0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views10 pagesComputer Network
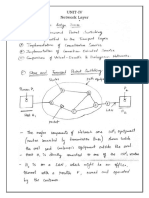
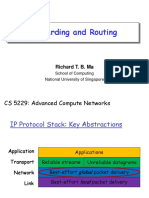
The document explains two routing algorithms used in computer networks: Distance Vector Routing and Link State Routing. Distance Vector Routing involves routers sharing information about the shortest paths to other routers based on the number of hops, while Link State Routing requires routers to learn the entire network topology and use algorithms like Dijkstra's to determine the best paths. Examples illustrate how each routing method operates and updates routing tables based on neighbor information.
Uploaded by
Meera SCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views10 pagesComputer Network
The document explains two routing algorithms used in computer networks: Distance Vector Routing and Link State Routing. Distance Vector Routing involves routers sharing information about the shortest paths to other routers based on the number of hops, while Link State Routing requires routers to learn the entire network topology and use algorithms like Dijkstra's to determine the best paths. Examples illustrate how each routing method operates and updates routing tables based on neighbor information.
Uploaded by
Meera SCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd