Professional Documents
Culture Documents
4 - 3 - Continuity
Uploaded by
Nica Cielo B. LibunaoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
4 - 3 - Continuity
Uploaded by
Nica Cielo B. LibunaoCopyright:
Available Formats
Continuity
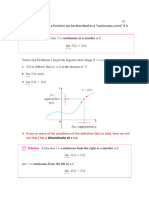
Continuity of a Function at a Number
A function f is continuous at a if
1. f is defined at x = a;
that is, a is in the domain of f so the value of f(a) exists.
) (
lim
x f
a x
2. exists;
that is,
3.
) ( ) (
lim
a f x f
a x
=
) ( ) (
lim lim
x f x f
a x a x
+
=
If at least one of the three conditions fail to
hold at a, then the function is said to be
discontinuous at a.
c
y=f(x)
y
x
f(c)
Continuous
c
y=f(x)
y
x
f(c)
Not continuous
c
y=f(x)
y
x
Not continuous
c
y=f(x)
y
x
Not continuous
f(c)
c
y=f(x)
y
x
Not continuous
c
y=f(x)
y
x
Not continuous
Continuity of Rational and Polynomial
Functions
A polynomial function is continuous everywhere.
A rational function defined by
where N(x) and D(x) are both polynomial functions, is
continuous at every number a provided that .
0 ) ( = x D
) (
) (
) (
x D
x N
x f =
Consider the function defined by
Example:
Determine if f is continuous
at x = 3.
>
s +
=
3 , 3
3 ,
) (
2
x if x
x if x x
x f
Consider the function defined by
Example:
Determine if f is continuous at x = 2 and
at x = 1 .
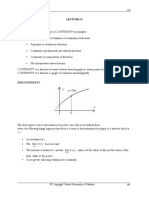
Continuity on an Interval
A function f is said to be continuous
) ( ) (
lim
a f x f
a x
=
+
on an open interval if and only if it is continuous at
every number in the open interval.
on the half-open interval [a, b) if and only if it is
continuous on the open interval (a, b) and
on the half-open interval (a, b] if and only if it is
continuous on the open interval (a, b) and
) ( ) (
lim
b f x f
b x
=
Continuity on an Interval
A function f is said to be continuous
) ( ) (
lim
a f x f
a x
=
+
on the closed interval [a , b] if and only if it is
continuous on the open interval (a, b) and
) ( ) (
lim
b f x f
b x
=
For each of the given functions, do the
following:
A. Sketch the graph of the given
function.
B. By observing where there is a break
in the graph, determine the number
at which the function is
discontinuous.
C. Verify, using the definition of
continuity, the 3 conditions to
determine the continuity of the
function at the possible point(s) of
discontinuity.
D. Find the largest interval or union of
intervals for which the given function
is continuous.
Exercises:
>
s +
=
1 , 3
1 , 3
) (
x x
x x
x f
=
=
=
3 , 2
3 , 3
) (
x
x x
x g
2
) (
=
x
x
x h
For each of the given functions, do the
following:
A. Sketch the graph of the given
function.
B. By observing where there is a break
in the graph, determine the number
at which the function is
discontinuous.
C. Verify, using the definition of
continuity, the 3 conditions to
determine the continuity of the
function at the possible point(s) of
discontinuity.
D. Find the largest interval or union of
intervals for which the given function
is continuous.
Exercises:
> +
< s +
<
=
2 5
2 1 , 3 2
1 ,
) (
2
x x
x x
x x
x g
>
< < +
s
=
1 4
1 1 , 4
1 , 3 2
) (
2
x x
x x x
x x
x f
For each of the given functions, do the
following:
A. Sketch the graph of the given
function.
B. By observing where there is a break
in the graph, determine the number
at which the function is
discontinuous.
C. Verify, using the definition of
continuity, the 3 conditions to
determine the continuity of the
function at the possible point(s) of
discontinuity.
D. Find the largest interval or union of
intervals for which the given function
is continuous.
Exercises:
>
=
< +
=
2 2 8
2 8
2 , 2 3
) (
2
x x x
x
x x
x g
<
+
>
=
2 ,
1
2 , 4
) (
2
2
x
x x
x
x x
x f
You might also like
- 2.3. Sự liên tục hàm sốDocument31 pages2.3. Sự liên tục hàm sốDo Phuong NamNo ratings yet
- Lec 9 Continuity PDFDocument41 pagesLec 9 Continuity PDFAbrar Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- CalculusDocument15 pagesCalculusrpdemaladeNo ratings yet
- Definition of Continuous at A Point:) (X ) (Lim ) (Lim ) (LimDocument3 pagesDefinition of Continuous at A Point:) (X ) (Lim ) (Lim ) (LimtemkimleangNo ratings yet
- m100 Chapter1 Part3Document26 pagesm100 Chapter1 Part3Vongola SunNo ratings yet
- Basic Calculus Module 3Document9 pagesBasic Calculus Module 3Russell VenturaNo ratings yet
- Grand Canyon, Arizona: Greg Kelly, Hanford High School, Richland, Washington Photo by Vickie Kelly, 2002Document10 pagesGrand Canyon, Arizona: Greg Kelly, Hanford High School, Richland, Washington Photo by Vickie Kelly, 2002Temesgen BihonegnNo ratings yet
- Calculus: Mrs. Dougherty's ClassDocument66 pagesCalculus: Mrs. Dougherty's ClassAbdullah SoomroNo ratings yet
- DerivativesDocument8 pagesDerivativesTrung BảoNo ratings yet
- 151 Exam 1 Review AU10Document3 pages151 Exam 1 Review AU10Nathan W. SerafiniNo ratings yet
- 28 Continuity & Diffrentiability Part 1 of 1Document23 pages28 Continuity & Diffrentiability Part 1 of 1Mehul JainNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Continuity: AMA140/150 CalculusDocument12 pagesLecture 3 - Continuity: AMA140/150 CalculusLuis Aguilar CapchaNo ratings yet
- Continuity 413Document69 pagesContinuity 413ChuyiyaNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Increasing and Decreasing Functions and 1 Derivative TestDocument2 pages3.3 Increasing and Decreasing Functions and 1 Derivative TestJudielyn SamsonNo ratings yet
- Calculus Review and Formulas: 1 FunctionsDocument11 pagesCalculus Review and Formulas: 1 FunctionsRaymond BalladNo ratings yet
- ContinuityDocument23 pagesContinuityMarjorie Palconit NoqueraNo ratings yet
- Recaping Last LecturesDocument31 pagesRecaping Last LecturesGhulam FareedNo ratings yet
- CH 01 Sec 06Document10 pagesCH 01 Sec 06datdude1415No ratings yet
- Continuity and Discontinuity of A FunctionDocument29 pagesContinuity and Discontinuity of A FunctionahronraquelNo ratings yet
- Maximum and MinimumDocument17 pagesMaximum and MinimumBehranne ObdNo ratings yet
- 1.5 The Continuity of A FunctionDocument4 pages1.5 The Continuity of A Functiontinashembofana84No ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Limits Section 2.6 Continuity: Lim F (X) F (A) - If F Is Not Continuous at A, Then A Is ADocument8 pagesChapter 2: Limits Section 2.6 Continuity: Lim F (X) F (A) - If F Is Not Continuous at A, Then A Is ADaniel DenningNo ratings yet
- ContinuityDocument12 pagesContinuityUɐƃnqnlUoɹNo ratings yet
- (3-1) Max and Min ValuesDocument10 pages(3-1) Max and Min ValuesAndrea DeteraNo ratings yet
- Worksheet # 17: Maxima and MinimaDocument1 pageWorksheet # 17: Maxima and MinimasubyNo ratings yet
- 7.9.1 Properties of Continuous FunctionsDocument9 pages7.9.1 Properties of Continuous FunctionsMohamad HaziqNo ratings yet
- Math 53 LE 3 Reviewer ProblemsDocument14 pagesMath 53 LE 3 Reviewer ProblemsJc QuintosNo ratings yet
- Continuity p1Document12 pagesContinuity p1Ayam MohsenNo ratings yet
- Class 11 ISC Maths ProjectDocument19 pagesClass 11 ISC Maths ProjectmanthanmahendrajagtapNo ratings yet
- Revision (Limits)Document2 pagesRevision (Limits)Tan Chin HuatNo ratings yet
- Continuity End Behavior and Limits 5Document39 pagesContinuity End Behavior and Limits 5Aroosha KhanNo ratings yet
- Continuity End Behavior and LimitsDocument39 pagesContinuity End Behavior and LimitsMohy SayedNo ratings yet
- Differentiability and Continuity: The Derivative and DifferenitiationDocument4 pagesDifferentiability and Continuity: The Derivative and Differenitiationthei_taz13No ratings yet
- FXH FX H: F (X) For All F (X) For AllDocument2 pagesFXH FX H: F (X) For All F (X) For AllBruce ShenNo ratings yet
- Xii Maths Activities For Term-1 Act No. 1-5Document17 pagesXii Maths Activities For Term-1 Act No. 1-5devchauhan0040No ratings yet
- Continuty and DifferentibilyDocument7 pagesContinuty and DifferentibilythinkiitNo ratings yet
- ch03 Ma1300Document13 pagesch03 Ma1300rimskysNo ratings yet
- Lecture-6, Continuous Functions, Cal-1 IBADocument15 pagesLecture-6, Continuous Functions, Cal-1 IBAOrochi ScorpionNo ratings yet
- Applicatios of DerivativesDocument19 pagesApplicatios of Derivativessohail66794154No ratings yet
- (Chap 3) Applications of DifferentationDocument34 pages(Chap 3) Applications of DifferentationTruong Cong Trinh (K17 DN)No ratings yet
- 1.6 One SidedLimits&ContinuityDocument4 pages1.6 One SidedLimits&Continuitybd87glNo ratings yet
- Final Notes For AB and BCDocument16 pagesFinal Notes For AB and BCsapabapjava2012No ratings yet
- Continuity: Lim LimDocument8 pagesContinuity: Lim LimKainat Komal KhanNo ratings yet
- Calculus I Notes On Limits and Continuity.: Limits of Piece Wise FunctionsDocument8 pagesCalculus I Notes On Limits and Continuity.: Limits of Piece Wise Functionsajaysharma19686191No ratings yet
- Math 150 Exam 3 Review SheetDocument3 pagesMath 150 Exam 3 Review SheetNguyen PhamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Mm34casDocument16 pagesChapter 12 Mm34casEric MoralesNo ratings yet
- Teaching ContinuityDocument10 pagesTeaching ContinuityNgo Anh ThuNo ratings yet
- Check Continuity of Functions and Determine DiscontinuitiesDocument3 pagesCheck Continuity of Functions and Determine Discontinuitiesksr131No ratings yet
- Name: MATH-2211 - Calculus-I - CRN 808 Test-3Document2 pagesName: MATH-2211 - Calculus-I - CRN 808 Test-3Ghislain DjedjeroNo ratings yet
- Limit & Continuity (New Handout)Document9 pagesLimit & Continuity (New Handout)Siti Khadijah Mohd ZainNo ratings yet
- Part 2 Continuous Functions and Their Properties: 2.1 DefinitionDocument17 pagesPart 2 Continuous Functions and Their Properties: 2.1 DefinitionmercyNo ratings yet
- School of Mathematics and Physics, The University of QueenslandDocument1 pageSchool of Mathematics and Physics, The University of QueenslandVincent LiuNo ratings yet
- ContinuityDocument3 pagesContinuityMohit KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Curve Sketching Test - Multiple Choice ADocument6 pagesCurve Sketching Test - Multiple Choice Agarth5100% (2)
- 3 01 Extrema On An IntervalDocument8 pages3 01 Extrema On An IntervaljakeNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Guided NotesDocument6 pages1.2 Guided NotesClaire KolakowskiNo ratings yet
- Cal1 Chapter 3Document80 pagesCal1 Chapter 3Vân Anh Nguyễn NgọcNo ratings yet
- 1 Functions As Models: 1.1 Four Ways To Represent A FunctionDocument3 pages1 Functions As Models: 1.1 Four Ways To Represent A FunctionChristian BaseaNo ratings yet
- Rule 117 - Motion To QuashDocument10 pagesRule 117 - Motion To QuashNica Cielo B. LibunaoNo ratings yet
- Rights of The AccusedDocument7 pagesRights of The AccusedNica Cielo B. LibunaoNo ratings yet
- Daan V SandiganbayanDocument3 pagesDaan V SandiganbayanNica Cielo B. LibunaoNo ratings yet
- Daan V SandiganbayanDocument3 pagesDaan V SandiganbayanNica Cielo B. LibunaoNo ratings yet
- Ibp V AtienzaDocument1 pageIbp V AtienzaNica Cielo B. LibunaoNo ratings yet
- 37 - Dujon v. Ampatuan, GR No. 188707 (Tan)Document2 pages37 - Dujon v. Ampatuan, GR No. 188707 (Tan)Nica Cielo B. LibunaoNo ratings yet
- 37 - Dujon v. Ampatuan, GR No. 188707 (Tan)Document2 pages37 - Dujon v. Ampatuan, GR No. 188707 (Tan)Nica Cielo B. LibunaoNo ratings yet
- 14 - People Vs Tumulak (Esber)Document1 page14 - People Vs Tumulak (Esber)Nica Cielo B. LibunaoNo ratings yet
- People V de JesusDocument2 pagesPeople V de JesusNica Cielo B. LibunaoNo ratings yet
- 01 US vs. Tayco (Alcazar)Document1 page01 US vs. Tayco (Alcazar)Nica Cielo B. LibunaoNo ratings yet
- 06 - US v. Chu Loy and Lee Kam (Bernardez)Document1 page06 - US v. Chu Loy and Lee Kam (Bernardez)Nica Cielo B. LibunaoNo ratings yet
- 18 - People v. BadillaDocument2 pages18 - People v. BadillaNica Cielo B. LibunaoNo ratings yet
- People VS Maongco (Guevarra)Document1 pagePeople VS Maongco (Guevarra)Nica Cielo B. Libunao0% (1)
- People Vs Casacop - PALMOSDocument2 pagesPeople Vs Casacop - PALMOSNica Cielo B. Libunao0% (1)
- People V BustineraDocument2 pagesPeople V BustineraNica Cielo B. LibunaoNo ratings yet
- 09 - San Juan vs. People, May 30, 2011Document2 pages09 - San Juan vs. People, May 30, 2011Nica Cielo B. Libunao100% (1)
- 22 Zanoria vs. Court of AppealsDocument2 pages22 Zanoria vs. Court of AppealsNica Cielo B. LibunaoNo ratings yet
- From Receiving Gifts, and For Private Parties To Give Gifts To ThemDocument1 pageFrom Receiving Gifts, and For Private Parties To Give Gifts To ThemNica Cielo B. LibunaoNo ratings yet
- 35 - People v. FabroDocument2 pages35 - People v. FabroNica Cielo B. LibunaoNo ratings yet
- 06 - US v. Chu Loy and Lee KamDocument1 page06 - US v. Chu Loy and Lee KamNica Cielo B. LibunaoNo ratings yet
- 4th Assignment - TITLE VDocument1 page4th Assignment - TITLE VNica Cielo B. LibunaoNo ratings yet
- Rosewood Processing, Inc. v. NLRCDocument2 pagesRosewood Processing, Inc. v. NLRCNica Cielo B. LibunaoNo ratings yet
- Final Response To Pastor LetterDocument3 pagesFinal Response To Pastor LetterMadeline CiakNo ratings yet
- Effect of CompensationDocument5 pagesEffect of CompensationKomal MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Trade Life Cycle1Document2 pagesTrade Life Cycle1ezefatNo ratings yet
- Precise Software SolutionsDocument2 pagesPrecise Software Solutionssaikat sarkarNo ratings yet
- How To Configure IP Address For Ethernet Port PrintersDocument6 pagesHow To Configure IP Address For Ethernet Port PrintersIsis DiazNo ratings yet
- Queuing Part 1 PDFDocument13 pagesQueuing Part 1 PDFabhaymainiNo ratings yet
- Brochure DronsparkDocument2 pagesBrochure DronsparksachinNo ratings yet
- Najo Modular Interface Quick StartDocument71 pagesNajo Modular Interface Quick StartAaron SmithNo ratings yet
- Ujjain Simhastha 2016Document4 pagesUjjain Simhastha 2016Nidhi MishraNo ratings yet
- D9Document88 pagesD9Luis Jesus100% (1)
- DISCIPLINEDocument2 pagesDISCIPLINESMK MULYA KENCANANo ratings yet
- Oracle r2rDocument12 pagesOracle r2rMichaelNo ratings yet
- Heat Flux Thermocouple MCTDocument2 pagesHeat Flux Thermocouple MCTIziNo ratings yet
- Collective SelfDocument3 pagesCollective Selfgabby tolentinoNo ratings yet
- Wuthering HeightsDocument26 pagesWuthering HeightsAbubakarr SankohNo ratings yet
- AndreasenJ Back To The FutureDocument6 pagesAndreasenJ Back To The FutureQilong ZhangNo ratings yet
- Boltanski. On Critique - EmancipationDocument102 pagesBoltanski. On Critique - EmancipationAndrea CavalheiroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document11 pagesChapter 1Crist John PastorNo ratings yet
- Illocutionary Acts Expressed Through Sign Language in "Silence Movie"Document74 pagesIllocutionary Acts Expressed Through Sign Language in "Silence Movie"vivianNo ratings yet
- Robots Drive SystemDocument28 pagesRobots Drive SystemDhalal AsmiNo ratings yet
- Sastec2 - Technical Offer - 220kv Gis JSPL - Angul - Rev CDocument18 pagesSastec2 - Technical Offer - 220kv Gis JSPL - Angul - Rev CRakesh Kumar Singh (Phase 1B)No ratings yet
- Producing Sketches and Drawings Part 5Document5 pagesProducing Sketches and Drawings Part 5Arkim MakhosaNo ratings yet
- Cse D 4th SemDocument65 pagesCse D 4th Sempoojamani1990No ratings yet
- Endnote X8: Research SmarterDocument9 pagesEndnote X8: Research SmarterMuhajir BusraNo ratings yet
- Analyses From The Semiological Point of View The Theme of Mozart S Symphony in G Minor K550Document39 pagesAnalyses From The Semiological Point of View The Theme of Mozart S Symphony in G Minor K550Renato HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Henry Corbin and The Archetypal RealmDocument2 pagesHenry Corbin and The Archetypal RealmZeteticus100% (2)
- Home AutomationDocument19 pagesHome AutomationsatyajitNo ratings yet
- Ecdis PDFDocument2 pagesEcdis PDFelkaNo ratings yet
- Aero 2Document2 pagesAero 2Chandrashekar MayuramNo ratings yet
- BIC3313-Internet Payment Systems-Assignment 1Document2 pagesBIC3313-Internet Payment Systems-Assignment 1Borotho MolemoNo ratings yet