Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Deep Learning Part 2
Uploaded by
statistikatiusd0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views16 pagesThe document provides examples of machine learning applications and discusses different types of machine learning:
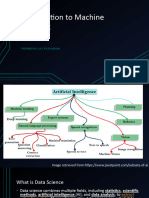
- Applications include detecting tumors, forecasting revenue, detecting fraud, classifying news, flagging offensive comments, summarizing documents, creating chatbots, and recommending products.
- The three main types are supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning. Supervised learning uses labeled training data to learn input-output mappings, unsupervised learning finds patterns in unlabeled data, and reinforcement learning involves an agent learning policies through trial-and-error interactions with an environment.
Original Description:
Original Title
Deep Learning part 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides examples of machine learning applications and discusses different types of machine learning:
- Applications include detecting tumors, forecasting revenue, detecting fraud, classifying news, flagging offensive comments, summarizing documents, creating chatbots, and recommending products.
- The three main types are supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning. Supervised learning uses labeled training data to learn input-output mappings, unsupervised learning finds patterns in unlabeled data, and reinforcement learning involves an agent learning policies through trial-and-error interactions with an environment.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views16 pagesDeep Learning Part 2
Uploaded by
statistikatiusdThe document provides examples of machine learning applications and discusses different types of machine learning:
- Applications include detecting tumors, forecasting revenue, detecting fraud, classifying news, flagging offensive comments, summarizing documents, creating chatbots, and recommending products.
- The three main types are supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning. Supervised learning uses labeled training data to learn input-output mappings, unsupervised learning finds patterns in unlabeled data, and reinforcement learning involves an agent learning policies through trial-and-error interactions with an environment.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 16
• Examples of Applications
Detecting tumors in brain scans.
• Forecasting a company’s revenue next year based on many
performance metrics
• Detecting credit card fraud
• Automatically classifying news articles
• Automatically flagging offensive comments on discussion
forums
• Summarizing long documents automatically
• Examples of Applications
Creating a chatbot or a personal assistant
• Making an app react to voice commands
• Segmenting clients based on their purchases so that you can
design a different marketing strategy for each segment
• Examples of Applications
Representing a complex, high-dimensional dataset in a clear
and insightful diagram
• Recommending a product that a client may be interested in,
based on past purchases
• Building an intelligent bot for game
• Types of Machine Learning
According to the amount and type of supervision they get
during training
• Supervised Learning:
• used most in real-world applications,
• most rapid advancements and innovation
• Unsupervised Learning
• the most widely used form of machine
learning after supervised learning
• Reinforcement Learning
Supervised Learning
• Supervised learning refers to algorithms that
learn x to y or input to output mappings
• The key characteristic of supervised learning is
that you give your learning algorithm examples
to learn from, including the right answers
(correct label y for a given input x).
Supervised Learning
• By seeing correct pairs of input x and desired
output label y that the learning algorithm
eventually learns to take just the input alone
without the output label and gives a
reasonably accurate prediction or guess of the
output.
Supervised Learning
• If the input x is an email and the output y is this
email, spam or not spam, this gives you your
spam filter.
Supervised Learning
• Classification problem: we're trying to predict
only a small number of possible outputs or
categories.
Supervised Learning
• Regression problem: we're trying to predict a
number from infinitely many possible numbers
• Unsupervised learning
In unsupervised learning, the training data is unlabeled. The
system tries to learn without a teacher to find some structure
or some pattern or just find something interesting in the data.
• We call it unsupervised because we’re not trying to supervise
the algorithm.
• A typical problem in unsupervised learning is clustering,
anomaly detection and dimension reduction.
Unsupervised learning
(clustering)
Unsupervised learning
• Anomaly detection
(anomaly detection)
is used to detect unusual events.
This turns out to be really important for fraud
detection in the financial system, where unusual
events, unusual transactions could be signs of fraud
and for many other applications.
Unsupervised learning
• The dimensionality
(dimensionality
reduction reduction)
lets you take a big data-
set and almost magically compress it to a much
smaller data-set while losing as little information as
possible.
•
Reinforcement Learning
The learning system, called an agent in this context, can
observe the environment, select and perform actions, and get
rewards in return (or penalties in the form of negative
rewards).
• It must then learn by itself what is the best strategy, called a
policy, to get the most reward over time.
• A policy defines what action the agent should choose when it
is in a given situation.
• It is not very widely applied in commercial applications yet
today, but it is one of the pillars of machine learning and has
lots of exciting research backing it up and improving it every
single day.
Reinforcement Learning
Course Contents
• Perceptron and Multi-layer Perceptrons
• Regression
• Classification
• Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN)
• Computer vision
• Long Short Term Memory (LSTM)
• Time series
You might also like
- L3 - Supervised and Unsupervised LearningDocument24 pagesL3 - Supervised and Unsupervised LearningGaurav Rohilla100% (1)
- RegressionDocument109 pagesRegressionPranati Bharadkar100% (2)
- Lecture - 32 - 33Document65 pagesLecture - 32 - 33spandansahil15No ratings yet
- ML - With - Python - TaggedDocument43 pagesML - With - Python - TaggedAnthony Corneau100% (1)
- Supervised and Unsupervised LearningDocument19 pagesSupervised and Unsupervised LearningKINGS T.ENo ratings yet
- SCSA3015 Deep Learning Unit 1 Notes PDFDocument30 pagesSCSA3015 Deep Learning Unit 1 Notes PDFpooja vikirthiniNo ratings yet
- Intro To Machine LearningDocument25 pagesIntro To Machine LearningPRAGYA SINGH BAGHEL STUDENTS JAIPURIA INDORENo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document19 pagesLecture 1Blue WhaleNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Machine LearningDocument32 pagesIntroduction To Machine LearningmrhiraruNo ratings yet
- Unit-4object Segmentation Regression Vs Segmentation Supervised and Unsupervised Learning Tree Building Regression Classification Overfitting Pruning and Complexity Multiple Decision TreesDocument25 pagesUnit-4object Segmentation Regression Vs Segmentation Supervised and Unsupervised Learning Tree Building Regression Classification Overfitting Pruning and Complexity Multiple Decision TreesShalinichowdary ThulluriNo ratings yet
- 1 Leaning IntroductionDocument29 pages1 Leaning Introductionlookup.itsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document30 pagesLecture 1Atul PatilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Machine LearningDocument29 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Machine LearningKenneth Kibet NgenoNo ratings yet
- Chap-6 Machine Learning IntroductionDocument40 pagesChap-6 Machine Learning IntroductionshubhNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Machine LearningDocument23 pagesIntroduction To Machine LearningSushil PokharkarNo ratings yet
- Machine LearningDocument29 pagesMachine LearningCubic SectionNo ratings yet
- 1.supervised and UnsupervisedDocument42 pages1.supervised and Unsupervisedrajthakre81No ratings yet
- Inductive Learning and Machine LearningDocument321 pagesInductive Learning and Machine LearningjNo ratings yet
- ML 1 2 3Document54 pagesML 1 2 3Shoba NateshNo ratings yet
- Inductive Learning and Machine LearningDocument321 pagesInductive Learning and Machine Learningj100% (1)
- Machine Learning TechniquesDocument45 pagesMachine Learning TechniquesfareenfarzanawahedNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning AlgorithmsDocument25 pagesMachine Learning Algorithmsaskarova.anel.2004No ratings yet
- Lect3 Machine LearningDocument27 pagesLect3 Machine LearningAmrin MulaniNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning: Dr. R. B. Chadge YCCE, NagpurDocument24 pagesMachine Learning: Dr. R. B. Chadge YCCE, Nagpursuraj meshramNo ratings yet
- 1 IntroductionDocument12 pages1 Introductionhahadevi235No ratings yet
- Unit 4 Machine Learning Tools, Techniques and ApplicationsDocument78 pagesUnit 4 Machine Learning Tools, Techniques and ApplicationsJyothi PulikantiNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence: Slide 6Document42 pagesArtificial Intelligence: Slide 6fatima hussainNo ratings yet
- Unit 2-MLDocument39 pagesUnit 2-MLPerike Chandra Sekhar100% (1)
- w1 - Introduction To MLDocument41 pagesw1 - Introduction To MLSwastik SindhaniNo ratings yet
- Computer Science & Engineering: Apex Institute of TechnologyDocument16 pagesComputer Science & Engineering: Apex Institute of Technologymudit nNo ratings yet
- Big Data and Decision IntelligenceDocument129 pagesBig Data and Decision IntelligenceppNo ratings yet
- 02 MLDocument23 pages02 MLSulax Suresh100% (2)
- Machine Learning and Web Scraping Lesson02Document29 pagesMachine Learning and Web Scraping Lesson02patrice mvogoNo ratings yet
- ML Full Slides FinalDocument458 pagesML Full Slides Final21053259No ratings yet
- 20ECE633T Machine Learning in VLSIDocument81 pages20ECE633T Machine Learning in VLSIUMAMAHESWARI P (RA2113004011004)No ratings yet
- ML - Full Slides Srikanth AllamshattyDocument369 pagesML - Full Slides Srikanth Allamshatty21053259No ratings yet
- Module 1 ML Mumbai UniversityDocument47 pagesModule 1 ML Mumbai University2021.shreya.pawaskarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Tổng Quan Về Học MáyDocument19 pagesLecture 3 - Tổng Quan Về Học MáyVăn MỹNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning: in TeluguDocument14 pagesMachine Learning: in Telugua baluNo ratings yet
- Aiml McaDocument38 pagesAiml McaVishal AnandNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Introduction To MLDocument69 pagesUnit-1 Introduction To MLRahul VashisthaNo ratings yet
- Machine LearningDocument15 pagesMachine LearningSahil RatanNo ratings yet
- Learning: Chapter 17: Rich & KnightDocument30 pagesLearning: Chapter 17: Rich & KnightRupinder AulakhNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document76 pagesUnit 221131A4232 CHUKKALA PRUDHVI RAJNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Machine LearningDocument29 pagesIntroduction To Machine LearningAayush KansaraNo ratings yet
- ML Unit 1 NotesDocument134 pagesML Unit 1 NotesAnkit MauryaNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning by SahilDocument15 pagesMachine Learning by SahilNaman SharmaNo ratings yet
- Machine LearningDocument40 pagesMachine Learningshyamalhp001No ratings yet
- Lecture 1 (UNIT 1)Document25 pagesLecture 1 (UNIT 1)Jyothika joshyNo ratings yet
- Intelligent Techniques AssignmentDocument7 pagesIntelligent Techniques AssignmentMano_Bili89No ratings yet
- Introduction MLDocument47 pagesIntroduction MLssignnNo ratings yet
- FinalDocument95 pagesFinalFarhan Rahman AnikNo ratings yet
- Ai Machine LearningDocument27 pagesAi Machine Learningsahaj deep KaurNo ratings yet
- MACHINE LEARNING FOR BEGINNERS: A Practical Guide to Understanding and Applying Machine Learning Concepts (2023 Beginner Crash Course)From EverandMACHINE LEARNING FOR BEGINNERS: A Practical Guide to Understanding and Applying Machine Learning Concepts (2023 Beginner Crash Course)No ratings yet
- Unit - 5.1 - Introduction To Machine LearningDocument38 pagesUnit - 5.1 - Introduction To Machine LearningHarsh officialNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 PDFDocument135 pagesUnit 1 PDFjvgirish74No ratings yet
- Module 1 PPTDocument122 pagesModule 1 PPTharkamals.it.21No ratings yet
- Prescriptive Analytics - Research Material: Data AnalysisDocument12 pagesPrescriptive Analytics - Research Material: Data Analysisapi-592322284No ratings yet
- Mastering Machine Learning Basics: A Beginner's CompanionFrom EverandMastering Machine Learning Basics: A Beginner's CompanionNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection System Evasion Techniques A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionFrom EverandIntrusion Detection System Evasion Techniques A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNo ratings yet
- Software Testing StrategiesDocument25 pagesSoftware Testing Strategieshabado badoNo ratings yet
- CSVCassignmentDocument49 pagesCSVCassignmentThanh MinhNo ratings yet
- ParaView Users Guide DocumentationDocument530 pagesParaView Users Guide DocumentationDonatoNo ratings yet
- Cara Mengolah Promax FebbilDocument6 pagesCara Mengolah Promax FebbilNathalia ZachNo ratings yet
- Simple Phone - Call & SMS Using GSM Module & ArduinoDocument33 pagesSimple Phone - Call & SMS Using GSM Module & Arduinobilla narasimhaNo ratings yet
- DataSheet XNP-6550RH ENDocument4 pagesDataSheet XNP-6550RH ENDang ThuNo ratings yet
- Gas Management SystemDocument32 pagesGas Management SystemAnkur YadavNo ratings yet
- TAFC R20 Release NotesDocument16 pagesTAFC R20 Release NotesGreeni MarcoNo ratings yet
- AUTOMOBILE SERVICE STATION FinalDocument92 pagesAUTOMOBILE SERVICE STATION FinalAnsh VermaNo ratings yet
- East West Institute of Technology: Sadp NotesDocument30 pagesEast West Institute of Technology: Sadp Notesmeghana S MNo ratings yet
- Vaishnav Kshirsagar Assignment 5 B52Document4 pagesVaishnav Kshirsagar Assignment 5 B52ShubhamNo ratings yet
- Data EngineeringDocument6 pagesData Engineeringjohn949No ratings yet
- Object Oriented Analysis and Design NotesDocument62 pagesObject Oriented Analysis and Design Notesvraj patelNo ratings yet
- How To Setup Govroam For Government Organisations: CookbookDocument63 pagesHow To Setup Govroam For Government Organisations: CookbookricklcyNo ratings yet
- Polymorphism in JavaDocument54 pagesPolymorphism in JavaTechVeerendra's Software SolutionsNo ratings yet
- Analysing Networks With NMAP: OWASP Ruhrpott Meetup March 2019Document35 pagesAnalysing Networks With NMAP: OWASP Ruhrpott Meetup March 2019Fshhan arethusaNo ratings yet
- Ivin Resume Nov 2022Document1 pageIvin Resume Nov 2022Ivin KuriakoseNo ratings yet
- Hospital Manage-WPS OfficeDocument20 pagesHospital Manage-WPS OfficePranita PawarNo ratings yet
- Learning Awk and SedDocument14 pagesLearning Awk and SedyNo ratings yet
- The Art of Multiprocessor Programming Second Edition Maurice Herlihy Full ChapterDocument67 pagesThe Art of Multiprocessor Programming Second Edition Maurice Herlihy Full Chapterlillian.tirado682100% (3)
- Data Sheet TT01Document3 pagesData Sheet TT01Leandro Silva SantosNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between A Library and A PackageDocument32 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between A Library and A PackageNamita SahuNo ratings yet
- Computer Applications Sem 1Document5 pagesComputer Applications Sem 1Undead ban100% (1)
- Serial Communication in Win32Document31 pagesSerial Communication in Win32Arya JamshidiNo ratings yet
- Object Oriented ProgrammingDocument2 pagesObject Oriented ProgrammingBiantoroKunartoNo ratings yet
- E18905 PRIME B560M-A v2 UM WEBDocument34 pagesE18905 PRIME B560M-A v2 UM WEBatlasflame777No ratings yet
- TEMPLATEDocument10 pagesTEMPLATERuksarNo ratings yet
- Computer Organization EECS 2021: Lab "M" Report Building The CpuDocument41 pagesComputer Organization EECS 2021: Lab "M" Report Building The CpuRoman KovalchykNo ratings yet
- ACW Manual v3Document2 pagesACW Manual v3Reef VolutionsNo ratings yet
- BlueCoat PacketShaper 11.10 GuideDocument1,596 pagesBlueCoat PacketShaper 11.10 GuideArnoldNo ratings yet