Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Connector: Basic Parts Bin
Uploaded by
porepreeOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Connector: Basic Parts Bin
Uploaded by
porepreeCopyright:
Available Formats
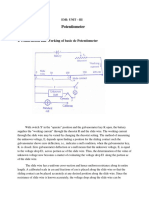
BASIC PARTS BIN Connector The round dot in the Basic parts bin is a connector.
Use it to join wires in a circuit. A connector has four terminals, one on each side. It can join up to four wires. Connectors are created automatically when you stretch a wire so that it touches another wire. Connector behaviour is affected by the settings in the iring tab of the Circuit!"chematic #ptions dialog bo$. %esistor A resistor&s resistance is measured in ohms. It can have any value from ' to ( '. The %esistance, %, of a resistor instance is calculated using the following e)uation* % + %o , - . / TC.,0T 1 To2 / TC3,40T1To2536 7 The resistor is ideal, with the temperature co1efficient set to 8ero. To include resistors in the Temperature Analysis, set the temperature co1efficients TC. and TC3 in the resistor properties dialog bo$. Capacitor A capacitor stores electric energy in the form of an electrostatic field. It affects AC relative to capacitance and fre)uency and 9C depending on capacitance alone. Its capacitance, measured in farads, can be any value from p: to :. Inductor An inductor stores energy in an magnetic field created by changes in current flowing through it. Its ability to oppose a change in current flow is called inductance 0;2, which is measured in henrys. It can have any value from <= to =. Transformer Transformers are one of the most common and useful applications of inductance. They can step up or step down an input primary voltage 0>.2 to a secondary voltage 0>32. The relationship is given by >.!>3 + n, where n is the ratio of the primary turns to the secondary turns. The parameter n can be adjusted by editing the transformer&s model. %elay The magnetic relay is a coil with a specified inductance 0;c, in henries2 that causes a contact to open or close when a specified current 0Ion, in A2 charges it. The contact remains in the same position until the current falls below the holding value 0Ihd, in A2, at which point it returns to its original position. "witch The single1pole, double1throw switch can be closed or opened 0turned on or off2 by pressing a ?ey on the ?eyboard. @ou specify the ?ey that controls the switch by typing its name in the >alue tab of the Circuit!Component Aroperties dialog bo$. :or e$ample, if you want the switch to close or open when the spacebar is pressed, type space in the >alue tab, then clic? #B. To use... Type... "pacebar space CDTC% CDTC% letters a to 8 the letter 0e.g. a2 numbers E to Fthe number 0e.g. .2 Time19elay "witch The time1delay switch has two values, time on 0Ton2 and time off 0Toff2. It has an infinitely high resistance at Toff 0when the switch is open2 and an infinitely low resistance at Ton 0when the switch is closed2. Ton cannot be e)ual to Toff. Both values must be greater than 8ero.
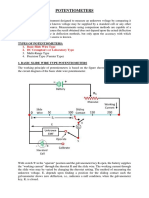
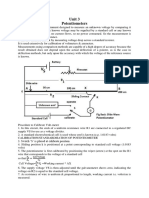
>oltage1Controlled "witch The voltage1controlled switch has two values, turn1on voltage 0>on2 and turn1off voltage 0>off2. It closes when the voltage across the controlling terminals is e)ual to or greater than the parameter >on. It opens when the voltage is e)ual to or less than >off. >oltage1controlled switches can be used to model digital gates. Current1Controlled "witch The current1controlled switch is similar to the voltage1controlled switch. hen the current through the controlling terminals is e)ual to Ion, the switch closes. hen the current e)uals Ioff, the switch opens. This switch can be used to model digital gates. Aull1Up %esistor The pull1up resistor has one end connected to >cc. The other end is connected to a point in a logic circuit that needs to be raised to a voltage level closer to >cc. Aotentiometer A potentiometer is much li?e a regular resistor, e$cept that you can change its resistance by adjusting its setting. In the >alue tab of the Circuit!Component Aroperties dialog bo$, you set the potentiometer&s resistance, initial setting 0as a percentage2 and increment 0as a percentage2. @ou also identify the ?ey 0GAG to GHG2 that you will use to control the setting. To decrease the potentiometer&s setting, press the identified ?ey. To increase the setting, press and hold "=I:T and press the identified ?ey. :or e$ample, say the potentiometer is set to IJK, the increment is JK and the ?ey is G%G. @ou press G%G, and the setting drops to IEK. @ou press G%G again, and it drops to LJK. @ou press "=I:T and G%G, and the setting rises to IEK. %esistor Aac? This component is a pac?age containing eight resistors, side by side. The terminals for each resistor are directly opposite each other. The values of all resistors are the same and can be set globally by dragging a resistor pac? into the circuit window, double1clic?ing it and entering the value in the >alue tab of the dialog bo$ that appears. >oltage1Controlled Analog "witch The voltage controlled switch has a function similar to that performed by a mechanical #n!#ff switch e$cept that the #n!#ff conditions are selected by a control voltage. hen the control voltage is below a selected value, the switch is off and the input and output signals are disconnected. hen the control voltage is above the selected value, the switch is on and the input and output signals are connected. In the e$ample shown below, the analog switch is used to periodically sample a sine wave input signal 0lower waveform on the display2 at intervals determined when the control signal is high, above I.F> for this model. hen the control voltage drops below I.M> the switch is turned off and the output drops to 8ero. The sampled waveform at the output is the upper waveform on the display. Inputs may be any waveshape and any 0reasonable2 values. This type of sampling is utili8ed in time division multiple$ systems. #bserve the C#DT%#; 0switching2 waveform and the output to confirm switching operation. "ampling rate may be changed by changing the fre)uency of the C;#CB generator. An e$ample of an IC performing this function is the (C.IE.N, a .I pin IC which includes four individual analog switches with individual switching control inputs.
Aolari8ed Capacitor The polari8ed capacitor must be connected with the right polarity. #therwise, an error message will appear. Its capacitance, measured in farads, can be any value from p: to :. >ariable Capacitor The variable capacitor is simulated as an open circuit with a current across the capacitor forced to 8ero by a large impedance value. >alues are set in the same way as those for the potentiometer. >ariable Inductor This component acts e$actly li?e a regular inductor, e$cept that its setting can be adjusted. The variable inductor is simulated as an open circuit with a current across the inductor forced to 8ero by a large impedance value. >alues are set in the same way as for the potentiometer. Coreless Coil This component is a conceptual model that you can use as a building bloc? to create a wide variety of inductive and magnetic circuit models. Typically, you would use the coreless coil together with the magnetic core to build up systems that moc? the behavior of linear and nonlinear magnetic components. #utput is in the form of a voltage proportional to the product of input current and number of turns, and represents the magnetomotive force 0mmf2 which is produced. The output voltage behaves li?e a magnetomotive force in a magnetic circuit, that is, when the coreless coil is connected to the magnetic core or some other resistive device, a current flows. (agnetic Core This component is a conceptual model that you can use as a building bloc? to create a wide variety of inductive and magnetic circuit models. It may be used in a wide variety of linear and non1linear magnetic component designs. Typically, you would use the magnetic core together with the coreless coil to build up systems that moc? the behavior of linear and nonlinear magnetic components. The two magnetic modeling components are combined in the nonlinear transformer. It ta?es as input a voltage which it treats as a magnetomotive force 0mmf2 value. This input voltage, in many cases, would be obtained from the coreless coil. Donlinear Transformer This component is based on a general model that can be customi8ed for different applications. It is implemented using a magnetic core and coreless coil as building bloc?s, together with resistors and inductors. Using this transformer, you can model physical effects such as nonlinear magnetic saturation, primary and secondary winding losses, primary and secondary lea?age inductances, and core geometric si8e.
You might also like
- Electronic Circuit Symbols: Power Supplies Component Circuit Symbol Function of ComponentDocument8 pagesElectronic Circuit Symbols: Power Supplies Component Circuit Symbol Function of ComponentImran AhmedNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Ac Voltage ControllerDocument7 pagesResearch Paper On Ac Voltage Controlleraflbojhoa100% (1)
- Nouveau Document Microsoft WordDocument7 pagesNouveau Document Microsoft WordAbdelkarim MessaoudiNo ratings yet
- Potentiometers: Nstrument Ransformers ANDDocument26 pagesPotentiometers: Nstrument Ransformers ANDDIVYA PRASOONA CNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics LabDocument6 pagesPower Electronics LabRafeyNo ratings yet
- Modified Space Vector Modulated Z Source Inverter With Effective DC Boost and Lowest Switching StressDocument8 pagesModified Space Vector Modulated Z Source Inverter With Effective DC Boost and Lowest Switching StressMounika DivyaNo ratings yet
- Car Battery MonitorDocument39 pagesCar Battery MonitorroopavennelaNo ratings yet
- Logarithmic and Antilogarithmic AmplifierDocument6 pagesLogarithmic and Antilogarithmic AmplifierSamuel Eduardo Toro GómezNo ratings yet
- ELEC3105 Lab4Document10 pagesELEC3105 Lab4James AllenNo ratings yet
- UNIT IV Part 1 PotentometersDocument12 pagesUNIT IV Part 1 PotentometersmahiNo ratings yet
- Potentiometer: 1. Construction and Working of Basic DC PotentiometerDocument11 pagesPotentiometer: 1. Construction and Working of Basic DC PotentiometerKumar SanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 10Document25 pagesLesson 10Mohammad KhazaalNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6 Electronic SwitchingDocument18 pagesExperiment 6 Electronic SwitchingrekcahNo ratings yet
- EE 215 - Laboratory 4 - First Order Circuits: AuthorsDocument6 pagesEE 215 - Laboratory 4 - First Order Circuits: AuthorsÁo ĐenNo ratings yet
- 2 038 PDFDocument11 pages2 038 PDFAmit GauravNo ratings yet
- Basic Switching CircuitsDocument19 pagesBasic Switching Circuitsash1968No ratings yet
- Q 7) Explain The Basic Principle of Control in HVDCTDocument12 pagesQ 7) Explain The Basic Principle of Control in HVDCTrasashpujNo ratings yet
- Text: Power Electronics by Daniel W. Hart Mcgraw HillDocument34 pagesText: Power Electronics by Daniel W. Hart Mcgraw HillWilliam LowNo ratings yet
- EE215 Lab 4Document6 pagesEE215 Lab 4vhiep195No ratings yet
- Conv DC-DC Paper ENglishDocument5 pagesConv DC-DC Paper ENglishpepe890305No ratings yet
- 555 Timer IC: The Important Features of The 555 Timer AreDocument5 pages555 Timer IC: The Important Features of The 555 Timer AreChara GalaNo ratings yet
- BuzzerDocument5 pagesBuzzerHehe_09No ratings yet
- Question BankDocument11 pagesQuestion BankRohini MukunthanNo ratings yet
- Series and Parallel CircuitsDocument7 pagesSeries and Parallel Circuitsyzavelita100% (1)
- Cable Fault DetectorDocument25 pagesCable Fault DetectorHarshalNo ratings yet
- Voltage DividerDocument11 pagesVoltage DividerLorshiel Anne TusingNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Introduction of Solid State Relays: Phase and Amplitude Comparators: Amplitude ComparatorsDocument3 pagesUnit 5 - Introduction of Solid State Relays: Phase and Amplitude Comparators: Amplitude ComparatorsShubham KhandareNo ratings yet
- PotentiometersDocument23 pagesPotentiometersbhaskaratarun239bNo ratings yet
- SE/NE 555 Timer. It Is Basically A Monolithic Timing Circuit That Produces Accurate and Highly Stable Time Delays orDocument12 pagesSE/NE 555 Timer. It Is Basically A Monolithic Timing Circuit That Produces Accurate and Highly Stable Time Delays orEFraim Manzano FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Ic Voltage RegulatorsDocument11 pagesIc Voltage RegulatorsshreyashNo ratings yet
- 23 Seriesand Parallel CircDocument7 pages23 Seriesand Parallel CircAshley O'Neal50% (2)
- Fire Detection and ControlDocument16 pagesFire Detection and ControlvaisnanyNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument87 pagesLab ManualSrividya KondaguntaNo ratings yet
- Power System Lab-IIDocument14 pagesPower System Lab-IIharshadeepmukherjee529No ratings yet
- XK3101 (KM05) User ManualDocument17 pagesXK3101 (KM05) User ManualmanhNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation Lab ManualDocument14 pagesInstrumentation Lab ManualAmulyaNo ratings yet
- INVERSOR 10 KVA UNIDADE OPERATIVA GUIA - Hgi10k PDFDocument8 pagesINVERSOR 10 KVA UNIDADE OPERATIVA GUIA - Hgi10k PDFNelson Leitao RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Inductance and Capacitance Meter Adapter Using 74HC132Document6 pagesInductance and Capacitance Meter Adapter Using 74HC132Miguelangel Bravo MigoneNo ratings yet
- LAB No: 10: To Build and Analyze DC/DC Buck ConverterDocument10 pagesLAB No: 10: To Build and Analyze DC/DC Buck ConverterManahil AshrafNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronics Measurement 4th Sem B.Tech.Document41 pagesElectrical and Electronics Measurement 4th Sem B.Tech.Saksham KumarNo ratings yet
- Report - Automatic Power Factor Improvement Using ArduinoDocument27 pagesReport - Automatic Power Factor Improvement Using ArduinoLynn LucyNo ratings yet
- Load Inverter Solar Panel: Chapter ThreeDocument13 pagesLoad Inverter Solar Panel: Chapter ThreeMakesh MäKzNo ratings yet
- Testing of Continuity in Switches and LoadDocument7 pagesTesting of Continuity in Switches and LoadVikas UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Voltage Comparator Information and CircuitsDocument10 pagesVoltage Comparator Information and CircuitsmstgofcoNo ratings yet
- Potentiometers: DefinitionDocument4 pagesPotentiometers: DefinitionjayNo ratings yet
- Lampemetre 2Document12 pagesLampemetre 2trkonjic100% (1)
- Unit 2-3Document38 pagesUnit 2-3vidhya sNo ratings yet
- Lect 4Document37 pagesLect 4eba yohannesNo ratings yet
- Lecture 27: Uni-Directional Current Control With BjtsDocument3 pagesLecture 27: Uni-Directional Current Control With BjtsHuzaifa RehanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 27: Uni-Directional Current Control With BjtsDocument3 pagesLecture 27: Uni-Directional Current Control With BjtsHuzaifa RehanNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document6 pagesUnit 3dhub324No ratings yet
- What Is The Power ElectronicsDocument16 pagesWhat Is The Power ElectronicsashammoudaNo ratings yet
- Comparison and Simulation of Full Bridge and LCL-T Buck DC-DC Converter SystemsDocument5 pagesComparison and Simulation of Full Bridge and LCL-T Buck DC-DC Converter SystemsKrishnaveni Subramani SNo ratings yet
- Analog To Digital Converter and Vise VersDocument7 pagesAnalog To Digital Converter and Vise VersSpyx MeniNo ratings yet
- Temperature Control Utilizing SSRDocument2 pagesTemperature Control Utilizing SSRAtakan OzturKNo ratings yet
- Intelligent Fire Detector With Automatic Water Sprinkler System To Avoid Fire AccidentsDocument11 pagesIntelligent Fire Detector With Automatic Water Sprinkler System To Avoid Fire Accidentssk THOUFIQNo ratings yet
- Switched Inductor Z-Source Matrix Converter Operation and AnalysisDocument9 pagesSwitched Inductor Z-Source Matrix Converter Operation and AnalysisA'Platinum EngNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 16052020 045213pm 19062023 052331pmDocument49 pagesChapter 6 16052020 045213pm 19062023 052331pmAbdullah ZamirNo ratings yet
- Pparatus and Material RequiredDocument4 pagesPparatus and Material RequiredANAND TALARINo ratings yet
- Digital Techniques Handout 4 - RevDocument1 pageDigital Techniques Handout 4 - RevporepreeNo ratings yet
- Digital Techniques Handouts 1-3Document1 pageDigital Techniques Handouts 1-3porepreeNo ratings yet
- Advanced Communication Systems 1: Technological University of The Philippines-Visayas City of Talisay, Negros OccidentalDocument1 pageAdvanced Communication Systems 1: Technological University of The Philippines-Visayas City of Talisay, Negros OccidentalporepreeNo ratings yet
- List of Mobile Number PrefixesDocument3 pagesList of Mobile Number PrefixesporepreeNo ratings yet
- List of Mobile Number PrefixesDocument3 pagesList of Mobile Number PrefixesporepreeNo ratings yet
- Manual FW230 PDFDocument16 pagesManual FW230 PDFaze20100% (1)
- ST2001HI: High Voltage Fast-Switching NPN Power TransistorDocument6 pagesST2001HI: High Voltage Fast-Switching NPN Power TransistorGilbertoAdonayGutierrez100% (1)
- Tcet1100 TDK FerriteDocument9 pagesTcet1100 TDK FerriteRyn YahuFNo ratings yet
- Communications Past Board April 2005 With AnswersDocument8 pagesCommunications Past Board April 2005 With Answersjun dee100% (2)
- Rfid Security SystemDocument22 pagesRfid Security SystemAnkita ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- XR7 Driving LightDocument1 pageXR7 Driving LightPurple IndustriesNo ratings yet
- HM628128D Series: 1 M SRAM (128-Kword 8-Bit)Document20 pagesHM628128D Series: 1 M SRAM (128-Kword 8-Bit)Roni SocompiNo ratings yet
- Littelfuse TVS Diode TPSMA6L Datasheet PDFDocument6 pagesLittelfuse TVS Diode TPSMA6L Datasheet PDFsnobic9379No ratings yet
- Altivar 66 ATV66 User Installation ManualDocument120 pagesAltivar 66 ATV66 User Installation ManualAndi PermanaNo ratings yet
- Adruino RF Module XboxDocument6 pagesAdruino RF Module Xboxspdlcr5No ratings yet
- SCR100 Charger Installation & Operating Instructions, 2002-09-02Document38 pagesSCR100 Charger Installation & Operating Instructions, 2002-09-02priyanka236No ratings yet
- Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design PerspectiveDocument78 pagesDigital Integrated Circuits: A Design PerspectiveGayathriRajiNo ratings yet
- Hall Effect and Measurement of Hall CoefficientDocument15 pagesHall Effect and Measurement of Hall CoefficientHarsh Purwar83% (18)
- Fourier Series Are Helpful Tools For Analyzing Electronic Circuits.Document14 pagesFourier Series Are Helpful Tools For Analyzing Electronic Circuits.hamza abdo mohamoudNo ratings yet
- HD 74 Ls 10 PDocument6 pagesHD 74 Ls 10 PalexarotNo ratings yet
- ECE SolutionsDocument14 pagesECE SolutionsLaura CarsonNo ratings yet
- Index Profile Measurements of Fibers andDocument34 pagesIndex Profile Measurements of Fibers andArchana AgrawalNo ratings yet
- EC2402 - OCN Two Marks Questions and AnswersDocument37 pagesEC2402 - OCN Two Marks Questions and AnswersshanmugachitraNo ratings yet
- Embedded Systems: Bhushan. H. DDocument17 pagesEmbedded Systems: Bhushan. H. DBhushan H DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Csla 2 ElDocument5 pagesCsla 2 ElPedro CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- Joule ThiefDocument1 pageJoule ThiefLeonardo SeadiNo ratings yet
- Class Xii Chemistry Question Banks Solid StateDocument2 pagesClass Xii Chemistry Question Banks Solid StateKrishan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Resistance ExerciseDocument2 pagesResistance ExerciseD7ooM 612100% (1)
- HW 1Document5 pagesHW 1BrimwoodboyNo ratings yet
- Programmable Unijunction TransistorDocument2 pagesProgrammable Unijunction TransistorBaquiran John Paul Baquiran100% (1)
- Em Project SquidDocument31 pagesEm Project SquidOng Yern Yee100% (1)
- Full Bridge ConverterDocument7 pagesFull Bridge ConverterPalinda AttanayakeNo ratings yet
- Bike Turning SignalDocument9 pagesBike Turning SignalZorez ShabkhezNo ratings yet
- The Role of Fuse in Low Voltage SystemsDocument5 pagesThe Role of Fuse in Low Voltage Systemsjob_pNo ratings yet