Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study Aminophylline
Uploaded by
Asusej Pard DeqCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Study Aminophylline
Uploaded by
Asusej Pard DeqCopyright:
Available Formats
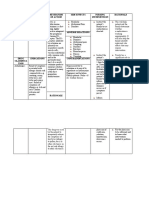
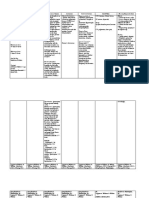
Drug Name
Dosage & Route
Action
Indication
Contraindication
Adverse Effects
Nursing Responsibility
AMINOPHYLLINE (theophylline ethylenediamide) (am-in-off'i-lin) Corophyllin , Paladron , Phyllocontin, Somophyllin, Somophyllin-DF, Truphylline Classifications: BRONCHODILATOR (RESPIRATORY SMOOTH MUSCLE RELAXANT); XANTHINE
Bronchospasm Adult: IV Loading Dose 6 mg/kg over 30 min IV Maintenance Dose nonsmoker, 0.5 mg/kg/h; smoker, 0.75 mg/kg/h; CHF or cirrhosis, 0.25 mg/kg/h PO nonsmoker, 0.5 mg/kg/h times 24 h in 4 divided doses; smoker, 0.75 mg/kg/h times 24 h in 4 divided doses; CHF or cirrhosis, 0.25 mg/kg/h times 24 h in 4 divided doses Child: IV Loading Dose 6 mg/kg IV over 30 min IV Maintenance Dose 19 y, 1 mg/kg/h; >9 y, 0.75 mg/kg/h PO 19 y, 1 mg/kg/h times 24 h in 4 divided doses; >9 y, 0.75 mg/kg/h times 24 h in 4 divided doses Infant: PO/IV 611 mo, 0.87 g/kg/h; 26 mo, 0.5 mg/kg/h Neonate: PO/IV 0.16 mg/kg/h Neonatal Apnea Neonate: PO/IV Loading Dose 5 mg/kg PO/IV Maintenance Dose 5 mg/kg/d divided q12h
Aminophylline is a salt of theophylline with effects similar to those of other xanthines (e.g., caffeine and theobromine). Action is dependent on theophylline content (approximately 80%) and is measured as theophylline in the serum.
To prevent and relieve symptoms of acute bronchial asthma and treatment of bronchospasm associated with chronic bronchitis and emphysema.
Hypersensitivity to xanthine derivatives or to ethylenediamine component; cardiac arrhythmias. Safety during pregnancy (category C) or lactation is not established.
CNS: Nervousness, restlessness, depression, insomnia, irritability, headache, dizziness, muscle hyperactivity, convulsions. CV: Cardiac arrhythmias, tachycardia (with rapid IV), hyperventilation, chest pain, severe hypotension, cardiac arrest. GI: Nausea, vomiting, anorexia, hematemesis, diarrhea, epigastric pain.
Assessment & Drug Effects
Monitor for S&S of toxicity (generally related to theophylline serum levels over 20 mg/mL). Observe patients receiving parenteral drug closely for signs of hypotension, arrhythmias, and convulsions until serum theophylline stabilizes within the therapeutic range. Note: High incidence of toxicity is associated with rectal suppository use due to erratic rate of absorption. Monitor & record vital signs and I&O. A sudden, sharp, unexplained rise in heart rate may indicate toxicity. Lab tests: Monitor serum theophylline levels. Note: Older adults, acutely ill, and patients with severe respiratory problems, liver dysfunction, or pulmonary edema are at greater risk of toxicity due to reduced drug clearance. Note: Children appear more susceptible to CNS stimulating effects of xanthines (nervousness, restlessness, insomnia, hyperactive reflexes, twitching, convulsions). Dosage reduction may be indicated.
You might also like
- Legalization of Medical Marijuana in The PhilippinesDocument114 pagesLegalization of Medical Marijuana in The PhilippinesJed Daet71% (38)
- Nsg2hpb Exam PDFDocument23 pagesNsg2hpb Exam PDFCourtney B100% (1)
- ALBUTEROL Drug StudyDocument4 pagesALBUTEROL Drug StudyBea Dela Cena100% (2)
- Aminophylline Drug StudyDocument1 pageAminophylline Drug StudyEmman Balido67% (3)
- Management of Postoperative Pain With AcupunctureDocument384 pagesManagement of Postoperative Pain With AcupunctureCica Jovic100% (1)
- MbcmanualDocument113 pagesMbcmanualapi-376080864No ratings yet
- Chapter 21 Antidepressant AgentsDocument4 pagesChapter 21 Antidepressant AgentsNicolle Lisay IlaganNo ratings yet
- Drug Study of AminophyllineDocument6 pagesDrug Study of AminophyllineFrancis CorpuzNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - AminophyllineDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY - AminophyllineKian Herrera100% (1)
- AMINOPHYLLINEDocument2 pagesAMINOPHYLLINEmusiclover017100% (1)
- THEOPHYLLINE - Drug StudyDocument2 pagesTHEOPHYLLINE - Drug Studyeric macabiogNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Midazolam: RecommendedDocument5 pagesDrug Study: Midazolam: RecommendedShara Lailanie A. AzisNo ratings yet
- Prednisone Drug StudyDocument3 pagesPrednisone Drug StudyNiziu BearsNo ratings yet
- Beclomethasone Dipropionate (Drug Study)Document2 pagesBeclomethasone Dipropionate (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888100% (1)
- Drug Study FORTDocument3 pagesDrug Study FORTLysa Mae EleazarNo ratings yet
- BetamethasoneDocument3 pagesBetamethasoneMichael KuzbytNo ratings yet
- Benzonatate (Drug Study)Document1 pageBenzonatate (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888No ratings yet
- Drug Study Table OkDocument29 pagesDrug Study Table OkRifa'atul Mahmudah100% (1)
- Dextromethorphan HydrobromideDocument2 pagesDextromethorphan Hydrobromideapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Doxazosin MesylateDocument2 pagesDoxazosin Mesylateapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Chlorpheniramine MaleateDocument3 pagesChlorpheniramine Maleateapi-3797941100% (1)
- FluticasoneDocument4 pagesFluticasonevanNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyOlive Keithy Ascaño ReyesNo ratings yet
- Nalbuphine (Nubain)Document2 pagesNalbuphine (Nubain)Adrianne Bazo100% (1)
- SERETIDEDocument3 pagesSERETIDETempoNo ratings yet
- Brompheniramine Maleate (Drug Study)Document2 pagesBrompheniramine Maleate (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888No ratings yet
- Theophylline Drug StudyDocument3 pagesTheophylline Drug StudyCheezy Bread100% (5)
- AtroventDocument2 pagesAtroventKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- EpinephrineDocument3 pagesEpinephrinealexjerimiahNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY Amoxicillin PDFDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY Amoxicillin PDFMc SantosNo ratings yet
- Cetirizine 2Document2 pagesCetirizine 2ianNo ratings yet
- Drug Study EntecavirDocument4 pagesDrug Study EntecavirClarimae AwingNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Amphotericin B, Meropenem, Furosemide, Ciprofloxacin, Pentoxifylline, Pip-Tazo, Midazolam, VecuroniumDocument12 pagesDrug Study Amphotericin B, Meropenem, Furosemide, Ciprofloxacin, Pentoxifylline, Pip-Tazo, Midazolam, Vecuroniumpaupaulala100% (4)
- Drug Study AmpicillinDocument6 pagesDrug Study AmpicillinDgjj Compuiter100% (1)
- Drug Study For AntaminDocument1 pageDrug Study For AntaminJILLIAN MARIE BARREDO100% (1)
- Drug Study AmbroxolDocument2 pagesDrug Study AmbroxoledemNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyBrix John PortellanoNo ratings yet
- NeostigmineDocument4 pagesNeostigmineDonna Lyn B. DizonNo ratings yet
- Succunylcholine (Anectine) : University of San Carlos College of Nursing Drug StudyDocument1 pageSuccunylcholine (Anectine) : University of San Carlos College of Nursing Drug StudyFederico AndalesNo ratings yet
- ChlorphenamineDocument1 pageChlorphenaminereinaNo ratings yet
- Neuromuscular Junction Blocking AgentsDocument9 pagesNeuromuscular Junction Blocking AgentsSyvNo ratings yet
- Amoxicillin TrihydrateDocument1 pageAmoxicillin TrihydrateHoney Que BullivantNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mecahnism of Action Indication Side Effects Generic NameDocument2 pagesDrug Name Mecahnism of Action Indication Side Effects Generic NamehahahaNo ratings yet
- Chlorthalidone HygrotonDocument2 pagesChlorthalidone HygrotonLIEZEL GRACE VELAYONo ratings yet
- Ranitidine HydrochlorideDocument2 pagesRanitidine HydrochlorideIvan Liquiran AvenadoNo ratings yet
- Atropine Sulfate Drug STudyDocument2 pagesAtropine Sulfate Drug STudyLiway100% (1)
- Generic Name:: Norgestimate and Ethinyl EstradiolDocument5 pagesGeneric Name:: Norgestimate and Ethinyl EstradiolJay VillasotoNo ratings yet
- HYOSCINEDocument1 pageHYOSCINEzyr2189No ratings yet
- Drug Study For MGDocument1 pageDrug Study For MGSandra MedinaNo ratings yet
- 4th Rot Drug StudyDocument3 pages4th Rot Drug StudyAaron GarciaNo ratings yet
- AminophyllineDocument9 pagesAminophyllineZaira BataloNo ratings yet
- GellzDocument2 pagesGellzGelLz LacidaNo ratings yet
- PCU Medication ListDocument11 pagesPCU Medication ListreneecolemanNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyRosemarie CarpioNo ratings yet
- 9 Ketamine Drug StudyDocument7 pages9 Ketamine Drug Studyshadow gonzalezNo ratings yet
- IntralipidDocument3 pagesIntralipidGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyBlessyl Mae EstenzoNo ratings yet
- MCN Postpartal Psychosis Drug Study and NCPDocument2 pagesMCN Postpartal Psychosis Drug Study and NCPWinell GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mode of Action Indications Side Effects Nursing Interventions Generic NameDocument6 pagesDrug Name Mode of Action Indications Side Effects Nursing Interventions Generic Namedodong skyroseNo ratings yet
- Quetiapine Drug StudyDocument3 pagesQuetiapine Drug StudyEula Angelica Oco100% (1)
- Final Salbu-IpraDocument3 pagesFinal Salbu-IpraGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Name Description Indication Contraindication Adverse Reaction Special ConsiderationDocument6 pagesName Description Indication Contraindication Adverse Reaction Special ConsiderationHye JinNo ratings yet
- AminophyllineDocument3 pagesAminophyllineAmna Kazmi ShehzadNo ratings yet
- Forcadilla Medsurg Drug StudyDocument12 pagesForcadilla Medsurg Drug StudyKeir Mrls ForcadillaNo ratings yet
- Forcadilla-Medsurg Drug StudyDocument9 pagesForcadilla-Medsurg Drug StudyKeir Mrls ForcadillaNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric NursingDocument93 pagesPsychiatric Nursingjunie100% (5)
- Salbuterol Generic NameDocument4 pagesSalbuterol Generic NamejunieNo ratings yet
- Nursing Review BulletsDocument53 pagesNursing Review BulletscauldroNo ratings yet
- Early Education in Calamba and BiñanDocument4 pagesEarly Education in Calamba and Biñanjunie100% (1)
- Thermoregulation in Very LowDocument4 pagesThermoregulation in Very LowjunieNo ratings yet
- Unang YakapDocument1 pageUnang YakapjunieNo ratings yet
- NCM Checklist - Back RubDocument2 pagesNCM Checklist - Back RubYanna Habib-MangotaraNo ratings yet
- ANTE, Aubrey Nicole S. CH8-Assessment - NCM117Document11 pagesANTE, Aubrey Nicole S. CH8-Assessment - NCM117Aubrey AnteNo ratings yet
- IOL Calculation in Complex Corneal ConditionsDocument8 pagesIOL Calculation in Complex Corneal ConditionsShimaa MersalNo ratings yet
- Technology - Transfer - Manual - Copiar PDFDocument154 pagesTechnology - Transfer - Manual - Copiar PDFAnonymous XguKEyWNo ratings yet
- IndianJResHomoeopathy113184-5328698 144806Document12 pagesIndianJResHomoeopathy113184-5328698 144806Y.rajuNo ratings yet
- Case History, Diagnosis and Treatment PlanningDocument45 pagesCase History, Diagnosis and Treatment Planningdr parveen bathla100% (1)
- Research DesignsDocument123 pagesResearch DesignslucaNo ratings yet
- List of Generic Drugs For Which Rates Are Available: Slno Name of The Medicine Rate Shelf LifeDocument4 pagesList of Generic Drugs For Which Rates Are Available: Slno Name of The Medicine Rate Shelf LifekeshavNo ratings yet
- Abdominal ParacentesisDocument31 pagesAbdominal Paracentesisbala kumaaranNo ratings yet
- Millimeter Wave Therapy Device ManualDocument13 pagesMillimeter Wave Therapy Device ManualUrsulescu AurelianNo ratings yet
- Crowding 180601115625 PDFDocument109 pagesCrowding 180601115625 PDFVishal SharmaNo ratings yet
- 590 LA Aloe VeraDocument407 pages590 LA Aloe Veralennisavila100% (2)
- Breast AssesementDocument18 pagesBreast AssesementDevy IselaNo ratings yet
- Natural Aromatase InhibitorsDocument69 pagesNatural Aromatase InhibitorsIme Muško OsječkoNo ratings yet
- Water Quality Index of Perlis River, MalaysiaDocument6 pagesWater Quality Index of Perlis River, MalaysiaKuna KunavathiNo ratings yet
- (RestoDent) Pathophysiology of CariesDocument30 pages(RestoDent) Pathophysiology of CariesZara Sebastianne Garcia100% (1)
- Melbourne Doctor Upset by Defective DePuy ASR Hip ImplantDocument2 pagesMelbourne Doctor Upset by Defective DePuy ASR Hip ImplantKaiser Gornick LLPNo ratings yet
- The Sadomasochism Checklist: A Tool For The Assessment of Sadomasochistic BehaviorDocument11 pagesThe Sadomasochism Checklist: A Tool For The Assessment of Sadomasochistic BehaviorMichael Tavera OsorioNo ratings yet
- Learn Reiki and Javedaan by JhmirzaDocument150 pagesLearn Reiki and Javedaan by Jhmirzaasifmujteba2587100% (2)
- Linden Playful MetaphorsDocument6 pagesLinden Playful MetaphorsfolkmNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationChloie Marie RosalejosNo ratings yet
- Interferon Drug StudyDocument3 pagesInterferon Drug Studyjogzzz13100% (1)
- Tinnitus Today September 1986 Vol 11, No 3Document8 pagesTinnitus Today September 1986 Vol 11, No 3American Tinnitus AssociationNo ratings yet
- A Fairly Sad Tale by Dorothy ParkerDocument3 pagesA Fairly Sad Tale by Dorothy ParkerswhitmansalkinNo ratings yet
- Assael 2003Document7 pagesAssael 2003Varun bharathiNo ratings yet