R F E R E N C E
RN A I NT E
HRUDYA KRISHNAN. K
ROLL NO : BO1314
� RNA INTERFERENCE
RNA interference is a mechanism that
inhibits gene expression at the stage of
translation or by hindering the transcription
of specific genes.
RNA interference include RNA from
viruses and transposons.
It is a biological process in which RNA
molecule inhibits gene expression typically
by causing depression of specific RNA
molecule.
�RNAi is cellular mechanism that
degrades unwanted RNAs in the
cytoplasm but not in the nucleus
Andrew Fire and Craig C Mello
shared the 2010 Nobel prize in
physiology medicine for their work on
RNA i in the nematode
worm ,Caenorabditis elegans which
they published in 1998.
� PTGS IN PLANTS
The discovery of Jogenson and Napolin in
1990.
They were trying to make Petunias more
purple
Over expression of Petunia gene
Entered homologous RNA.
Expected : more pigments
Observed : white sectors
Cosupression : Loss of mRNAs of both
endo and transgene
��In this mechanism RNA is processed into
shortest interfering ( siRNAs) that guide the
targeted cleavage of homologous RNA.
Two type of small ribonucleic acid (RNA)
molecules are involved - micro RNA(mi RNA)
and small interfering RNA (siRNA).
MicroRNA : Micro RNAs are genomically
encoded non- coding RNAs that help to
regulate gene expression , particularly during
devlopment .
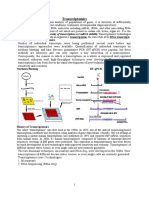
�MECHANISM OF RNA
INTERFERENCE: ROLE OF DICER
Cells ( plants and animals ) undergoing
RNAi contained small fragmentsof the RNA
being supressed .
A nuclease was purified from Drosophila
embryos that still had small fragments
associated with it, both sense and antisense
Dicer is the endonuclease that degrades
Double stranded RNA into 21-24
fragments,and in higher eukaryotes also
pulls the strands apart via helicase activity
�SiRNA : Product of RNA degradces as a
small RNA pieces of 25 nucleotides of both
sense and antisense polarity.
Mi RNA typically base pairing to a target
and inhibit translation of many different
mRNAs with similar sequences
In contrast SiRNAs typically basepair
perfectly and induce mRNA cleavage only in
a single , specific target.
�MECHANISM
Silensing triggers in the form of double-
stranded RNA in the cell as synthetic
RNAs , replicating viruses or may be
transcribed from nuclear genes.
These are recognized and processed into
small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) by dicer.
The duplex Si RNAs are passed to RISC
(RNA-induced silencing complx) and it is
catalysed by Argonaute.
�The complex become activated by
unwinding of the duplex.
The unwound SiRNA basepairs with
complementary mRNA thus guiding
the RNA machinery to 3’ untranslated
regions of the target mRNA .
The target mRNA is effectively
cleaved and subsequently degraded
resulting in gene silensing.
����RNAi charecteristics
Homology of the dsRNA and the
target gene or mRNA is required.
Target mRNA is lost (degraded)
after RNAi
The effect is non- stoichiometric;
small amounts of dsRNA can wipe out
an excess of mRNAssRNA does not
work as well as dsRNA
�ADVANTAGES OF RNAi
Down regulation of gene expression
simplifies ‘knock out’ analysis
Easier than use of antisense
oligonucleotides
Si RNA is more effective and sensitive at
lower concentration
Cost effective
High specificity
Middle region 9-14 are more sensitive
�Ease of transfection by use of vector
With siRNA, the researchers can
simultaneously perform experiments
in all cell type of interest,can be
labelled
��RNAi FUNCTIONS
To regulate expression of protein
coding genes
To mediate resistance to both
exogenous parasitic and endogenous
pathogenic nucleic acid.
To used experimentally to block gene
expression
�RNAi APPLICATIONS
Genome wide RNAi screening
Defense against infection by viruses
Potential therapeutic use
Prevents viral infection
Inhibit the expression of viral
antigens
In functional genomics
In agriculture and biotechnology
� YOU
A N K
TH