0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views27 pagesOcean Basin Structure and Evolution Guide
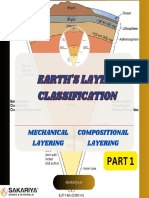
The document discusses the structure and evolution of ocean basins, detailing their formation from volcanic activity and tectonic processes. It outlines the stages of ocean basin evolution, including embryonic, juvenile, mature, declining, terminal, and suturing phases, along with their geological features and importance. Additionally, it covers plate movements and their effects on geological formations such as mountains, trenches, and volcanic activity.
Uploaded by
henrydacaymat.45Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views27 pagesOcean Basin Structure and Evolution Guide
The document discusses the structure and evolution of ocean basins, detailing their formation from volcanic activity and tectonic processes. It outlines the stages of ocean basin evolution, including embryonic, juvenile, mature, declining, terminal, and suturing phases, along with their geological features and importance. Additionally, it covers plate movements and their effects on geological formations such as mountains, trenches, and volcanic activity.
Uploaded by
henrydacaymat.45Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd