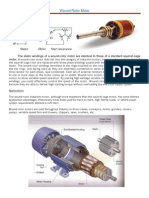
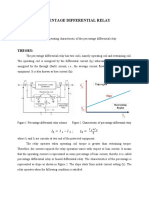
Induction Motor Locked Rotor
Protection
Understanding the importance and
methods
Your Name
Date
� Introduction to Induction Motors
• • Definition: Induction motor basics
• • Components: Stator, Rotor, Windings
• • Applications: Pumps, fans, compressors
� What is Locked Rotor Condition?
• • Rotor unable to start rotating
• • Causes: Mechanical jamming, excessive load
• • Importance: High current draw leading to
overheating and damage
� Consequences of Locked Rotor
Condition
• • Thermal Damage: Overheating, insulation
breakdown
• • Mechanical Stress: Excessive torque,
mechanical failure
• • Electrical Stress: High current draw affecting
other components
� Locked Rotor Protection Methods
• • Thermal Overload Relays
• • Magnetic Circuit Breakers
• • Electronic Protection Relays
� Thermal Overload Relay Details
• • Bimetallic strip or electronic sensors detect
heat.
• • Advantages: Cost-effective, simple, reliable.
• • Limitations: Slower response time compared
to electronic relays.
� Magnetic Circuit Breakers
• • Instantaneous trip under high current
conditions.
• • Advantages: Fast response to protect against
short circuits or locked rotor.
• • Application: Typically used with thermal
overload relays.
� Electronic Protection Relays
• • Real-time monitoring of motor parameters.
• • Programmable settings for specific motor
protection.
• • Communication capabilities with control
systems.
• • Benefits: Precise protection, adaptable, used
in complex systems.
�Comparison of Protection Methods
• • Thermal Overload Relays: Cost-effective,
slower response.
• • Magnetic Circuit Breakers: Fast response,
used with relays.
• • Electronic Relays: Precise, real-time
monitoring, adaptable.
�Implementation and Best Practices
• • Importance of understanding motor
specifications.
• • Routine Testing: Regular maintenance
checks.
• • Customization: Tuning protection settings to
specific motor applications.
� Case Study/Example
• • Real-world scenario where locked rotor
protection was crucial.
• • Outcome: How proper protection prevented
damage or downtime.
� Conclusion
• • Recap the importance of locked rotor
protection.
• • Final Thoughts: Select the right protection
method based on motor and application.
�Q&A