0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views21 pagesDecision Control Statements 1690351742158
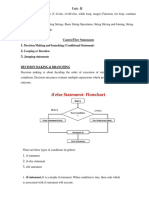
The document provides an overview of control statements in Python, detailing their types: sequential, selection, and iterative control. It includes examples of various control structures such as if statements, loops (while and for), and special statements like break, continue, and pass. Additionally, it explains the use of else statements with loops and the range() function for generating sequences.
Uploaded by
sanzyCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views21 pagesDecision Control Statements 1690351742158
The document provides an overview of control statements in Python, detailing their types: sequential, selection, and iterative control. It includes examples of various control structures such as if statements, loops (while and for), and special statements like break, continue, and pass. Additionally, it explains the use of else statements with loops and the range() function for generating sequences.
Uploaded by
sanzyCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 21