100% found this document useful (1 vote)
97 views33 pagesInternal Audit Training in Wolaita Zone
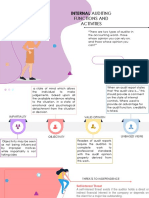
The document summarizes a capacity development training for internal auditors of the public sector in Wolaita Zone, Ethiopia organized by Wolaita Sodo University's College of Business and Economics. The 4-day training had 3 modules and was led by 5 project team members. The objectives were to enable participants to independently conduct internal audits according to methodology and apply knowledge from the theoretical training. Modules covered audit professionalism, internal controls, risk assessment, planning, fieldwork, reporting and follow-up. The training discussed the historical development and definitions of auditing, professional ethics and qualifications for internal auditors.
Uploaded by
mathewosCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
97 views33 pagesInternal Audit Training in Wolaita Zone
The document summarizes a capacity development training for internal auditors of the public sector in Wolaita Zone, Ethiopia organized by Wolaita Sodo University's College of Business and Economics. The 4-day training had 3 modules and was led by 5 project team members. The objectives were to enable participants to independently conduct internal audits according to methodology and apply knowledge from the theoretical training. Modules covered audit professionalism, internal controls, risk assessment, planning, fieldwork, reporting and follow-up. The training discussed the historical development and definitions of auditing, professional ethics and qualifications for internal auditors.
Uploaded by
mathewosCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd