0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views32 pagesPerDevWeek Maam Jeanne
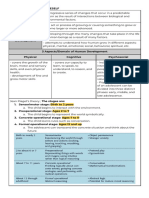
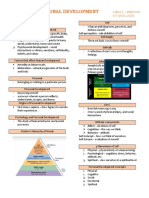
Development is a progressive series of changes influenced by biological and environmental factors, encompassing physical, cognitive, and psychosocial growth. Human development involves understanding how individuals grow and adapt throughout life, shaped by heredity, environment, and maturation. Self-development is crucial for personal success, guiding individuals in realizing their potentials and setting goals.
Uploaded by
Soup pasCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views32 pagesPerDevWeek Maam Jeanne
Development is a progressive series of changes influenced by biological and environmental factors, encompassing physical, cognitive, and psychosocial growth. Human development involves understanding how individuals grow and adapt throughout life, shaped by heredity, environment, and maturation. Self-development is crucial for personal success, guiding individuals in realizing their potentials and setting goals.
Uploaded by
Soup pasCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd