0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views18 pagesJava Linked List Overview and Methods
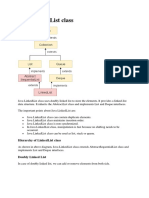
The document provides an overview of Linked Lists in Java, highlighting their characteristics such as maintaining insertion order, allowing duplicates and null values, and implementing Queue and Deque interfaces. It contrasts Linked Lists with Array Lists, explaining the structure of a doubly-linked list and various methods for adding and retrieving elements. Additionally, it includes code examples demonstrating the use of Linked List methods like addFirst, addLast, offer, peek, and toArray.
Uploaded by
Sekhar AripakaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views18 pagesJava Linked List Overview and Methods
The document provides an overview of Linked Lists in Java, highlighting their characteristics such as maintaining insertion order, allowing duplicates and null values, and implementing Queue and Deque interfaces. It contrasts Linked Lists with Array Lists, explaining the structure of a doubly-linked list and various methods for adding and retrieving elements. Additionally, it includes code examples demonstrating the use of Linked List methods like addFirst, addLast, offer, peek, and toArray.
Uploaded by
Sekhar AripakaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd