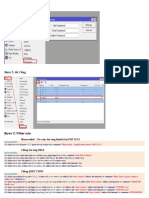
Digital Certificates
Digital Certificate Real Example
Go to Bank Nizwa website (https://www.banknizwa.om/) and click on the view
certificate link as shown below.
Once you click on the view certificate link, the Windows certificate viewer tool will
open and show the certificate owned by Bank Nizwa. This certificate, as you can see
in the "Issued by" field is issued by DigiCert ShA2 Secure Server CA.
02/15/2024 MODULE 4 - INFORMATION SECURITY 17
Digital Certificates Example
02/15/2024 MODULE 4 - INFORMATION SECURITY 18
Digital Certificates Example
02/15/2024 MODULE 4 - INFORMATION SECURITY 19
Encryption and Decryption
Encryption is a security technique that converts readable data
(plaintext form) to prevent unauthorized access. into unreadable
characters (ciphertext form)
Decryption is the inverse process of encryption that allows
only authorized parties with the necessary decryption information to
read the encrypted files.
02/15/2024 MODULE 4 - INFORMATION SECURITY 20
Encryption and Decryption
02/15/2024 MODULE 4 - INFORMATION SECURITY 21
Privacy issues
Firewall
A firewall is a hardware and/or software that
protects a network’s resources from intrusion by
users on another network such as the Internet.
It filters and controls the traffic flow of information
coming into and out of a network to decide which
traffic to allow access to and which traffic to block.
02/15/2024 MODULE 4 - INFORMATION SECURITY 22
Antivirus Software
An antivirus program is a type of utility
program used to protect a computer
against viruses by scanning and
removing any computer viruses found in
memory, on storage devices, or on
incoming files. Most antivirus software
has the capability also to protect against
worms, Trojans and spyware.
02/15/2024 MODULE 4 - INFORMATION SECURITY 23
Antivirus Software Examples
02/15/2024 MODULE 4 - INFORMATION SECURITY 24
Security Features in Windows 10
Windows 10 features a series of tools to help you protect your computer from
threats like viruses and other malware.
The three main security tools in Windows 10 are:
▫ User Account Control
▫ Windows Defender
▫ Windows Firewall
02/15/2024 MODULE 4 - INFORMATION SECURITY 25
User Account Control
User Account Control: is a tool that warns you when someone or something attempts to
change your computer system settings.
This helps protect your computer against accidental changes or malicious software
altering your settings.
User Account Control can be to: Low, Moderate or High:
Low: never notify you
Moderate: notify you only when an application tries to make changes to your computer
High: notify you when programs or you try to make changes to your computer
02/15/2024 MODULE 4 - INFORMATION SECURITY 26
User Account Control
You can change this setting to your desired level by following these steps:
Step 1− Open the Control Panel by searching for it in the Search bar.
Step 2− After the Control Panel is open, choose User Accounts
Step 3- Click on “Change User Account Control settings”
Step 4- In the User Account Control Settings, you can move the
slider to the desired position
02/15/2024 MODULE 4 - INFORMATION SECURITY 27
Windows Defender
Windows Defender is an antivirus and malware protection included in
the windows operating system.
It allows you to scan your computer for malicious software, while also
checking each file or the program you open.
02/15/2024 MODULE 4 - INFORMATION SECURITY 28
Windows Defender
You can change this setting to your desired level by following these steps:
Step 1− Go to SETTINGS and select Update & security.
Step 2 – Click on Windows Security.
Step 3− Click on “Virus & threat protection”
Step 4− Click on Manage settings
Here you can:
a) Turn off/Turn on Real-time protection
b) Turn off/Turn on Cloud-delivered protection
which allows Defender to send Microsoft information about security threats it finds.
02/15/2024 MODULE 4 - INFORMATION SECURITY 29
Windows Firewall
Windows Firewall prevents unauthorized access from outside to get
into your computer.
02/15/2024 MODULE 4 - INFORMATION SECURITY 30
Windows Firewall
If you want to customize your Firewall, follow these steps:
Step 1− Open the Control Panel by searching for it in the Search bar.
Step 2- Choose Windows Firewall.
Step 3− In the Windows Firewall window, you can turn it on or off or
choosing when to protect your computer.
02/15/2024 MODULE 4 - INFORMATION SECURITY 31
Oman Data Protection Legislation
02/15/2024 MODULE 4 - INFORMATION SECURITY 32
SUMMARY
This module covered the topic of Information security.
It discussed the basic concepts of Information security and some related topics.
In addition, it included the different types of malware and what can be done to stop them.
It also illustrated the different security features available in Windows 10.
Finally, the module discussed the available Oman Data Protection Legislation.
02/15/2024 MODULE 4 - INFORMATION SECURITY 33
GUIDE QUESTIONS
1. Define the following terms:
a. Antivirus software
b. Backup
c. Trojan Malware
d. Password
e. Spyware
2. How can users safeguard against computer Viruses, Worms, Trojan Horses, and spyware?
3. How do antivirus programs detect and identify a virus?
4. What types of devices/security tools that are available at your college to protect
computers/network against malware?
02/15/2024 MODULE 4 - INFORMATION SECURITY 34
REFERENCES
1. CERT, O. N. (n.d.). Retrieved from
https://cert.gov.om/library_information_glossary.aspx
2. CompTIA. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.comptia.org/home
3. Fink, K. (2004). Knowledge Potential Measurement and Uncertainty. Deutscher
Universitä tsverlag.
4. Gary B. Shelly, Thomas J. Cashman, Misty E. Vermaat. (2006). Discovering Computers:
Fundamentals, Third Edition (Shelly Cashman Series). Boston, MA, USA: Course Technology
Press.
5. Keyser, T. (2005). Security policy, The Information Governance Toolkit. CRC Press.
6. mimecat. (n.d.). Safeguard Your Company With Electronic Mail Security From Mimecast.
Retrieved from mimecast.com/content/electronic-mail-security/
7. Portal, T. O. (n.d.). Retrieved from
https://omanportal.gov.om/wps/portal/index/strategiesandpolicies/!ut/p/a1/hc7LDoIwEA
XQb3HBlhksEnFXMT4xxGAUujFoSsEUSmqV3xeNGxMfs7uTczMDDBJgdXYrRWZ
KVWfykZl3iDaO58wjXA2RBEjHQeS6DsWYeB1IO4BfhuK h7YkxCcIUb-
Yr3arin2yW669EOPTCbuC_w4sQQmpDo-301pfSRDAUzznGuu7avu1
02/15/2024 MODULE 4 - INFORMATION SECURITY 35
You might also like
- Cybersecurity for Beginners : Learn the Fundamentals of Cybersecurity in an Easy, Step-by-Step Guide: 1From EverandCybersecurity for Beginners : Learn the Fundamentals of Cybersecurity in an Easy, Step-by-Step Guide: 1No ratings yet
- Cyber Security Basics: An IntroductionDocument34 pagesCyber Security Basics: An IntroductionVikram hostNo ratings yet
- Passing OSCP With 100 Points in 12 Hours in First Attempt With Oscp Preparation Guide, 2021Document47 pagesPassing OSCP With 100 Points in 12 Hours in First Attempt With Oscp Preparation Guide, 2021somethng100% (1)
- Information Security and Cypersecurity-2Document27 pagesInformation Security and Cypersecurity-2donweenaNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security Risks in Maritime IndustryDocument79 pagesCyber Security Risks in Maritime IndustryMark Bryan ParamaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cyber Security Handbook PDFDocument104 pagesIntroduction To Cyber Security Handbook PDFVjay MadhamNo ratings yet
- Computer Security Ethics and PrivacyDocument40 pagesComputer Security Ethics and PrivacyLouie De La TorreNo ratings yet
- Network Security FundamentalsDocument21 pagesNetwork Security FundamentalsQistina AbdulNo ratings yet
- Information Security: The CIA Triangle and BeyondDocument55 pagesInformation Security: The CIA Triangle and Beyondsaket kumarNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security BacicsDocument53 pagesCyber Security BacicsJoël KangalaNo ratings yet
- Cyber SecurityDocument19 pagesCyber SecurityRymar DabloNo ratings yet
- Ransomware in The Healthcare IndustryDocument19 pagesRansomware in The Healthcare IndustryNattagit jiteurtragoolNo ratings yet
- Overcoming internet security problemsDocument6 pagesOvercoming internet security problemsDipu RaiNo ratings yet
- Materi Chpt.5 E-Commerce Security and Payment SystemsDocument37 pagesMateri Chpt.5 E-Commerce Security and Payment Systemsdonny antaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Security Privacy and Data IntegrityDocument97 pagesChapter 6 Security Privacy and Data IntegrityUsman ShaukatNo ratings yet
- Research Activity HDLDocument4 pagesResearch Activity HDLShin TeoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 (CSS)Document10 pagesUnit 1 (CSS)hasansyedamanNo ratings yet
- protect against well known attacksDocument4 pagesprotect against well known attackstheguest1No ratings yet
- Cyber SecurityDocument5 pagesCyber Securityjoel pabadoraNo ratings yet
