0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views6 pagesChapter 12 Memory
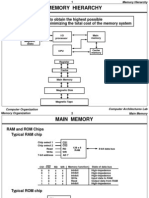
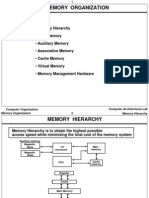
The document provides an overview of memory organization in computer systems, detailing various types of memory including main memory, auxiliary memory, and cache memory. It explains the memory hierarchy aimed at optimizing access speed and cost, as well as the connection of memory to the CPU through data and address buses. Additionally, it includes specifics about RAM and ROM chip configurations and their address mapping.
Uploaded by
Abinaya TCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views6 pagesChapter 12 Memory
The document provides an overview of memory organization in computer systems, detailing various types of memory including main memory, auxiliary memory, and cache memory. It explains the memory hierarchy aimed at optimizing access speed and cost, as well as the connection of memory to the CPU through data and address buses. Additionally, it includes specifics about RAM and ROM chip configurations and their address mapping.
Uploaded by
Abinaya TCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd