Professional Documents
Culture Documents
UFP72 Formula Sheet
Uploaded by
Irosha SharonCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
UFP72 Formula Sheet
Uploaded by
Irosha SharonCopyright:
Available Formats
ANC FOUNDATION YEAR MATHEMATICS
PROBABILITY & STATISTICS UNIT
REFERENCE FORMULAS
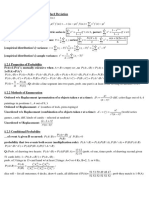
PROBABILITY
Pr ( A∪B )=Pr ( A )+Pr ( B)−Pr( A∩B ) Pr ( A∩B )=Pr ( A|B)Pr( B)
Pr( A ' )=1−Pr( A )
For a discrete random variable X with Expected value (or mean) E( X )=μ and
2
Standard deviation σ (and Variance Var( X )=σ ) :
E( X )=∑ x Pr( X =x) ; 2 2
Var ( X )=E(( X−μ ) )=E( X )−μ
2
For a binomial variable X with trial probability p, and for n trials,
Pr( X =x )=n C x p x (1− p )n−x ; E( X )=np ; Var ( X )=np(1−p )
For the Standard normal variable E( Z )=0 ; Var (Z )=1 ;
If w=−z <0 , then Pr ( Z<w )=1−Pr( Z <z ) .
For the Normal variable X, where E( X )=μ and the Standard deviation is σ , the transformed variable
X−μ x−μ
Z= z=
σ is standard; Pr ( X <x )=Pr ( Z< z ) where σ .
STATISTICS
∑x
The mean, x , of a series n observations is x=
n where ∑x is the sum of all the observations.
The sample Standard deviation is
s=
√ ∑ ( x−x )2
n−1 2
; the variance is equal to s .
n ∑ xy −∑ x ∑ y
The Pearson’s correlation coefficient r =
√ ¿¿
n= number of data pairs in the set
The least squares regression line which fits a set of bivariate data is y=mx+b where,
n ∑ xy−∑ x ∑ y
m= c=Y −m X
n ∑ x −( ∑ x )
2 2
You might also like
- Applied Statistics Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesApplied Statistics Cheat Sheetkaungwaiphyo89No ratings yet
- Formula PDFDocument7 pagesFormula PDFPramit BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Stat 5002 Final Exam Formulas W 21Document7 pagesStat 5002 Final Exam Formulas W 21PaolaCastelwhiteNo ratings yet
- Probability and Statistics Formula SheetDocument2 pagesProbability and Statistics Formula SheetBose Chan100% (1)
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Formulae SheetDocument11 pagesFormulae Sheetthyanh.vuNo ratings yet
- STATISTICS FORMULAE SHEET CHEATDocument4 pagesSTATISTICS FORMULAE SHEET CHEATWaqar MughalNo ratings yet
- Statistics FormulasDocument2 pagesStatistics FormulasJayson S. Verdeflor100% (1)
- S289-231formula Sheet m2Document2 pagesS289-231formula Sheet m2Sania SamiNo ratings yet
- Linear Transformations If Y Ax + B, Then y A X+B and SDocument2 pagesLinear Transformations If Y Ax + B, Then y A X+B and SmichaelNo ratings yet
- Probability Equations: P (A B) P (A) +P (B)Document4 pagesProbability Equations: P (A B) P (A) +P (B)Mike SerafinoNo ratings yet
- Inferential AnalysisDocument9 pagesInferential AnalysisAnkit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Probability and Statistics FormulasDocument3 pagesProbability and Statistics FormulasmichaelNo ratings yet
- STATISTICSDocument1 pageSTATISTICSCedrique PobreNo ratings yet
- Equation SheetDocument5 pagesEquation SheetArisha BasheerNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 Formula SheetDocument2 pagesQuiz 2 Formula SheetdawnNo ratings yet
- Cheat SheetDocument7 pagesCheat SheetChristos StiapisNo ratings yet
- SummaryDocument3 pagesSummaryKHÁNH NGÔ ĐÌNH BẢONo ratings yet
- Stats Formula SheetDocument5 pagesStats Formula Sheetmsmithmail21No ratings yet
- π= x= μ= λ= σ σ = x= P (0 z) = a= b= N= n= μ s= df= P (0 t) =: SymbolsDocument11 pagesπ= x= μ= λ= σ σ = x= P (0 z) = a= b= N= n= μ s= df= P (0 t) =: SymbolsDiva Tertia AlmiraNo ratings yet
- Materials SB: N) K X XDocument11 pagesMaterials SB: N) K X XNgô Hoàng Bích KhaNo ratings yet
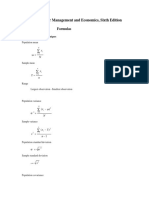
- Statistics For Management and Economics, Sixth Edition: FormulasDocument15 pagesStatistics For Management and Economics, Sixth Edition: FormulasMOHAMMED FOUZANNo ratings yet
- IB Internal Assessment FormulasDocument1 pageIB Internal Assessment Formulaselopezsierra937No ratings yet
- Calculating variance and standard deviation using subscripts and superscriptsDocument1 pageCalculating variance and standard deviation using subscripts and superscriptsAlexandra Mae AmssNo ratings yet
- MAT361 Formulae 3Document2 pagesMAT361 Formulae 3Fatin DewanNo ratings yet
- Formulae-posterDocument2 pagesFormulae-posterhemishab2007No ratings yet
- Función de Probabilidad F (X) Probabilidad Acumulada: Si X, y Son Independientes: E Xy E (X) E (Y)Document2 pagesFunción de Probabilidad F (X) Probabilidad Acumulada: Si X, y Son Independientes: E Xy E (X) E (Y)Jose PinedaNo ratings yet
- Formulas For The Final ExamDocument3 pagesFormulas For The Final ExamTrisha Faith AlberNo ratings yet
- Introductory Statistics Formulas and TablesDocument10 pagesIntroductory Statistics Formulas and TablesP KaurNo ratings yet
- Course Reference Sheet - Revision 2Document6 pagesCourse Reference Sheet - Revision 2mattbutler1401No ratings yet
- Open Formula For Probability Distribution 1Document3 pagesOpen Formula For Probability Distribution 1Atiwag, Micha T.No ratings yet
- Statistics Revision Sheet SummaryDocument9 pagesStatistics Revision Sheet SummaryZira GreyNo ratings yet
- Summary of Probability 2 1Document3 pagesSummary of Probability 2 1PeArL PiNkNo ratings yet
- Stat NotesDocument14 pagesStat NotesTreanungkur MalNo ratings yet
- BQQ6214 STATISTICAL FORMULAE (1)Document3 pagesBQQ6214 STATISTICAL FORMULAE (1)Robert OoNo ratings yet
- BU255 - All Formulas 2022fallDocument9 pagesBU255 - All Formulas 2022fallTony TheodoropoulosNo ratings yet
- MA 207 TSC Power Series and Legendre PolynomialsDocument38 pagesMA 207 TSC Power Series and Legendre PolynomialsAnonymous SomeoneNo ratings yet
- mcd1110 Sample Test 2b 2012 02Document19 pagesmcd1110 Sample Test 2b 2012 02dharma alexanderNo ratings yet
- 1 Statistical Project: 2.1 1 Qualitative VariableDocument8 pages1 Statistical Project: 2.1 1 Qualitative VariablehelinNo ratings yet
- Generalized Linear Models: FX Axb C DX Axb C DXDocument11 pagesGeneralized Linear Models: FX Axb C DX Axb C DXAishat OmotolaNo ratings yet
- L4 Normal Z VariableDocument29 pagesL4 Normal Z VariableVishal KumarNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument2 pagesFormula SheetSwarnabha RayNo ratings yet
- B 2 Stochasticprocesses 2020Document5 pagesB 2 Stochasticprocesses 2020ARISINA BANERJEENo ratings yet
- Lecture 24Document9 pagesLecture 24Kenya LevyNo ratings yet
- Statistics For Management and Economics, Tenth Edition FormulasDocument11 pagesStatistics For Management and Economics, Tenth Edition Formulaskumar030290No ratings yet
- BDM 2 DocumentDocument2 pagesBDM 2 DocumentMốc MyNo ratings yet
- Notes On P-Adic NumberDocument13 pagesNotes On P-Adic NumberdmtriNo ratings yet
- Variance and Standard Deviation Math 217 Probability and StatisticsDocument3 pagesVariance and Standard Deviation Math 217 Probability and StatisticsThầy Trung Cấp TốcNo ratings yet
- 094f25423f6ce2621022dce1c913be4c_formulasheetforfinalDocument3 pages094f25423f6ce2621022dce1c913be4c_formulasheetforfinalRak ADURNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12Document7 pagesLecture 12Dane SinclairNo ratings yet
- STAT2011 2017 Exam Formulae PDFDocument3 pagesSTAT2011 2017 Exam Formulae PDFeccentricftw4No ratings yet
- Ap23 FRQ Statistics - Pdf#page 16Document25 pagesAp23 FRQ Statistics - Pdf#page 16malvin.fedyanoNo ratings yet
- Normal DistributionDocument15 pagesNormal DistributionMarcLorenz OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Son2Document6 pagesSon2PUSHPA SAININo ratings yet
- AMA1110 Exercise - 9Document9 pagesAMA1110 Exercise - 9Brian LiNo ratings yet
- Probability Theory Notes Chapter 3 VaradhanDocument50 pagesProbability Theory Notes Chapter 3 VaradhanJimmyNo ratings yet
- 2 Gaussian Process PDFDocument55 pages2 Gaussian Process PDFนนฐ์ทกร บุญรักชาติNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument5 pagesFormula Sheet伍志棠No ratings yet
- Z and T Table With FormulasDocument2 pagesZ and T Table With FormulasJaspher Oyel BautistaNo ratings yet
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)From EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)No ratings yet
- Course Schedule - Sem Iii 2022Document1 pageCourse Schedule - Sem Iii 2022Irosha SharonNo ratings yet
- 15th JulyDocument8 pages15th JulyIrosha SharonNo ratings yet
- GMA Beggars Sep 2013 OriginalarticleDocument6 pagesGMA Beggars Sep 2013 OriginalarticleIrosha SharonNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document3 pagesTutorial 2Irosha SharonNo ratings yet
- FinancialRatioAnalysis KelaniCablesPLCVsACLPLC 2015to2019Document21 pagesFinancialRatioAnalysis KelaniCablesPLCVsACLPLC 2015to2019Irosha SharonNo ratings yet
- Globalization's impact on culture, trade and inequalityDocument2 pagesGlobalization's impact on culture, trade and inequalityIrosha SharonNo ratings yet
- Probability Distributions Lecture Note 4Document6 pagesProbability Distributions Lecture Note 4Irosha SharonNo ratings yet
- Why Sri Lankans overlook health and safetyDocument32 pagesWhy Sri Lankans overlook health and safetyIrosha SharonNo ratings yet
- WritingDocument1 pageWritingIrosha SharonNo ratings yet
- IB English The Kite Runner Full TextDocument374 pagesIB English The Kite Runner Full TextLE0% (3)
- Paraphrasing TestDocument1 pageParaphrasing TestIrosha SharonNo ratings yet
- Probability Distributions Lecture Note 3Document5 pagesProbability Distributions Lecture Note 3Irosha SharonNo ratings yet
- Gattaca by Andrew M. Niccol: This Screenplay Has Been Converted To A PDF File by Screentalk™Document122 pagesGattaca by Andrew M. Niccol: This Screenplay Has Been Converted To A PDF File by Screentalk™jbx225No ratings yet
- Probability Distributions Lecture Note 5Document5 pagesProbability Distributions Lecture Note 5Irosha SharonNo ratings yet
- Document 3Document4 pagesDocument 3Irosha SharonNo ratings yet
- Current State of Competitive ValorantDocument9 pagesCurrent State of Competitive ValorantIrosha SharonNo ratings yet
- Non-Biomedical Consent Form TemplateDocument14 pagesNon-Biomedical Consent Form TemplateIrosha SharonNo ratings yet
- Template Information and Consent Letter 2018Document5 pagesTemplate Information and Consent Letter 2018Irosha SharonNo ratings yet
- Second DraftDocument1 pageSecond DraftIrosha SharonNo ratings yet