Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Statistics For Management and Economics, Seventh Edition Formulas
Uploaded by
Rahul PanwarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Statistics For Management and Economics, Seventh Edition Formulas
Uploaded by
Rahul PanwarCopyright:
Available Formats
Statistics for management and Economics, Seventh Edition
Formulas
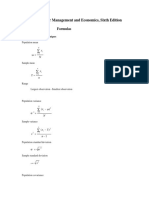
Numerical Descriptive techniques
Population mean
=
N
x
N
i
i
1
Sample mean
n
x
x
n
i
i
1
Range
Largest observation - Smallest observation
Population variance
2
=
N
) x (
N
i
i
1
2
Sample variance
2
s =
1
) (
1
2
n
x x
n
i
i
Population standard deviation
=
2
Sample standard deviation
s =
2
s
Population covariance
N
) y )( x (
N
i
y i x i
xy
Sample covariance
1
1
n
) y y )( x x (
s
n
i
i i
xy
Population coefficient of correlation
y x
xy
Sample coefficient of correlation
y x
xy
s s
s
r
Slope coefficient
2
1
x
s
) y , x cov(
b
y-intercept
x b y b
1 0
Probability
Conditional probability
P(A|B) = P(A and B)/P(B)
Complement rule
P(
C
A
) = 1 P(A)
Multiplication rule
P(A and B) = P(A|B)P(B)
Addition rule
P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B) - P(A and B)
Bayes Law Formula
) A | B ( P ) A ( P . . . ) A | B ( P ) A ( P ) A | B ( P ) A ( P
) A | B ( P ) A ( P
) B | A ( P
k k 2 2 1 1
i i
i
+ + +
Random Variables and Discrete Probability Distributions
Expected value (mean)
E(X) =
x all
) x ( xP
Variance
V(x) =
x all
) x ( P ) x (
2 2
Standard deviation
2
Covariance
COV(X, Y) =
) y , x ( P ) y )( x (
y x
Coefficient of Correlation
y x
) Y , X ( COV
Laws of expected value
1. E(c) = c
2. E(X + c) = E(X) + c
3. E(cX) = cE(X)
Laws of variance
1.V(c) = 0
2. V(X + c) = V(X)
3. V(cX) =
2
c
V(X)
Laws of expected value and variance of the sum of two variables
1. E(X + Y) = E(X) + E(Y)
2. V(X + Y) = V(X) + V(Y) + 2COV(X, Y)
Laws of expected value and variance for the sum of more than two variables
1.
k
i
i
k
i
i
X E X E
1 1
) ( ) (
2.
k
i
i
k
i
i
X V X V
1 1
) ( ) ( if the variables are independent
Mean and variance of a portfolio of two stocks
E(Rp) = w1E(R1) + w2E(R2)
V(Rp) =
2
1
w V(R1) +
2
2
w V(R2) + 2
1
w
2
w COV(R1, R2)
=
2
1
w
2
1
+
2
2
w
2
2
+ 2
1
w
2
w
1
Mean and variance of a portfolio of k stocks
E(Rp) =
k
i
i i
R E w
1
) (
V(Rp) =
+
+
k
i
k
i j
j i j i
k
i
i i
R R COV w w w
1 1 1
2 2
) , ( 2
Binomial probability
P(X = x) =
)! x n ( ! x
! n
x n x
) p ( p
1
np
) p ( np 1
2
) p ( np 1
Poisson probability
P(X = x) =
! x
e
x
Continuous Probability Distributions
Standard normal random variable
X
Z
Exponential distribution
/ 1
x
e ) x X ( P
>
x
e 1 ) x X ( P
<
2 1
x x
1 2 2 1
e e ) x X ( P ) x X ( P ) x X x ( P
< < < <
F distribution
2 1
, , 1 A
F
=
1 2
, ,
1
A
F
Sampling Distributions
Expected value of the sample mean
) (X E
x
Variance of the sample mean
) (X V
n
x
2
2
Standard error of the sample mean
n
x
Standardizing the sample mean
n
X
Z
/
Expected value of the sample proportion
)
(P E
p
p
Variance of the sample proportion
n
p p
P V
p
) 1 (
)
(
2
Standard error of the sample proportion
n
p p
p
) 1 (
Standardizing the sample proportion
n p p
p P
Z
) 1 (
Expected value of the difference between two means
) (
2 1
X X E 2 1
2 1
x x
Variance of the difference between two means
2
2
2
1
2
1 2
2 1
2 1
) (
n n
X X V
x x
+
Standard error of the difference between two means
2
2
2
1
2
1
2 1
n n
x x
+
Standardizing the difference between two sample means
2
2
2
1
2
1
2 1 2 1
) ( ) (
n n
X X
Z
Introduction to Estimation
Confidence interval estimator of
n
z x
/
2
t
Sample size to estimate
2
2
,
_
W
z
n
/
Introduction to Hypothesis Testing
Test statistic for
n /
x
z
Inference about One Population
Test statistic for
n / s
x
t
Confidence interval estimator of
n
s
t x
/ 2
t
Test statistic for
2
2
2
2
1
s ) n (
Confidence interval Estimator of
2
LCL =
2
2
2
1
/
s ) n (
UCL =
2
2 1
2
1
/
s ) n (
Test statistic for p
n / ) p ( p
p p
z
1
Confidence interval estimator of p
n / ) p ( p z p
/
t 1
2
Sample size to estimate p
2
2
1
,
_
W
) p ( p z
n
/
Confidence interval estimator of the total of a large finite population
1
]
1
t
n
s
t x N
/ 2
Confidence interval estimator of the total number of successes in a large finite population
1
1
]
1
t
n
p ( p
z p N
/
1
2
Confidence interval estimator of
when the population is small
1
2
t
N
n N
n
s
t x
/
Confidence interval estimator of the total in a small population
,
_
t
1
2
N
n N
n
s
t x N
/
Confidence interval estimator of p when the population is small
1
1
2
t
N
n N
n
) p ( p
z p
/
Confidence interval estimator of the total number of successes in a small population
,
_
t
1
1
2
N
n N
n
) p ( p
z p N
/
Inference About Two Populations
Equal-variances t-test of
2 1
,
_
2 1
2
2 1 2 1
1 1
n n
s
) ( ) x x (
t
p
2
2 1
+ n n
Equal-variances interval estimator of
2 1
,
_
+ t
2 1
2
2 2 1
1 1
n n
s t ) x x (
p /
2
2 1
+ n n
Unequal-variances t-test of
2 1
,
_
2
2
2
1
2
1
2 1 2 1
n
s
n
s
) ( ) x x (
t
1 1
2
2
2
2
2
1
2
1
2
1
2
2
2
2 1
2
1
n
) n / s (
n
) n / s (
) n / s n / s (
Unequal-variances interval estimator of
2 1
2
2
2
1
2
1
2 2 1
n
s
n
s
t ) x x (
/
+ t
1 1
2
2
2
2
2
1
2
1
2
1
2
2
2
2 1
2
1
n
) n / s (
n
) n / s (
) n / s n / s (
t-Test of
D
D D
D D
n / s
x
t
1
D
n
t-Estimator of
D
D
D
/ D
n
s
t x
2
t
1
D
n
F-test of
2
2
2
1
/
F =
2
2
2
1
s
s
1
1 1
n and 1
2 2
n
F-Estimator of
2
2
2
1
/
LCL =
2 1
2
2
2
2
1
1
, , /
F
s
s
,
_
UCL =
1 2
2
2
2
2
1
, , /
F
s
s
,
_
z-Test and estimator of
2 1
p p
Case 1:
,
_
2 1
2 1
1 1
1
n n
) p ( p
) p p (
z
Case 2:
2
2 2
1
1 1
2 1 2 1
1 1
n
) p ( p
n
) p ( p
) p p ( ) p p (
z
z-estimator of
2 1
p p
2
2 2
1
1 1
2 2 1
1 1
n
) p ( p
n
) p ( p
z ) p p (
/
+
t
Analysis of Variance
One-way analysis of variance
SST =
k
j
j j
) x x ( n
1
2
SSE =
j
n
i
j ij
k
j
) x x (
1
2
1
MST =
1 k
SST
MSE =
k n
SSE
F =
MSE
MST
Two-way analysis of variance (randomized block design of experiment)
SS(Total) =
b
i
ij
k
j
) x x (
1
2
1
SST =
k
i
j
) x ] T [ x ( b
1
2
SSB =
b
i
i
) x ] B [ x ( k
1
2
SSE =
+
b
i
i j ij
k
j
) x ] B [ x ] T [ x x (
1
2
1
MST =
1 k
SST
MSB =
1 b
SSB
MSE =
1 b k n
SSE
+
F =
MSE
MST
F=
MSE
MSB
Two-factor experiment
SS(Total) =
a
i
b
j
r
k
ijk
) x x (
1 1 1
2
SS(A) =
a
i
i
) x ] A [ x ( rb
1
2
SS(B) =
b
j
j
) x ] B [ x ( ra
1
2
SS(AB) =
+
a
i
b
j
j i ij
) x ] B [ x ] A [ x ] AB [ x ( r
1 1
2
SSE =
a
i
b
j
r
k
ij ijk
) ] AB [ x x (
1 1 1
2
F =
MSE
) A ( MS
F =
MSE
) B ( MS
F =
MSE
) AB ( MS
Least Significant Difference Comparison Method
LSD =
,
_
+
j i
/
n n
MSE t
1 1
2
Tukeys multiple comparison method
g
n
MSE
) , k ( q
Chi-Squared Tests
Test statistic for all procedures
k
1 i
i
2
i i 2
e
) e f (
Simple Linear Regression
Sample slope
2
1
x
xy
s
s
b
Sample y-intercept
x b y b
1 0
Sum of squares for error
SSE =
n
i
i i
) y y (
1
2
Standard error of estimate
2
n
SSE
s
Test statistic for the slope
1
1 1
b
s
b
t
Standard error of
1
b
2
1
1
x
b
s ) n (
s
s
Coefficient of determination
2 2
2
2
y x
xy
s s
s
R
2
1
) y y (
SSE
i
Prediction interval
2
2
2 2
1
1
1
x
g
n , /
s ) n (
) x x (
n
s t y
+ + t
Confidence interval estimator of the expected value of y
2
2
2 2
1
1
x
g
n , /
s ) n (
) x x (
n
s t y
+ t
Sample coefficient of correlation
y x
xy
s s
s
r
Test statistic for testing
= 0
2
1
2
r
n
r t
Multiple Regression
Standard Error of Estimate
1
k n
SSE
s
Test statistic for
i
i
b
i i
s
b
t
Coefficient of Determination
2 2
2
2
y x
xy
s s
s
R
2
1
) y y (
SSE
i
Adjusted Coefficient of Determination
Adjusted
) n /( ) y y (
) k n /( SSE
R
i
1
1
1
2
2
Mean Square for Error
MSE = SSE/k
Mean Square for Regression
MSR = SSR/(n-k-1)
F-statistic
F = MSR/MSE
Durbin-Watson statistic
n
i
i
n
i
i i
e
) e e (
d
1
2
2
2
1
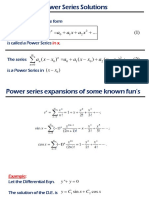
Time Series Analysis and Forecasting
Exponential smoothing
1
) 1 (
+
t t t
S w wy S
Nonparametric Statistical techniques
Wilcoxon rank sum test statistic
1
T T
E(T) =
2
1
2 1 1
) n n ( n + +
12
1
2 1 2 1
) n n ( n n
T
+ +
T
) T ( E T
z
Sign test statistic
x = number of positive differences
n .
n . x
z
5
5
Wilcoxon signed rank sum test statistic
+
T T
E(T) =
4
1) n ( n +
24
1 2 1 ) n )( n ( n
T
+ +
T
) T ( E T
z
Kruskal-Wallis Test
) n (
n
T
) n ( n
H
k
j
j
j
1 3
1
12
1
2
+
1
1
]
1
Friedman Test
) k ( b T
) k )( k ( b
F
k
j
j r
1 3
1
12
1
2
+
1
1
]
1
Spearman rank correlation coefficient
b a
ab
S
s s
s
r
Spearman Test statistic for n > 30
1 n r z
S
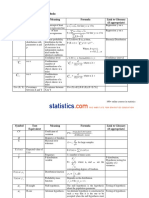
Statistical Process Control
Centerline and control limits for x chart using S
Centerline = x
Lower control limit =
n
S
x 3
Upper control limit =
n
S
x 3 +
Centerline and control limits for the p chart
Centerline =
p
Lower control limit =
n
) p ( p
p
1
3
Upper control limit =
n
) p ( p
p
+
1
3
Decision Analysis
Expected Value of perfect Information
EVPI = EPPI - EMV*
Expected Value of Sample Information
EVSI = EMV' - EMV*
You might also like
- Statistics For Management and Economics 9th Edition Gerald Keller Test Bank PDFDocument7 pagesStatistics For Management and Economics 9th Edition Gerald Keller Test Bank PDFa852314876No ratings yet
- Test Bank For Statistics For Management and Economics 11th Edition by KellerDocument9 pagesTest Bank For Statistics For Management and Economics 11th Edition by Kellera16185576650% (2)
- Index NumberDocument51 pagesIndex NumberMeer ShowkeenNo ratings yet
- Statistics For Management and Economics, 9th Edition Keller ISM PDFDocument869 pagesStatistics For Management and Economics, 9th Edition Keller ISM PDFHumaira70% (10)
- Solution Manual For Statistics For Management and Economics 10th Edition Gerald KellerDocument23 pagesSolution Manual For Statistics For Management and Economics 10th Edition Gerald KellerSrikanthBussa27% (11)
- Cost Revenue Profit FunctionDocument19 pagesCost Revenue Profit FunctionKevin Dauz Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Statistics For Management and Economics, Tenth Edition FormulasDocument11 pagesStatistics For Management and Economics, Tenth Edition Formulaskumar030290No ratings yet
- Statistics For Management and Economics, Sixth Edition: FormulasDocument15 pagesStatistics For Management and Economics, Sixth Edition: FormulasMOHAMMED FOUZANNo ratings yet
- AP Statistics Formula Sheet: B P B A PDocument2 pagesAP Statistics Formula Sheet: B P B A PRocket FireNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument5 pagesFormula Sheet伍志棠No ratings yet
- Equation SheetDocument5 pagesEquation SheetArisha BasheerNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument2 pagesFormula SheetSwarnabha RayNo ratings yet
- Formulae SheetDocument11 pagesFormulae Sheetthyanh.vuNo ratings yet
- AP Statistics Formula Sheet: (I) Descriptive Statistics (II) ProbabilityDocument2 pagesAP Statistics Formula Sheet: (I) Descriptive Statistics (II) ProbabilityKent BrouwerNo ratings yet
- Mca4020 SLM Unit 07Document22 pagesMca4020 SLM Unit 07AppTest PINo ratings yet
- 0 MathReviewDocument18 pages0 MathReviewDhananjay ChopadeNo ratings yet
- Stats FormulaDocument2 pagesStats FormulaNam TranNo ratings yet
- EGR 601 Formulas (v2)Document11 pagesEGR 601 Formulas (v2)Kawser AhmedNo ratings yet
- Econ 140 (Spring 2018) - Section 1: 1 Random Variable (RV)Document7 pagesEcon 140 (Spring 2018) - Section 1: 1 Random Variable (RV)Mashiat MutmainnahNo ratings yet
- Summary of Probability 2 1Document3 pagesSummary of Probability 2 1PeArL PiNkNo ratings yet
- S289-231formula Sheet m2Document2 pagesS289-231formula Sheet m2Sania SamiNo ratings yet
- OCR A Level Mathematics Sample Question PaperDocument40 pagesOCR A Level Mathematics Sample Question PaperANo ratings yet
- Statistics BI: Models of Random Outcomes. What Is A Model?Document22 pagesStatistics BI: Models of Random Outcomes. What Is A Model?Pedro GouvNo ratings yet
- Quadratic FormsDocument5 pagesQuadratic FormsMajety S LskshmiNo ratings yet
- Formula PDFDocument7 pagesFormula PDFPramit BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Qm Summary Final: h μ x σ σ s s σ s ρ δ dDocument13 pagesQm Summary Final: h μ x σ σ s s σ s ρ δ dJan BorowskiNo ratings yet
- Statistics FormulasDocument2 pagesStatistics FormulasJayson S. Verdeflor100% (1)
- Probability and Statistics Symbols TableDocument3 pagesProbability and Statistics Symbols TableChindieyciiEy Lebaiey CwekZrdoghNo ratings yet
- Materials SB: N) K X XDocument11 pagesMaterials SB: N) K X XNgô Hoàng Bích KhaNo ratings yet
- FormulasDocument21 pagesFormulasSamantha Marie RebolledoNo ratings yet
- Econ2280 Tutorial 1 Review Notes PDFDocument4 pagesEcon2280 Tutorial 1 Review Notes PDFKelvin ChanNo ratings yet
- Statistics SymbolsDocument7 pagesStatistics Symbolsapi-3857574100% (4)
- Statistiške Formule Za Menadžment I Ekonomiju Statistics For Management and Economics FormulasDocument12 pagesStatistiške Formule Za Menadžment I Ekonomiju Statistics For Management and Economics FormulasalNo ratings yet
- Sept 2017 - Final - With MemoDocument5 pagesSept 2017 - Final - With MemoBrian ZambeziNo ratings yet
- Fe Engineering Probability StatisticsDocument9 pagesFe Engineering Probability Statisticsvzimak2355No ratings yet
- Midterm Formula SheetDocument3 pagesMidterm Formula SheetShahd AlhamaydaNo ratings yet
- Stats Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesStats Cheat Sheetkaungwaiphyo89No ratings yet
- Expectation Value: Symbol Symbol Name Meaning / Definition ExampleDocument2 pagesExpectation Value: Symbol Symbol Name Meaning / Definition Examplerijalul fikriNo ratings yet
- Linear Transformations If Y Ax + B, Then y A X+B and SDocument2 pagesLinear Transformations If Y Ax + B, Then y A X+B and SmichaelNo ratings yet
- 03 ESCh4 Part1newDocument86 pages03 ESCh4 Part1new何謹成No ratings yet
- Open BookDocument22 pagesOpen Bookabhishekrai11111990No ratings yet
- End of Stage 1/AS Mathematics:: Mathematics A (H230, H240) Paper 2: Pure Mathematics and MechanicsDocument21 pagesEnd of Stage 1/AS Mathematics:: Mathematics A (H230, H240) Paper 2: Pure Mathematics and MechanicsrebeccaNo ratings yet
- Probability Equations: P (A B) P (A) +P (B)Document4 pagesProbability Equations: P (A B) P (A) +P (B)Mike SerafinoNo ratings yet
- Stat NotesDocument14 pagesStat NotesTreanungkur MalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7Document6 pagesLecture 7Agha Zeeshan Khan SoomroNo ratings yet
- Parameter EstimationDocument34 pagesParameter EstimationJose Leonardo Simancas GarciaNo ratings yet
- Formulario GEIDocument3 pagesFormulario GEISergio Reinoso FuertesNo ratings yet
- ECMT1020 Formulas 2021Document9 pagesECMT1020 Formulas 2021Darius ZhuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11Document33 pagesLecture 11sumaya100% (1)
- CHAPTER 2. Random Variables and Probability DistributionsDocument22 pagesCHAPTER 2. Random Variables and Probability DistributionsQuyên Nguyễn HảiNo ratings yet
- MV - Canonical Correlation (Final)Document48 pagesMV - Canonical Correlation (Final)NadiaNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2019-20 MAT2002 ETH VL2019205002983 Reference Material I 09-Mar-2020 M5 PDFDocument7 pagesWINSEM2019-20 MAT2002 ETH VL2019205002983 Reference Material I 09-Mar-2020 M5 PDFAditya KrishnaNo ratings yet
- BU255 - All Formulas 2022fallDocument9 pagesBU255 - All Formulas 2022fallTony TheodoropoulosNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10Document22 pagesLecture 10ruff ianNo ratings yet
- Types of Discrete Random VariablesDocument3 pagesTypes of Discrete Random VariablesChukwu chinelo MatildaNo ratings yet
- Statistics PacketDocument17 pagesStatistics Packetmafroosahamed73No ratings yet
- StatsymbolsDocument8 pagesStatsymbolsNiranjan KaushikNo ratings yet
- Course Reference Sheet - Revision 2Document6 pagesCourse Reference Sheet - Revision 2mattbutler1401No ratings yet
- UFP72 Formula SheetDocument1 pageUFP72 Formula SheetIrosha SharonNo ratings yet
- Función de Probabilidad F (X) Probabilidad Acumulada: Si X, y Son Independientes: E Xy E (X) E (Y)Document2 pagesFunción de Probabilidad F (X) Probabilidad Acumulada: Si X, y Son Independientes: E Xy E (X) E (Y)Jose PinedaNo ratings yet
- Ctenocephalides Felis Felis vs. Ctenocephalides Canis (Siphonaptera: Pulicidae) : Some Issues in Correctly Identify These SpeciesDocument11 pagesCtenocephalides Felis Felis vs. Ctenocephalides Canis (Siphonaptera: Pulicidae) : Some Issues in Correctly Identify These SpeciesstfnhmwnNo ratings yet
- The Final Revesion of My Paper in Wulfenia Journal PDFDocument22 pagesThe Final Revesion of My Paper in Wulfenia Journal PDFAli Abdul-RahmanNo ratings yet
- Ted Owens - Flying Saucer Intelligences SpeakDocument34 pagesTed Owens - Flying Saucer Intelligences SpeakHomers SimpsonNo ratings yet
- IELTS Speaking Study Planner For September-December - 2023Document2 pagesIELTS Speaking Study Planner For September-December - 2023Althea Zhenya Antonio Claud100% (1)
- DB Qwik Site 5Document382 pagesDB Qwik Site 5vhin_d_2005No ratings yet
- Acknowledgemt: at The Outset of This Project, I Would Like To Express My Deep Gratitude To Mr. RajnishDocument6 pagesAcknowledgemt: at The Outset of This Project, I Would Like To Express My Deep Gratitude To Mr. RajnishPraveen SehgalNo ratings yet
- Kit Insert KolesterolDocument7 pagesKit Insert KolesterolArsita SetyaniNo ratings yet
- Servo Motor Control Application On A Local Interconnect Network (LIN)Document31 pagesServo Motor Control Application On A Local Interconnect Network (LIN)Diego CadoreNo ratings yet
- Science of Getting RichDocument150 pagesScience of Getting RichTony Okpere Jr.100% (4)
- Upgrad Course Plan - FinalDocument2 pagesUpgrad Course Plan - Finalmk_valiantNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Advertising: Tutorial 3Document29 pagesIntroduction To Advertising: Tutorial 3Hung LeNo ratings yet
- Identity and Culture: The Human Condition: Rene MagritteDocument32 pagesIdentity and Culture: The Human Condition: Rene Magrittefebna80% (5)
- Robotech - TimelineDocument9 pagesRobotech - TimelineRobert BestNo ratings yet
- Interaction Diagrams Components: ObjectDocument4 pagesInteraction Diagrams Components: ObjectrekhathiyagarajanNo ratings yet
- B2 First Sample Paper 1 ListeningDocument7 pagesB2 First Sample Paper 1 ListeningLidiNo ratings yet
- CofisaDocument2 pagesCofisaTony Starks0% (1)
- P1 2012 Dec QDocument6 pagesP1 2012 Dec QBilal AliNo ratings yet
- Credit Card Customer AnalysisDocument18 pagesCredit Card Customer AnalysisBetka AbNo ratings yet
- Science of AstronomyDocument8 pagesScience of AstronomyUyên Thi Trịnh NguyênNo ratings yet
- Hardness Conversion Chart: Rockwell Rockwell Superficial Brinell Vickers ShoreDocument4 pagesHardness Conversion Chart: Rockwell Rockwell Superficial Brinell Vickers ShoreedwardpranantaNo ratings yet
- Priyajit's Resume NewDocument3 pagesPriyajit's Resume Newamrit mohantyNo ratings yet
- Weld Simulator PDFDocument4 pagesWeld Simulator PDFAmilin HatiaraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To HAZOPDocument39 pagesIntroduction To HAZOPapi-19846338100% (1)
- Solman PDFDocument71 pagesSolman PDFdav00034No ratings yet
- Accident and Incident Analysis Based On The AccideDocument12 pagesAccident and Incident Analysis Based On The AccideAnees Balqis YunezzafrinNo ratings yet
- US National Design Policy Summit ReportDocument90 pagesUS National Design Policy Summit Reportearthtomj100% (1)
- Itl 518 Project Based Learning Template 1Document24 pagesItl 518 Project Based Learning Template 1api-431944437100% (1)
- Manual For Adjustment Inventory For: School Students (AISS)Document6 pagesManual For Adjustment Inventory For: School Students (AISS)Priyansh Patel67% (3)
- Cri AssignmentDocument23 pagesCri AssignmentNyx JawadNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Analysis For Management Ch06Document119 pagesQuantitative Analysis For Management Ch06Qonita NazhifaNo ratings yet
- Mental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)From EverandMental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)No ratings yet
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsFrom EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Build a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.From EverandBuild a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Math Workshop, Grade K: A Framework for Guided Math and Independent PracticeFrom EverandMath Workshop, Grade K: A Framework for Guided Math and Independent PracticeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Limitless Mind: Learn, Lead, and Live Without BarriersFrom EverandLimitless Mind: Learn, Lead, and Live Without BarriersRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormFrom EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Images of Mathematics Viewed Through Number, Algebra, and GeometryFrom EverandImages of Mathematics Viewed Through Number, Algebra, and GeometryNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingFrom EverandMathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Fluent in 3 Months: How Anyone at Any Age Can Learn to Speak Any Language from Anywhere in the WorldFrom EverandFluent in 3 Months: How Anyone at Any Age Can Learn to Speak Any Language from Anywhere in the WorldRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (80)
- ParaPro Assessment Preparation 2023-2024: Study Guide with 300 Practice Questions and Answers for the ETS Praxis Test (Paraprofessional Exam Prep)From EverandParaPro Assessment Preparation 2023-2024: Study Guide with 300 Practice Questions and Answers for the ETS Praxis Test (Paraprofessional Exam Prep)No ratings yet