0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views88 pagesNervous System Examination Guide
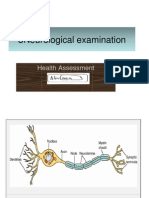
The document outlines the assessment of the nervous system, including history taking, cranial nerve examination, motor and sensory system evaluations, and reflex testing. It details various mental functions, cranial nerve tests, motor system assessments, and sensory evaluations, along with the characteristics of upper and lower motor neuron lesions. The document serves as a comprehensive guide for neurological examination and diagnosis.
Uploaded by
GaganCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views88 pagesNervous System Examination Guide
The document outlines the assessment of the nervous system, including history taking, cranial nerve examination, motor and sensory system evaluations, and reflex testing. It details various mental functions, cranial nerve tests, motor system assessments, and sensory evaluations, along with the characteristics of upper and lower motor neuron lesions. The document serves as a comprehensive guide for neurological examination and diagnosis.
Uploaded by
GaganCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd