0% found this document useful (0 votes)
207 views22 pagesGec 4 - The Contemporary World
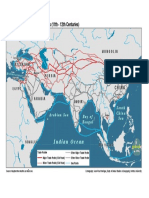
The document provides an introduction to globalization, defining it as a complex process of worldwide economic, cultural, political, and technological exchanges. It outlines the history of globalization through various eras, including the Silk Road, Age of Discovery, and the waves of globalization from the 19th century to the present. Additionally, it categorizes globalization into different types such as economic, military, cultural, ecological, political, and technological, highlighting their interconnections and impacts.
Uploaded by
Moamar H MohammadCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
207 views22 pagesGec 4 - The Contemporary World
The document provides an introduction to globalization, defining it as a complex process of worldwide economic, cultural, political, and technological exchanges. It outlines the history of globalization through various eras, including the Silk Road, Age of Discovery, and the waves of globalization from the 19th century to the present. Additionally, it categorizes globalization into different types such as economic, military, cultural, ecological, political, and technological, highlighting their interconnections and impacts.
Uploaded by
Moamar H MohammadCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd