0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views56 pagesLecture 01
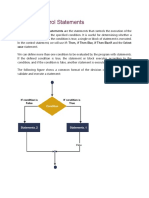
The document provides an introduction to visual programming, outlining its history and significance in simplifying user interaction with computers through graphical interfaces. It details course content on various programming concepts such as variables, control statements, and loops, particularly focusing on VB.NET. Additionally, it includes examples and explanations of programming constructs like If-Then statements, loops, and nested loops.
Uploaded by
ishuwarafCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views56 pagesLecture 01
The document provides an introduction to visual programming, outlining its history and significance in simplifying user interaction with computers through graphical interfaces. It details course content on various programming concepts such as variables, control statements, and loops, particularly focusing on VB.NET. Additionally, it includes examples and explanations of programming constructs like If-Then statements, loops, and nested loops.
Uploaded by
ishuwarafCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd