Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Topical Test 1: Introduction To Physics
Uploaded by
etaawieOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Topical Test 1: Introduction To Physics
Uploaded by
etaawieCopyright:
Available Formats
55/2
NAMA: ______________________________________________
TINGKATAN: ______________
TOPICAL TEST 1: INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICS
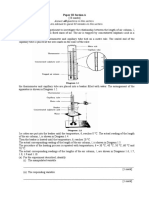
Diagram 1 shows a vernier calipers used to measure external diameter of a water pipe.
Diagram 1 (a) (i) Name the part labelled P. [1 mark] (ii) What is the function of P? [1 mark] (b) (i) Write down the reading, in cm, for the diameter of the water pipe. [1 mark] (ii) Why is the external diameter measured at different positions?
[1 mark] (c) State one advantage of using a callipers compared with using a ruler in millimeters for making this measurement. [1 mark] 2 Physics quantities Type of quantity Velocity Density Momentum Electric charge Force Unit SI
Table 1 Complete the Table 1 by writing down the type of quantity and the corresponding S.I. units in the spaces provided.
55/2
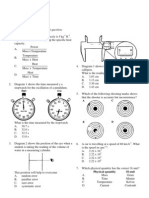
[5 marks] Diagram 2.1 shows the meniscus of water in a measuring cylinder. X, Y and Z are three eye positions while measuring the volume of the water.
(a)
Diagram 2.1 (i) Which positions of the eye is correct while taking the reading of the volume of water? [1 mark] (ii) Give one reason for the answer in (a)(i). [1 mark]
(b) The water in the measuring cylinder is replaced with 20 cm3 of mercury. (i) In Diagram 2.2, draw the meniscus of the mercury in the measuring cylinder.
Diagram 2.2 [1 mark] (ii) Explain what causes the shape of the meniscus of mercury you have drawn in (d)(i). __________________________________________________________________________ [1 mark]
Diagram 3.1
Diagram 3.2
55/2
Diagram 3.1 shows a micrometer screw gauge with a zero error. Ahmad determines the thickness of a piece of paper using the following method. 50 pieces of the papers are placed between anvil and spindle of the micrometer screw gauge. The spindle is moved closer to anvil by rotating ratchet until a tick sound is heard and the reading of micrometer screw gauge is shown in Diagram 3.2.
(a) What is the zero reading of the micrometer screw gauge? [1 mark] (b) What is the actual thickness of 50 pieces of the papers?
[1 mark] (c) Calculate the thickness of one piece of the paper.
[1 mark] (d) While taking measurement, Ahmad is advised to rotate the rachet but not the thimble. Why? [1 mark]
Section B
5 Diagram 4.1 and 4.2 shows a vernier calipers and a micrometer screw gauge used to measure the diameter of a glass rod.
Diagram 4.1
55/2
Diagram 4.2
(a)
(i) What is meant by accuracy of a measurement? [1 mark / 1 markah] (ii) With reference to Diagram 4.1 and Diagram 4.2, compare the diameter readings taken and scales in both measuring instruments. Relate the diameter readings with the scale used to make a deduction regarding the relation between the sensitivity and accuracy.
[5 marks] (b) Explain why a zero error affects the accuracy and sensitivity of a measuring instrument. [4 marks] (c) (i) State two differences between random error and systematic error. [2 marks] (d) In an archery competition, a participant aims at the bulls eye of a target. Each participant is allowed to have five trials. Complete the spaces below to represent the type of shots distribution after the arrows hit at the target. (i) A distribution which is accurate and consistent.
55/2
(ii)A distribution which is not accurate and not consistent.
(iii) A distribution which is not accurate but consistent.
(iv) A distribution which is accurate but not consistent.
[8 marks]
55/2
Section A PAPER 3
1.
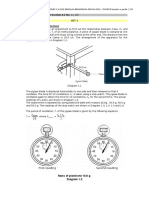
A student carries out an experiment to determine relative density, R of a liquid P. The apparatus set-up for this experiment is shown in Diagram 1.1.
Diagram 1.1 The student starts the experiment by placing a total slotted mass of m = 60 g which is attached to one end of the spring. The scale reading, h on the half-meter rule is recorded with the aid of the pin. The experiment is repeated with total mass of 80 g, 100 g, 120 g, 140 g and 160 g. The corresponding scale readings are shown in Diagrams 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 1.5, 1.6 and 1.7. Slotted masses with hanger are removed and replaced by an object, Q attached to the spring. The scale reading, h0 = 15.6 cm is recorded.
(a) For the experiment described, identify:
55/2
(i) The manipulated variable [1 mark] (ii) The responding variable [1 mark] (iii) The constant variable [1 mark] (b) (i) Record the readings, h, of the spring in Diagram 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 1.5, 1.6 and 1.7. [2 marks] (ii) Tabulate your results for all values of m and h in the space below.
[2 marks] (c) On the graph paper , plot a graph of h against m. [5 mark]
(d) Based on your graph in 1(c), state the relationship between h and m.
[1 mark]
You might also like
- 1 A Student Carries Out An Experiment To Investigate The Relationship Between Current andDocument5 pages1 A Student Carries Out An Experiment To Investigate The Relationship Between Current andneoo1No ratings yet
- PAPER 3 f5Document12 pagesPAPER 3 f5Norhafizah JaharudinNo ratings yet
- Paper IIIDocument4 pagesPaper IIIyokecheng20003826No ratings yet
- 4531/1 Nama Fizik Kertas 1 Solaf 2011 TingkatanDocument14 pages4531/1 Nama Fizik Kertas 1 Solaf 2011 TingkatanMrs PoovanNo ratings yet
- 0625 w15 QP 62Document16 pages0625 w15 QP 62Leen AbbasNo ratings yet
- Paper 6 (62) PracticeDocument24 pagesPaper 6 (62) PracticeninabalisurfNo ratings yet
- Atp Physics Paper ViDocument8 pagesAtp Physics Paper ViYashodhaNo ratings yet
- Section A: F4 Physics/Introduction of physics/JLYC/2016Document3 pagesSection A: F4 Physics/Introduction of physics/JLYC/2016Jarnice Ling Yee ChingNo ratings yet
- All Markers Paper 1Document82 pagesAll Markers Paper 1Muhtasim Ibne kamalNo ratings yet
- QST Paper FormatDocument6 pagesQST Paper FormatboltuNo ratings yet
- Physics Paper 2Document13 pagesPhysics Paper 2Adam K C Tiong100% (1)
- F5 Phy Mid-Year Exam 2013 p3Document8 pagesF5 Phy Mid-Year Exam 2013 p3Fillipmilk YapNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/52Document12 pagesCambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/52Susan GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Combined Science 0653/61Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Combined Science 0653/61septina restuNo ratings yet
- F4 Physics Chapter 1 AssessmentDocument7 pagesF4 Physics Chapter 1 AssessmentShrivibbilan SentilkumarNo ratings yet
- Binder 2Document79 pagesBinder 2oscholten06No ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/62Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/62Desire KandawasvikaNo ratings yet
- Physics P6 Mock QP 2016 O-NDocument10 pagesPhysics P6 Mock QP 2016 O-Nda_reaper_dasNo ratings yet
- 702 02 SPDocument12 pages702 02 SPHerman HermanNo ratings yet
- X A-Plus Module SBP Physics 2013 - 2Document15 pagesX A-Plus Module SBP Physics 2013 - 2Siti Arbaiyah AhmadNo ratings yet
- Name School Name Class/Section: Physics October 2015Document12 pagesName School Name Class/Section: Physics October 2015Michael LeungNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument12 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationHany ElGezawyNo ratings yet
- SL Paper3Document14 pagesSL Paper3MilsonNo ratings yet
- Trial Kedah SPM 2013 FIZIK SKEMA K3 SET ADocument0 pagesTrial Kedah SPM 2013 FIZIK SKEMA K3 SET ACikgu FaizalNo ratings yet
- HydrometerDocument13 pagesHydrometerShubhrajit MaitraNo ratings yet
- Zero Error Weighing Machine StructureDocument4 pagesZero Error Weighing Machine StructureRaymond Cheang Chee-CheongNo ratings yet
- Form 4 - Physics ExercisesDocument9 pagesForm 4 - Physics Exercisesnik mohamad solehin100% (3)
- University of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument12 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationHaider AliNo ratings yet
- SOP-Procedure Calibration of Metal TapesDocument12 pagesSOP-Procedure Calibration of Metal Tapeshaharamesh100% (1)
- Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/62Document12 pagesCambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/62AdilNo ratings yet
- Phy 119 - 2020 - 2021 - Exam - ADocument4 pagesPhy 119 - 2020 - 2021 - Exam - AomaNo ratings yet
- 9702 Physics Advanced Practical Skills 1 Paper 03 Visually ImpairedDocument24 pages9702 Physics Advanced Practical Skills 1 Paper 03 Visually Impairedazharphysics13No ratings yet
- P32004 QuestionDocument9 pagesP32004 Questionzarinah22No ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/52Document12 pagesCambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/52Nisha zehraNo ratings yet
- 0625 w18 QP 42 PDFDocument20 pages0625 w18 QP 42 PDFBoy AvrelNo ratings yet
- 0625 w18 QP 42Document20 pages0625 w18 QP 42NyonikaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Problem Set 2016Document5 pagesTopic 1 Problem Set 2016Aayesha TariqNo ratings yet
- Phy 3 Trial 2015Document8 pagesPhy 3 Trial 2015vyvianNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: PHYSICS 5054/41Document12 pagesCambridge O Level: PHYSICS 5054/41NomanNo ratings yet
- Confidential 4531/3 Section A: Answer All Questions in This SectionDocument10 pagesConfidential 4531/3 Section A: Answer All Questions in This SectionIedah MohdNo ratings yet
- Paper 3 March 2023Document28 pagesPaper 3 March 2023icedgoblinNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/32Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/32chitooNo ratings yet
- KOLEKSI SOALAN TRIAL FIZIK SPM 2015 WordDocument542 pagesKOLEKSI SOALAN TRIAL FIZIK SPM 2015 WordNadia Saidon100% (1)
- Question Paper 3 (Topic 4 - Heat P3)Document15 pagesQuestion Paper 3 (Topic 4 - Heat P3)Nur Syidah100% (1)
- SL Paper2Document26 pagesSL Paper2aftabNo ratings yet
- PMPH130 Labs - 2024Document15 pagesPMPH130 Labs - 2024DAVIES TEMBONo ratings yet
- Physics A: Unit 2: Approved Specimen Question PaperDocument13 pagesPhysics A: Unit 2: Approved Specimen Question PaperCka DohaNo ratings yet
- Paper 3. Worksheet: (25 Marks)Document4 pagesPaper 3. Worksheet: (25 Marks)LINA FERNANDA GARCÍA MARTÍNEZ-Egresado 2021No ratings yet
- Trial SPM Paper 3Document14 pagesTrial SPM Paper 3dchana87No ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/52Document12 pagesCambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/52arif asgarNo ratings yet
- 5054 s16 QP 22 PDFDocument16 pages5054 s16 QP 22 PDFAhmediqraNo ratings yet
- Lab1 SampleDocument20 pagesLab1 SampleLee MingHweeNo ratings yet
- Exp 1Document7 pagesExp 1Hafiz SallehNo ratings yet
- A Student Determines The Mass MG of A Metre Ruler by A Balancing MethodDocument12 pagesA Student Determines The Mass MG of A Metre Ruler by A Balancing Methodwesjanet189No ratings yet
- Paper 6 0625 Physics October November 2018 Solved V 62Document11 pagesPaper 6 0625 Physics October November 2018 Solved V 62KoniNo ratings yet
- Introducing Measurements in The LaboratoryDocument4 pagesIntroducing Measurements in The LaboratoryKristel Aira SacedaNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Measurement Techniques-Cie Ial Physics-Theory Qp-UnlockedDocument20 pages2.2 Measurement Techniques-Cie Ial Physics-Theory Qp-Unlockedmaze.putumaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: PHYSICS 5054/42Document12 pagesCambridge O Level: PHYSICS 5054/42Abdul Rehman NaveedNo ratings yet