Presentations for PowerPoint
INDUSTRIAL
MAINTENANCE
and
MECHATRONICS
�27 Motor Controls
�Learning Objectives (1 of 5)
• Describe the basic functions of motor control circuits.
• Select and size fuses and circuit breakers to be used in a control
circuit.
• Describe how to size conductors.
NOARK Electric North America
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.
�Learning Objectives (2 of 5)
• Discuss input devices and types of contacts in a control circuit,
including pushbuttons and indicators.
• Discuss types of switches used in a control circuit.
Chaowalit/[Link]
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.
�Learning Objectives (3 of 5)
• Interpret control circuit symbols and
internal wiring arrangement diagrams.
• Discuss motor starters and contactors
used in a control circuit.
• Distinguish types of overloads and
proper sizing.
Goodheart-Willcox Publisher
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.
�Learning Objectives (4 of 5)
• Understand reversing motor starters and reversing drum switches in
DC, single-phase AC, and three-phase AC motors.
• Troubleshoot a motor starter to find possible failures in the motor
and control circuit.
NOARK Electric North America
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.
�Learning Objectives (5 of 5)
• Describe output device functions
including relays and timers.
• Explain the operational difference
between an on-delay and contact-
controlled off-delay timer.
• Describe solenoids and how they
may fail in a fluid system.
Automation Direct; Field Controls
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.
�Basic Motor Controls
• Start and stop loads
• Perform sequence of events
• Control output relative to input
• Automatically control system
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.
�Digital Motor Control Circuits
• Either on or off
• Carry out timed events, sequences, interlocks
• Inputs are operator or process controlled
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.
�Fuses in Control Circuits
• One-time use devices
• Different voltage levels, types, sizes, ratings
• Low-voltage branch-circuit fuses used on motors
Ideal Industries, Inc.
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.
�Procedure: Removing Fuses
1. Use appropriate fuse removal tool
2. Ensure power is locked out and tagged
out
3. With multimeter, ensure power is off on
sides of fuse
4. Grab fuse at center line with tool
5. Firmly and quickly pull fuse
6. Inspect removed fuse
Ideal Industries, Inc.
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.
�Procedure: Inserting Fuses
1. Ensure fuse markings are in correct position
2. Grab fuse in center with tool
3. Make contact with holder on both sides
4. Ensure fuse is centered and ends clear the holder
5. Firmly push fuse into holder
6. Use tool if only one end entered
7. Inspect fuse and label placement
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.
� Safety Note: Use an Appropriate
Torque Wrench
• Never exceed torque specifications on any terminals
• Threads can easily be damaged
• Can result in loose connection, possibly causing arc flash and burns or
fire
• If unsure of torque by feel, use an appropriate torque wrench
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.
�Circuit Breakers
• Protect from overloads and short circuits
• Offer various tripping options and displays
• Molded-case circuit breaker common
NOARK Electric North America
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.
�Guidelines for Sizing
• FLC from NEC tables determines conductor size, short circuit
protection, ground protection
• FLC on nameplate determines overload devices
• FLC × 1.25 must be less than conductor ampacity rating
• Breaker protecting branch circuit sized using NEC Table 430.52
• Fuses sized depending on type
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.
� Safety Note: Fuses and Circuit
Breakers Do Not Replace LOTO
• Do not rely on a fuse or circuit breaker
• One ampere can kill you
• Lock out, tag out, and ensure no circuit voltage is present
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.
�Input Devices
• Normally open
• Maximum resistance when not actuated
• Nearly no resistance when actuated
• Normally closed
• No resistance when not actuated
• Maximum resistance when actuated
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.
�Contacts
• Hard contacts
• Little resistance when closed
• Infinite resistance when open
• Momentary contacts
• Return to normal when pressure released
• Maintained contacts
• Remain active until deactivated
Goodheart-Willcox Publisher
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.
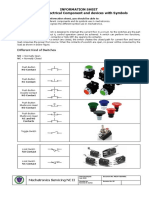
�Symbols for Pushbuttons and Switches
Goodheart-Willcox Publisher
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.
�Pushbuttons
• Multiple blocks can mount to one base
NKK Switches; NOARK Electric North America; NOARK Electric North America
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.
�Indicators
• Use power unit for base
• May be operators
• May be push-to-test
NOARK Electric North America; NKK Switches
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.
�Switches
• May be illuminated with power
unit
• Have up to four positions
• Are maintained or spring-return
momentary contacts
• May have multiple contact
blocks connected
NOARK Electric North America; Goodheart-Willcox Publisher
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.
�Switch Contacts
• SPST switch
• Single arm makes single throw
• SPDT switch
• Single arm and two throw positions
• Switches adjusted to open/close at set point
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.
�Limit Switches
• Physically contact element
• Convert mechanical movement to electrical output
• Adjustment affects circuit operation and timing
Chaowalit/[Link]; Goodheart-Willcox Publisher
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.
�Magnetic Reed Contacts
• Used on miniature switches
• Sealed contacts actuated by internal magnet
• Limited amperage rating
Goodheart-Willcox Publisher
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.
�Float Switches
• Activate when liquid reaches certain level
• Types:
• External
• Internal Counterweight
• Magnetic reed
Float
Goodheart-Willcox Publisher
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.
�Temperature Switches
• Open/close at certain temperature
• Bimetallic or gas/vapor filled
• Sensing element mounted in thermowell
Automation Direct
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.
�Pressure Switches
• Convert pressure to mechanical movement
• Movement transferred to miniature switch
Sporlan Division, Parker Hannifin Corporation
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.
�Motor Starters and Contactors
• Contactor provides resistance at startup
• Removes resistance at running speed
• Motor starter operates like contactor
• Includes overload protection from current
spikes
• Multiple poles controlled by single coil
NOARK Electric North America; Goodheart-Willcox Publisher
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.
�Starter Sizes
Goodheart-Willcox Publisher
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.
�IEC Starter Characteristics
• Less expensive than NEMA starters
• Smaller and can mount on DIN rail inside control cabinets
• Have tighter band of overload ranges; can detect small overloads
faster
• Somewhat finger-safe
• Overload section ordered with small current range for overload
• May have integral stop, start, reset, and test buttons on front
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.
�NEMA Starter Characteristics
• Can withstand larger overloads without affecting operation of
overload section
• Larger, in larger cabinets, mounted to backplane
• Provide for wide range of overloads to fit into overload section
• If adjustable, overloads can usually be adjusted over wider range
• Mechanically stronger
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.
�Dual-Voltage Coils
• When energized, develops
magnetic field
• Shuts main contacts against
spring pressure
• Changes state of auxiliary
contacts
• When de-energized, contacts
open
• Motor stops
Goodheart-Willcox Publisher
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.
�Overloads
• Sense motor current
• Open contact when current
exceeds set value
• Starter coil de-energizes and
opens
• Motor shuts down
Goodheart-Willcox Publisher
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.
�Bimetallic Overload
Goodheart-Willcox Publisher
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.
�Melting Alloy Overload
Goodheart-Willcox Publisher
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.
�Magnetic Overload
• Works like clamp-on ammeter
• Each phase passes through overload section
• Transformer generates voltage proportional to current
• Electronic signal senses voltage
• Opens contact when greater than set point
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.
�Factors for Sizing Overloads
• Service factor of motor
• Horsepower and resulting current draw
• Environmental differences between motor and starter
• Manufacturer recommendations
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.
�Reversing Motor Starters
• Reverse rotation of motors
NOARK Electric North America; Goodheart-Willcox Publisher
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.
�Interlocks
• Prevent something that may cause
damage
• Ensure sequence occurs in safe
order
• Shut down system if failure occurs
• Prevent death and serious injury
• Cannot be changed, removed,
bypassed
Goodheart-Willcox Publisher
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.
�Reversing Drum Switches
• Reverse rotation of motors
• Switch line voltage to motor
Goodheart-Willcox Publisher
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.
� Safety Note: LOTO before Work on
Drum Switches
• Ensure power is locked out and tagged out
• High voltage possible on switch casing
• Never open switch with power on
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.
�Troubleshooting Overloads
• Two reasons overloads trip
• Higher than normal current draw
• Excessive heat in environment
• Thermistors sense winding
temperatures
• Change resistance as temperature
changes
Sporlan Division, Parker Hannifin Corporation; Goodheart-Willcox Publisher
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.
�Procedure: Finding Sources of Excess
Current
1. Check capacitors
A. Confirm capacitance matches specifications
B. Check if capacitor is internally grounded
C. When in doubt, replace capacitors
2. Check for shorts
3. Check that motor spins freely when load disconnected
4. Check alignment of mechanical elements
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.
�Troubleshooting Coils
• Noise results from contacts not sealing
• Open coils show high resistance
• Shorted coils trip breaker or open fuse
• Coils heat rapidly with low voltage
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.
�Troubleshooting Contacts
• Main contacts
• Check torque and wear if voltage drops
• Auxiliary contacts
• Replace if not operating with motor
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.
�Relays
• Convert electrical signals to mechanical action
• Specified by input voltage
• May be SPST, SPDT, DPDT
Automation Direct
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.
�Relay Diagrams
Goodheart-Willcox Publisher
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.
�On-Delay Timer
• Energizes output after preset
time elapses
• NOTC contacts open when
de-energized
• NCTO contacts closed when
de-energized
• Allows additional logic
possibilities
Goodheart-Willcox Publisher
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.
�Contact-Controlled Off-Delay Timer
• De-energizes after set time elapsed
Macromatic Industrial Controls; Goodheart-Willcox Publisher
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.
�Solenoid-Controlled Valves
• Energized solenoid develops
magnetic field
• Draws soft iron core into coil
• Initial current draw drops
• Reinforces magnetic field
• Excessive current and heat
cause solenoid failure
Automation Direct; Field Controls
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. May not be posted to a publicly accessible website.