0% found this document useful (0 votes)
70 views49 pagesUnderstanding Haemostasis Mechanisms
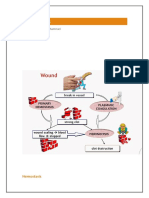
The document discusses mechanisms of hemostasis including vascular constriction, platelet plug formation, blood clot formation, and fibrinolysis. It provides details on how platelets, coagulation factors, and fibrin interact to form clots and stop bleeding from injured blood vessels.
Uploaded by
isackanthony880Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
70 views49 pagesUnderstanding Haemostasis Mechanisms
The document discusses mechanisms of hemostasis including vascular constriction, platelet plug formation, blood clot formation, and fibrinolysis. It provides details on how platelets, coagulation factors, and fibrin interact to form clots and stop bleeding from injured blood vessels.
Uploaded by
isackanthony880Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd