0% found this document useful (0 votes)
135 views36 pagesLecture 6-Controller Modes
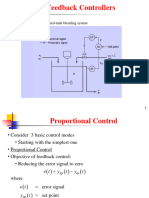
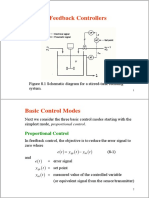
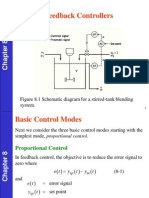
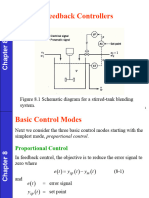
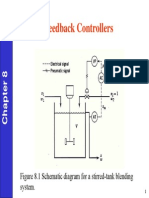
The document discusses various controller modes used to correct errors in control systems, including on/off, proportional, integral, and derivative modes. It explains the characteristics of each mode, such as the continuous and discontinuous operations, and highlights the importance of combining these modes for improved system performance, specifically through Proportional-Integral (PI), Proportional-Derivative (PD), and Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) controllers. The document emphasizes that the combination of these control actions enhances stability and reduces steady-state error in control systems.
Uploaded by
abdulnassor41000Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
Topics covered
- system response,
- block diagram,
- control system performance met…,
- control system parameters,
- control signal,
- control system variables,
- control system applications,
- error signal,
- control system trends,
- control system design principl…
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
135 views36 pagesLecture 6-Controller Modes
The document discusses various controller modes used to correct errors in control systems, including on/off, proportional, integral, and derivative modes. It explains the characteristics of each mode, such as the continuous and discontinuous operations, and highlights the importance of combining these modes for improved system performance, specifically through Proportional-Integral (PI), Proportional-Derivative (PD), and Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) controllers. The document emphasizes that the combination of these control actions enhances stability and reduces steady-state error in control systems.
Uploaded by
abdulnassor41000Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
Topics covered
- system response,
- block diagram,
- control system performance met…,
- control system parameters,
- control signal,
- control system variables,
- control system applications,
- error signal,
- control system trends,
- control system design principl…