- Group 1Document9 pagesGroup 1Raphy OctaNo ratings yet
- ICT - CSS Module 9: Network SecurityDocument12 pagesICT - CSS Module 9: Network SecurityKaylene VillaNo ratings yet
- CS361 Lec1Document41 pagesCS361 Lec1shreyansh.dwivedi21bNo ratings yet
- Definition of Computer SecurityDocument13 pagesDefinition of Computer SecuritysuhanitaNo ratings yet
- Bit324 Bit-029-920Document33 pagesBit324 Bit-029-920Muktar MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Writing Assignment: 3.3 Computer Security Risks 3.4 Computer Security MeasuresDocument11 pagesWriting Assignment: 3.3 Computer Security Risks 3.4 Computer Security MeasuresPrincess ChimChimNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Computer SecDocument11 pagesGroup 2 Computer Secjohn andrew villanNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 5 Network SecurityDocument36 pagesChapter - 5 Network SecuritySuman BhandariNo ratings yet
- Network security threats and controlsDocument6 pagesNetwork security threats and controlsKaleeswariNo ratings yet
- Unit Iv Network Security and FirewallDocument22 pagesUnit Iv Network Security and FirewallUjwal KoiralaNo ratings yet
- Final Written Assignment Scomp Anisyam k05Document15 pagesFinal Written Assignment Scomp Anisyam k05mohdanisyamsyamsuddinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - The Need For SecurityDocument17 pagesChapter 2 - The Need For SecurityAshura OsipNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 Security Threats To E-Business-15 May 2011Document16 pagesUnit-2 Security Threats To E-Business-15 May 201177ranga100% (1)
- Protect Yourself Online with Basic Cyber Safety TipsDocument23 pagesProtect Yourself Online with Basic Cyber Safety TipsARDI ARDINo ratings yet
- XII NetworkSecurityConceptsDocument34 pagesXII NetworkSecurityConceptsLakshya NayakNo ratings yet
- Assignments ScompDocument9 pagesAssignments ScompNurul AyuniNo ratings yet
- Group 6: CybersecurityDocument4 pagesGroup 6: CybersecurityCherlie Mae DumaluanNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Cyber SecurityDocument6 pagesIntroduction to Cyber SecurityRosetephanie ZalunNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security Tips 2020Document3 pagesCyber Security Tips 2020extortionchloride610No ratings yet
- Unit 5 Computer SecurityDocument12 pagesUnit 5 Computer SecurityPauline TorionNo ratings yet
- It Securiyt Ass 2 FinzlDocument90 pagesIt Securiyt Ass 2 FinzlBehailu DemissieNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security To Network SecurityDocument3 pagesCyber Security To Network SecuritysugaNo ratings yet
- Importance of Cybersecurity in Today's Connected WorldDocument6 pagesImportance of Cybersecurity in Today's Connected WorldDivyasriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Security Privacy and Data IntegrityDocument91 pagesChapter 6 Security Privacy and Data IntegrityUsman ShaukatNo ratings yet
- BS (Hons.) Information Technology: University of OkaraDocument9 pagesBS (Hons.) Information Technology: University of OkaraAbdul Manan SajidNo ratings yet
- Protect Your Computer and Personal Information with Cyber-Safety BasicsDocument23 pagesProtect Your Computer and Personal Information with Cyber-Safety BasicsLupin 3rdNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security: (Prof. Ashok K. Bhateja, IIT Delhi)Document10 pagesCyber Security: (Prof. Ashok K. Bhateja, IIT Delhi)Jatin GoyalNo ratings yet
- Privacy Unit1Document6 pagesPrivacy Unit1SwetankNo ratings yet
- Answers To Exercise 1 & 2. Excercise 1Document4 pagesAnswers To Exercise 1 & 2. Excercise 1Bree ElaineNo ratings yet
- c8 NoteDocument8 pagesc8 Notemuhammadfarisali00No ratings yet
- Chapter 1fundamental of Software SecurityDocument53 pagesChapter 1fundamental of Software SecurityAbiyot egataNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce SecurityDocument14 pagesE-Commerce SecurityAlex AmantelNo ratings yet
- Information Security System TopicsDocument17 pagesInformation Security System TopicsRanbom GuyNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four: E-Commerce Security and CryptographyDocument21 pagesChapter Four: E-Commerce Security and Cryptographyiyasu ayenekuluNo ratings yet
- Ecommerce: EsecurityDocument20 pagesEcommerce: EsecurityJoseph ContehNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide For CybersecurityDocument11 pagesReference Guide For CybersecurityHomiyar SukhiaNo ratings yet
- Dire Dawa University: College of Computing Department of Computer ScienceDocument8 pagesDire Dawa University: College of Computing Department of Computer ScienceAhadu techNo ratings yet
- Cit 101Document22 pagesCit 101agapenunmi16No ratings yet
- 1.1 Secure ComputingDocument5 pages1.1 Secure ComputingHemanth N PoojariNo ratings yet
- d2 PrintedDocument27 pagesd2 PrintededrisNo ratings yet
- networkingDocument12 pagesnetworkingwakgarielias4No ratings yet
- Cyber Security Seminar ProjectDocument29 pagesCyber Security Seminar ProjectSolomon SeyoumNo ratings yet
- 17 Cs 39Document17 pages17 Cs 39Saurabh ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- CSS Assignment One SolutionsDocument4 pagesCSS Assignment One Solutionskarthikrajakarthikraja372No ratings yet
- General Specifications: Models SS1WL1C, SS1WL1S Standard Whitelisting Software For Endpoint SecurityDocument2 pagesGeneral Specifications: Models SS1WL1C, SS1WL1S Standard Whitelisting Software For Endpoint Securityvalter-lazaro123No ratings yet
- Network Security v1.0 - Module 2Document52 pagesNetwork Security v1.0 - Module 2Ernesto Silverio FloresNo ratings yet
- Vineet Sharma KeyloggerDocument51 pagesVineet Sharma KeyloggervineetNo ratings yet
- Final PPT 2nd ReviewDocument18 pagesFinal PPT 2nd ReviewsaranNo ratings yet
- Thwarted Ransomware Attack Against TeslaDocument2 pagesThwarted Ransomware Attack Against TeslaTony DickNo ratings yet
- Bảo MậtDocument2 pagesBảo MậtMinh Nghia PhamNo ratings yet
- File Password Is 44556677Document1 pageFile Password Is 44556677Sameer GNo ratings yet
- Ids 13082016Document69 pagesIds 13082016Rai Widarta KesumaNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Cybercrime On Nigerian Youths: December 2020Document10 pagesThe Impact of Cybercrime On Nigerian Youths: December 2020Micah AnjiNo ratings yet
- IoT and Blockchain Security ChallengesDocument11 pagesIoT and Blockchain Security ChallengesYohanes Beato DionisiusNo ratings yet
- Kaspersky AntivirusDocument2 pagesKaspersky Antivirus健康生活園Healthy Life GardenNo ratings yet
- Keystroke Logging KeyloggingDocument14 pagesKeystroke Logging KeyloggingAnjaliNo ratings yet
- Chapter12 NokeyDocument10 pagesChapter12 NokeyNguyen Van Nam (K18 HCM)No ratings yet
- Thesis StatementDocument45 pagesThesis StatementcrenitepkNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 - Summer 2023answeredDocument5 pagesAssignment 2 - Summer 2023answeredHakim Al-HuribiNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection SystemDocument44 pagesIntrusion Detection SystemfdfddfNo ratings yet
- Application Hacking PPT-1Document23 pagesApplication Hacking PPT-1ShivaniNo ratings yet
- RAID 5 Best for Datacenter Tolerance and PerformanceDocument9 pagesRAID 5 Best for Datacenter Tolerance and PerformanceEksha MadanNo ratings yet
- Vulnerability and Threat AssessmentDocument14 pagesVulnerability and Threat AssessmentK RNo ratings yet
- Buffer Overflow AttacksDocument2 pagesBuffer Overflow AttacksBADR EDDINE JAMAINo ratings yet
- Security in Computing Unit 1Document60 pagesSecurity in Computing Unit 1Prathamesh BhosaleNo ratings yet
- kb4 Security Doc Youareatarget v9 PDFDocument1 pagekb4 Security Doc Youareatarget v9 PDFCorey MolinelliNo ratings yet
- 4-Info Security Essentials v3.3 (LUMS)Document16 pages4-Info Security Essentials v3.3 (LUMS)MahnoorNo ratings yet
- Ccs Module 2Document85 pagesCcs Module 2sreelayaNo ratings yet
- Bari - Webinar5 - Cybersecurity - Reflection - CPE4-1Document6 pagesBari - Webinar5 - Cybersecurity - Reflection - CPE4-1Sheina Marie BariNo ratings yet
- WebFilter - Quiz - Attempt Review2Document2 pagesWebFilter - Quiz - Attempt Review2DuangkamonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Protecting The OrganizationDocument17 pagesChapter 4 - Protecting The OrganizationS. M. AkashNo ratings yet