0% found this document useful (0 votes)
322 views28 pagesFiber Laser Cutting Machine
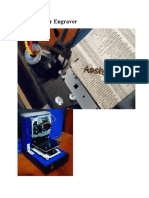
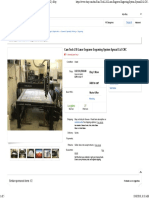
The document discusses laser cutting machines, describing their components and operation. It explains that a laser generates a focused, coherent light beam that is ideal for high-precision applications like cutting. Fiber lasers are highlighted as being particularly efficient and precise due to the light-guiding properties of the optical fiber.
Uploaded by
bubumosingCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
322 views28 pagesFiber Laser Cutting Machine
The document discusses laser cutting machines, describing their components and operation. It explains that a laser generates a focused, coherent light beam that is ideal for high-precision applications like cutting. Fiber lasers are highlighted as being particularly efficient and precise due to the light-guiding properties of the optical fiber.
Uploaded by
bubumosingCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd