0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views28 pagesLesson 7 XTH STD M2
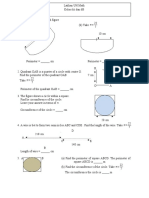
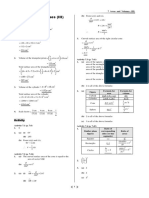
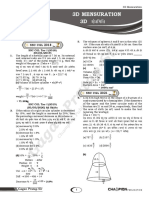
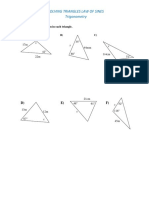
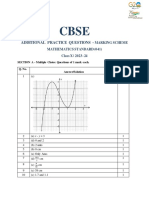
The document contains practice problems related to mensuration, including calculations for volumes and surface areas of various geometric shapes such as cones, spheres, cylinders, and frustums. It provides specific dimensions and formulas needed to solve each problem, along with the necessary conversions for units. Additionally, it includes exercises on sectors and segments of circles, emphasizing the application of mathematical principles in real-world contexts.
Uploaded by
madhurimestry32Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views28 pagesLesson 7 XTH STD M2
The document contains practice problems related to mensuration, including calculations for volumes and surface areas of various geometric shapes such as cones, spheres, cylinders, and frustums. It provides specific dimensions and formulas needed to solve each problem, along with the necessary conversions for units. Additionally, it includes exercises on sectors and segments of circles, emphasizing the application of mathematical principles in real-world contexts.
Uploaded by
madhurimestry32Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd