0% found this document useful (0 votes)
43 views46 pagesModule 4
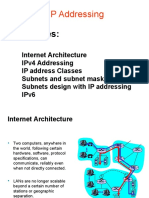
Module 4 covers configuring network addressing, focusing on IPv4 and IPv6 addressing schemes, subnetting, and troubleshooting tools. Key topics include understanding IP address formats, subnet masks, public vs. private addressing, and the use of tools like ipconfig and ping for network diagnostics. The module also introduces IPv6 addressing and its differences from IPv4, including address formats and types of addressing such as unicast, multicast, and anycast.
Uploaded by
rever69okCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
43 views46 pagesModule 4
Module 4 covers configuring network addressing, focusing on IPv4 and IPv6 addressing schemes, subnetting, and troubleshooting tools. Key topics include understanding IP address formats, subnet masks, public vs. private addressing, and the use of tools like ipconfig and ping for network diagnostics. The module also introduces IPv6 addressing and its differences from IPv4, including address formats and types of addressing such as unicast, multicast, and anycast.
Uploaded by
rever69okCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd