Name :
UniKL ID
�Acids react with metals
such
as K, Na, Ca, Mg, Al, Zn, Fe,
and Sn.
to
produce hydrogen gas and the
salt of the metal.
This
is a Single replacement reaction
2
�Molecular equations: 2K(s)+2HCl(aq) Zn(s)+2HCl(aq) 2KCl(aq)+ H2(g) ZnCl2(aq)+ H2(g)
�Acids react
with
carbonates and hydrogen
carbonates
to
produce carbon dioxide gas, a salt,
and water.
� 2HCl(aq)+CaCO3(s)
CO2(g)+CaCl2(aq) + H2O(l)
HCl(aq)+
NaHCO3(s)
CO2(g)+NaCl (aq) + H2O(l)
5
�Write the products of the following reactions of acids. A. Zn(s) + HCl(aq) B. MgCO3(s) + HCl(aq)
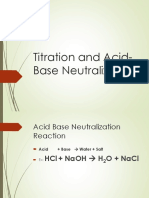
� Acid
react with base to form salt
and water is called NEUTRALIZATION
Because
the acid neutralize base /
base neutralize acid
7
�Four types of neutralization reactions :
1) 2)
Strong acid-strong base
Weak acid-strong base
3)
4)
Strong acid-weak base
Weak acid-weak base
8
Strong acid + strong base neutral salt + water
Strong acid + weak base acidic salt
+ water
Weak acid + strong base basic salt
+ water Weak acid + weak base neutral salt + water
9
�Example : neutralization of hydrochloric acid and Natrium hydroxide
HCl + NaOH acid base
NaCl + H2O salt water (neutral)
10
� Because
strong acid and strong
base all completely ionize, the net equation for the neutralization reaction is
H3O+ + OH the
H2O
pH of salt is 7 (neutral)
11
�Neutralization of HCN and NaOH Example : HCN + NaOH acid base NaCN + H2O salt water
12
� Because
weak acid is largely
undissociated, the strong base all
completely ionize, contain ion OH
in the product
The
salt has pH > 7
13
�Neutralization of Hydrochloric acid and ammonia Example : HCl +
acid
base
NH3
NH4Cl + H2O
salt
water
14
� Because
weak base is largely
undissociated, while the strong
acid all completely ionize,
produce ion H in the product
The
salt has pH < 7 (acidic)
15
�Example : neutralization of acid
hydrocyanate and ammonia Example : HCN + NH3 acid base NH4CN + H2O salt water
16
�Because weak base and weak acid is largely undissociated, the pH of
the salt is depends on type of
weak acid and weak base react.
17
�Write the balanced equation for the neutralization of magnesium hydroxide and nitric acid.
18
�STEP 1 Write the acid and base. Mg(OH)2 + HNO3
STEP 2 Balance H+ in acid with OH- in base.
Mg(OH)2+ 2HNO3
19
�Write the neutralization reactions for the following: A. HCl (aq) and Al(OH)3(aq)
B. C. D.
Ba(OH)2(aq) and H3PO4(aq) HCl (aq) and Al(OH)3 (aq) HCl (aq) and Mg(OH)2(aq)
20
The process in which the titrant is slowly added to the analyte until the
Titrant
equivalence concentration
point of
is the
Analyte
reached, from which the analyte can be determined.
21
The point in a titration at which the quantity of titrant is exactly sufficient for
stoichiometric reaction with the analyte.
Example:
2HCl + Mg(OH)2 MgCl
2 mol 1 mol
+ 2H2O
2 mol HCl sufficient react with 1 mol Mg(OH)2
22
Equivalent point can be determine by
using indicator.
A point in which there is a sudden
change in indicator color or pH in a
titration is called end point.
The more the end point close to the equivalent point, the more accurate of the titration result.
23
�pH of solution can
indicate with :
a)
b)
pH meter
pH indicator
�Indicator
In acid
In neutral
in base
Methyl orange
Bromophenol blue Methyl red & Methyl orange Litmus Bromothymol blue phenolphtalein
pink
yellow pink
orange
green orange
yellow
Biru yellow
red yellow Colorless
Purple green Colorless
blue blue Pink
����29
�At the equivalence point of an acid-base
titration, the moles of acid react with
mole of base follow the coefficient in balance equation : Mole of acid = mole of base
MacidVacid
mole of acid
mole of base
30
Mbase Vbase
�Example 1: 10.0 mL of a solution of potassium hydroxide was completely react with a 0.10 M solution of hydrochloric acid. 13.5 mL of the acid
was required for neutralization. Calculate
the concentration of the potassium hydroxide solution.
31
�Equation : HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) Balance : HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) Equation 1 mole HCl react with 1 mol NaOH Available mole acid : Mole = MV / 1000 = 0.1 x 13.5 / 1000 = 1.35 x 10-3 mole
32
�1.35 x 10-3 mole HCl react with 1.35 x 10-3 mole NaOH Concentration of NaOH, M = mole/ L = 1.35 x10 = 0.14 M
-3
mole / 0.01 L
33
�25.0 mL of phosphoric acid solution is fully neutralized with 16.2 mL of 1.025 M NaOH. What is the molarity of the H3PO4 ?
34
�Equation: NaOH (aq) +H3PO4 (aq)
Na3PO4 (aq)+ H2O (l)
Balance : 3NaOH(aq)+H3PO4 (aq)
Na3PO4 (aq)+ 3H2O (l)
Equation
3 mole NaOH react with 1 mole H3PO4
1 mole NaOH react with 1/3 mole H3PO4
35
�16.2ml, 1.025 M = 16.2 x 1.025/1000 = 0.0166 mole NaOH 0.0166 mole NaOH =1/3x 0.0166 mole H3PO4
= 5.535 x 10-3 mole
Molarity H3PO4 = 5.535 x 10-3 / 0.025 = 0.221 M H3PO4
36
�What volume of 1.45 M sodium hydroxide is necessary to completely neutralize 50 mL of 0.78 M phosphoric acid ?
37
�Equation: NaOH (aq) +H3PO4(aq)
Na3PO4 (aq)+ H2O (l) Balance : 3NaOH(aq)+H3PO4 (aq) Na3PO4 (aq)+ 3H2O (l) Equation
1 mole H3PO4 react with 3 mole NaOH 50 mL, 0.78 M H3PO4 = 0.039 mole H3PO4
38
�0.039 mole H3PO4 react with 3 x 0.039 = 0.117 mole NaOH
M = mole / L
L = 0.117 / 1.45 = 0.081 L
= 81 mL
39
�1) 50mL of 0.2 M NaOH neutralized 20mL of sulfuric acid. Determine the concentration of the acid. (Ans: 0.25M)
2) 25.0mL of 0.05M Ba(OH)2 neutralised
40.0mL of nitric acid. Determine the
concentration of the acid. (Ans: 0.0625M)
40
�Normality in acidbase titration
41
�At the equivalence point of an acid-base titration the equivalents of acid equals the equivalents of base:
Equivalents of acid = Equivalents of base
VacidNacid = VbaseNbase
42
�10.0 mL of an unknown acid required 20.0 mL
of 0.125 N NaOH to react.
(a) Calculate the normality of the unknown acid. (b) What is the molarity of the unknown acid if one mole of acid reacts two moles of base in the neutalization process?
43
�(a) equivalents of acid = equivalents of base VacidNacid = VbaseNbase Therefore Nacid = (20.0 mL)(0.125 N)/(10.0 mL) = 0.250 N (b) Macid = 0.250 N/2 = 0.125 M
44
�45
�1)
How many mL of a 3M NaOH solution are
required to completely neutralize 20.0 mL
of 1.5M H2SO4? (ans: 20 ml)
2)
What is the molarity of a solution of
Ca(OH)2 if 15.0 mL of the solution is required to neutralize 20.0 mL of 2M HCl? (ans: 1.33M)
46
�1)
What volume of 0.25M phosphoric acid is required to neutralize 30.0mL of 0.05M barium hydroxide? (ans: 4 mL)
2)
Calculate the mass of aluminum hydroxide
required to completely react with 20.0 mL
of 0.45M HCl. (ans: 0.239)
47
�48
�49
�Calculate the concentration of a nitric acid solution if a 20 ml sample of the acid required an average volume of 55
ml of a 0.047 mol/l solution of
Ba(OH)2 to reach the endpoint of the
titration. (ans: 0.258 M)
50
�2 HNO3 + Ba(OH)2 -----> Ba(NO3)2 + 2 H2 O Balance Base = 1 Balance Acid = 2
Given information Volume Acid = 20 ml Volume Base (average) = 55 ml Concentration of Base = 0.047 mol/l
MV (acid) / MV (base) = 2/1 M acid = 0.258 M
51
�If 3.12 mmol of Bi(OH)3 are completely neutralized by 25.00 mL of H2SO4 solution. Calculate the normality and the molarity of the H2SO4 solution.(Ans: 0.3744 N and 0.1872
M)
52
�2 Bi(OH)3 + 3 H2SO4 Bi2(SO4)3 + 6 H2O
MV MV
base acid
2 3
3.12 x 10-3 base = 2 M (0.025) acid 3 M
acid
= 3.12 x 10-3 x 3 2 x 0.025
Molarity H2SO4 = 0.1872 M Normality = 2 x 0.1872 = 0.3744 N
53
�A 0.243 g sample containing Ca(OH)2 was titrated with 22.7 mL of a 0.109 N solution of HCl. Calculate the weight % of Ca(OH)2 in the sample.
54
�Equivalent of HCl : N = Eq / L Eq = N x L = 0.109 x 0.0227 = 2.4743 x 10-3
Equivalents of acid = Equivalents of base in the neutralization reaction, Equivalents of base, Ca(OH)2 = 2.4743 x 10-3
55
�1 mole Ca(OH)2 = 2 Equivalent (2 OH-) 1 mole Ca(OH)2 = mole x mw = 1 x 74.08
gram 1 equivalent = 74.08/ 2 gram 1 equivalent = 37.04 gram 2.4743 x 10-3 equivalent = 0.0916 gram 0.243 gram sample contain 0.0916 gram of Ca(OH)2
% wt of Ca(OH)2 in sample = 0.0916 / 0.243 x
100 = 3.77 %
56
A 0.336 g sample containing oxalic acid H2C2O4 was titrated with 17.7 mL of a 0.0996 N NaOH solution. Calculate weight % of oxalic acid in the sample
57
�Equivalent of NaOH : N = Eq / L Eq = N x L =0.0996 x 0.017.7 = 1.7629 x 10-3 Equivalents of acid = Equivalents of base in the neutralization reaction Equivalents of acid, H2C2 O4 = 1.7629 x 10-3
58
�1 mole H2C2 O4 = 2 Equivalent (2 H+)
1 mole H2C2 O4 = mole x mw = 1 x 90.016 gram 1 equivalent = 90.016 /2 gram 1 equivalent = 45.008 gram 1.7629 x 10-3 equivalent = 0.07935 0.336 gram sample contain 0.07935 gram of
H2C2 O4
% wt of H2C2 O4 in sample = 0.07935 / 0.336 x 100 = 23.6 %
59
A 15.0 N mL sample of an acid requires 37.3 mL of 0.303 N NaOH for neutralization. Calculate the normality of the acid.
60
�Equivalents of acid = Equivalents of base
VacidNacid = VbaseNbase
15 (N) = 37.3 x 0.303
= 11.3079
N = 11.3079 / 15 = 0.753
61
If 900.4 mg of the diprotic acid, oxalic acid (H2C2O4) is exactly neutralized by 24.10 mL of NaOH solution. Calculate the normality of the NaOH solution (ans: 0.8299 N)
62
�Equivalents of acid = Equivalents of base in the neutralization reaction Equivalents of acid, H2C2 O4
1 mole H2C2 O4 = 2 Equivalent (2 H+)
1 mole H2C2 O4 = mole x mw = 1 x 90.016 gram 1 equivalent = 90.016 /2 gram 1 equivalent = 45.008 gram
900.4 mg (=0.9004 g) = 0.0200 equivalent
63
�Equivalent of NaOH = 0.0200 N = Eq / L = 0.0200 / 0.02410 = 0.8299 N
64
If take 32.75 mL of 0.1835 NaOH to titrate 23.42 mL of HCl solution. Calculate the normality of the HCl solution (ans: 0.2566 N)
65
�Equivalents of acid = Equivalents of base
VacidNacid = VbaseNbase
23.42 (N) = 32.75 x 0.1835
= 6.0096
= 11.3079 / 23.42
= 0.2566
66
�Vinegar is an aqueous solution of acetic acid, CH3COOH. Suppose you titrate a 20.9 mL sample of vinegar with 31.27
mL of a standardized 0.1084 N solution
of NaOH. What is the normality of acetic
acid in this vinegar? (ans: 0.162N)
67
�A Impure sample of ascorbic acid , with a
mass of 2.06 grams is dissolved in water. It
is titrated with 0.200 mol/l sodium
hydroxide.(The ascorbic acid reacts with
sodium hydroxide in a 1: 1 ratio). The sample required 46.0 ml to reach an endpoint using phenolphthalein as the indicator.
68
�a) Calculate
the number of moles of ascorbic
acid in the sample. (= to the number of
moles of sodium hydroxide).
b) Calculate
the mass of ascorbic acid in the
the % purity of the sample (mass
sample.
c) Calculate
of ascorbic acid/ mass of sample X 100).
69
�A 0.42 gram sample of acetylsalicylic acid (C9H8O4 , aspirin) is crushed and dissolved in water. The sample is titrated with 0.160
mol/l sodium hydroxide. The acetylsalicylic
acid reacts 1: 1 with the sodium hydroxide. The titration required an average volume of 12.50 ml of sodium hydroxide to reach the endpoint.
70
�a) Calculate the number of moles of acetylsalicylic acid. b) Calculate the mass of ascorbic acid in the sample. c) Calculate the % purity of the sample
71