0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views30 pagesInsulin Titration for Hyperglycemia Management
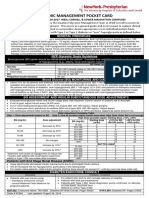
The document provides guidelines for managing hyperglycemia with intravenous insulin therapy. It discusses the indications for IV insulin, algorithms for initiating and adjusting the infusion rate, guidelines for monitoring blood glucose levels, and converting from IV to subcutaneous insulin when appropriate. Hyperglycemia is associated with increased mortality in critically ill patients.
Uploaded by
Uswatun Aortatika KhasanahCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views30 pagesInsulin Titration for Hyperglycemia Management
The document provides guidelines for managing hyperglycemia with intravenous insulin therapy. It discusses the indications for IV insulin, algorithms for initiating and adjusting the infusion rate, guidelines for monitoring blood glucose levels, and converting from IV to subcutaneous insulin when appropriate. Hyperglycemia is associated with increased mortality in critically ill patients.
Uploaded by
Uswatun Aortatika KhasanahCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd