Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Brand Name: Bactrim Generic Name: Sulfamethoxazole, Trimethoprim, Co-Trimoxazole Drug Classification
Uploaded by
ianecunar100%(2)100% found this document useful (2 votes)
3K views2 pagesBactrim is an antibiotic used to treat various respiratory, renal, and gastrointestinal infections like pneumonia, osteomyelitis, and toxoplasmosis. It works by inhibiting bacterial folic acid synthesis. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, rashes, and hematological issues. It should not be used in pregnancy or by those with liver or kidney impairment. Nurses should monitor patients for signs of infection, obtain cultures prior to use, inspect IV sites, and check blood work periodically during treatment.
Original Description:
Original Title
Brand Name: Bactrim Generic Name: Sulfamethoxazole, Trimethoprim, Co-Trimoxazole Drug Classification:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentBactrim is an antibiotic used to treat various respiratory, renal, and gastrointestinal infections like pneumonia, osteomyelitis, and toxoplasmosis. It works by inhibiting bacterial folic acid synthesis. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, rashes, and hematological issues. It should not be used in pregnancy or by those with liver or kidney impairment. Nurses should monitor patients for signs of infection, obtain cultures prior to use, inspect IV sites, and check blood work periodically during treatment.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(2)100% found this document useful (2 votes)
3K views2 pagesBrand Name: Bactrim Generic Name: Sulfamethoxazole, Trimethoprim, Co-Trimoxazole Drug Classification
Uploaded by
ianecunarBactrim is an antibiotic used to treat various respiratory, renal, and gastrointestinal infections like pneumonia, osteomyelitis, and toxoplasmosis. It works by inhibiting bacterial folic acid synthesis. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, rashes, and hematological issues. It should not be used in pregnancy or by those with liver or kidney impairment. Nurses should monitor patients for signs of infection, obtain cultures prior to use, inspect IV sites, and check blood work periodically during treatment.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
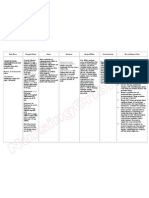
Brand name: Bactrim
Generic name: Sulfamethoxazole, Trimethoprim, Co-trimoxazole
Drug Classification: Antibiotics (Antibacterial)
Indication: Resp tract, renal GIT, GUT. Osteomyelitis, pneumocystis carinii pneumonia,
toxoplasmosis, actinomycetoma, acute brucellosis, nocardiosis
Mechanism of action: Interferes with bacterial growth by inhibiting bacterial folic acid synthesis
through competitive antagonism of PABA.
Dose: Tab 2 tab Forer tab. 1 tab infant & children TM 6 mg &SMZ 30 mg/kg body wt daily. To be
given in bid. Gonorrhea 5 tab bid or 2 ½ forte tab bid for 1 day.
Contraindication: Marked liver parenchymal damage; severe renal impairment; pregnancy.
Hypersensitivity.
Special Precaution: Hematological disorders; elderly; pregnancy; lactation; G6PD deficiency,
folate deficiency; impaired renal function, porphyria, thyroid dysfunction, history of
allergy or asthma.
Adverse Reactions:
CNS: fatigue, hallucinations, headache, insomnia, mental depression
GI: hepatic necrosis, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, stomatitis
GU: crystalluria
Derm: toxic epidermal necrolysis, rashes, photosensitivity
Hemat: agranulocytosis, leukopenia, megaloblastic anemia, thrombocytopenia
Local: phlebitis at IV site
Misc: allergic reactions including erythema multiforme, Stevens - Johnson syndrome,
fever.
Drug Interaction: Increased incidence of thrombocytopenia w/ thiazide diuretics in elderly. May
require dosage reduction of warfarin, phenytoin, digoxin, oral hypoglycemic agents. May
displace methitrexate from plasma protein –binding sites. Possible megaloblastic anemia
w/ high dose of pyrimethamine. Potentiates nephrotoxicity of cyclosporine (reversible).
Amantadine.
Form: Tablet- 80mg TMP/400mg SMZ, 160mg TMP/800mg SMZ;
Syrup- 40mg TMP/ 200mg SMZ per 5 mL;
Injection: 80mg TMP/ 400mg SMZ per 5mL in 5-, 10-, 20- and 30- mL vials
Pregnancy Risk Category: C; D if used near term.
Nursing Responsibilities:
Assess for infection (vital signs; appearance of wound, sputum, urine, and stool;
WBC) at beginning and during therapy.
Obtain specimens for culture and sensitivity before initiating therapy.
Inspect IV site frequently. Phlebitis is common.
Monitor CBC and urinalysis periodically during therapy.
You might also like
- Glipizide Glucotrol XL Drug CardDocument1 pageGlipizide Glucotrol XL Drug CardSheri490No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyBheiatriz de VeraNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studymike_steven12No ratings yet
- Hdu P&PDocument54 pagesHdu P&PianecunarNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Dexamethasone (Decilone)Document3 pagesDrug Study - Dexamethasone (Decilone)mikErlhNo ratings yet
- Critical Care NursingDocument10 pagesCritical Care Nursingianecunar100% (10)
- ClexaneDocument2 pagesClexaneianecunar100% (2)
- Cefazolin Sodium AncefDocument1 pageCefazolin Sodium AncefKristi WrayNo ratings yet
- Linezolid (Zyvox)Document1 pageLinezolid (Zyvox)ENo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Metronidazole (Flagyl)Document1 pageDrug Study - Metronidazole (Flagyl)Jule SantoyaNo ratings yet
- Chlorpheniramine Maleate: (klor-fen-AIR-uh-meen MAL-ee-ate)Document4 pagesChlorpheniramine Maleate: (klor-fen-AIR-uh-meen MAL-ee-ate)Nurginayah RusliNo ratings yet
- Gentamicin Pedia Drug StudyDocument3 pagesGentamicin Pedia Drug StudyGong AllenaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug Studyjanelle123 toribioNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Rocephin)Document2 pagesDrug Study (Rocephin)YakumaNo ratings yet
- AminophyllineDocument9 pagesAminophyllineZaira BataloNo ratings yet
- DexamethasoneDocument6 pagesDexamethasoneapi-3797941100% (1)
- CEFOXITINDocument30 pagesCEFOXITINJaessa FelicianoNo ratings yet
- AztreonamDocument2 pagesAztreonamHannahShaeHayesNo ratings yet
- NitrofurantoinDocument3 pagesNitrofurantoinapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Drug Study FORTDocument3 pagesDrug Study FORTLysa Mae EleazarNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - CefradoxilDocument13 pagesDrug Study - CefradoxilJohara G'naid0% (1)
- ZonisamideDocument2 pagesZonisamideRo-anne AkuNo ratings yet
- MetronidazoleDocument2 pagesMetronidazoleJm RomancapNo ratings yet
- Bearse Tablet InsertDocument2 pagesBearse Tablet InsertLeonard ByunNo ratings yet
- DRug Study PhenytoinDocument1 pageDRug Study Phenytoinmichelle marquezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - CaseDocument9 pagesDrug Study - CaseMay EvelynNo ratings yet
- AcetazolamideDocument2 pagesAcetazolamideAlexandra Antondy0% (1)
- BetamethasoneDocument3 pagesBetamethasoneMichael KuzbytNo ratings yet
- Brand Name: Diflucan Generic Name: Fluconazole Drug Classification: Antibiotics (Antifungal)Document2 pagesBrand Name: Diflucan Generic Name: Fluconazole Drug Classification: Antibiotics (Antifungal)ianecunar50% (2)
- PropranololDocument6 pagesPropranololanon_678895677No ratings yet
- MetoclopramideDocument3 pagesMetoclopramideapi-3797941100% (1)
- AMINOPHYLLINEDocument2 pagesAMINOPHYLLINEmusiclover017100% (1)
- OxytocinDocument1 pageOxytocinJoi Danielle Tabares IsturisNo ratings yet
- Dimenhydrinate PDFDocument2 pagesDimenhydrinate PDFWindy SengiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Delivery RoomDocument7 pagesDrug Study Delivery RoomkhleeoNo ratings yet
- Cefoxitin Sodium MefoxinDocument3 pagesCefoxitin Sodium MefoxinKristi WrayNo ratings yet
- Stugeron® TabletsDocument3 pagesStugeron® TabletsmahgadNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug FinalDocument7 pagesName of Drug FinalJaessa FelicianoNo ratings yet
- TergecefDocument2 pagesTergecefianecunar100% (3)
- AldactoneDocument2 pagesAldactoneianecunarNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ICUDocument5 pagesDrug Study ICUEcko MoawiaNo ratings yet
- GentamycinDocument3 pagesGentamycinKasandra Dawn Moquia BerisoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Cushing's SyndromeDocument5 pagesDrug Study Cushing's SyndromeSelena MarieNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyRowland PascuaNo ratings yet
- MG Drug StudyDocument3 pagesMG Drug StudySandra MedinaNo ratings yet
- Sal But AmolDocument2 pagesSal But AmolKay MirandaNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY MetroclopramideDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY MetroclopramideMimay Gabo Gonzales100% (6)
- Brompheniramine Maleate (Drug Study)Document2 pagesBrompheniramine Maleate (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888No ratings yet
- Drug Name Indication Action Adverse EffectsDocument4 pagesDrug Name Indication Action Adverse EffectsMaryjoy Gabriellee De La CruzNo ratings yet
- Meclizine Hydro ChlorideDocument3 pagesMeclizine Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941100% (1)
- Ofloxacin Drug StudyDocument4 pagesOfloxacin Drug StudyMikko Anthony Pingol Alarcon100% (1)
- Pilocarpine (Drug Monograph)Document1 pagePilocarpine (Drug Monograph)Muhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FDocument3 pagesDrug Study FFatima Love Ariate-ArcasetasNo ratings yet
- Clinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsDocument3 pagesClinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsENo ratings yet
- CyclosporineDocument2 pagesCyclosporineMuhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- Jam (Drug Study)Document11 pagesJam (Drug Study)Vincent QuitorianoNo ratings yet
- ClindamycinDocument2 pagesClindamycinchristineleesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: NCM 106 Pharmacology: Patient MonitoringDocument2 pagesDrug Study: NCM 106 Pharmacology: Patient Monitoringpoleene de leonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study KeterolacDocument2 pagesDrug Study KeterolacKillerBall RegioNo ratings yet
- Generic NameDocument3 pagesGeneric NamepachichoyNo ratings yet
- Trimethoprim Sulfamethoxazole (TMP SMZ) Co TrimoxazoleDocument1 pageTrimethoprim Sulfamethoxazole (TMP SMZ) Co TrimoxazoleRenmico Aquino0% (1)
- CotrimozaxoleDocument3 pagesCotrimozaxoleDane CunananNo ratings yet
- Drugs I N Der Mato Lo GyDocument85 pagesDrugs I N Der Mato Lo GySilviuNo ratings yet
- Anti ProtozoaDocument29 pagesAnti ProtozoaIsheanesu MugwisiNo ratings yet
- DiovanDocument2 pagesDiovanianecunar100% (1)
- Pathophy - Nephrotic SyndromeedDocument1 pagePathophy - Nephrotic Syndromeedianecunar100% (1)
- Drug Study - Tranexamic Acid (Cyclokapron)Document2 pagesDrug Study - Tranexamic Acid (Cyclokapron)mikErlhNo ratings yet
- Brand Name: Diamicron Generic Name: Gliclazide Indication: For Non-Insulin DependentDocument2 pagesBrand Name: Diamicron Generic Name: Gliclazide Indication: For Non-Insulin DependentianecunarNo ratings yet
- Brand Name: Dilzem Generic Name: Diltiazem Indications: Angina Pectoris IncludingDocument3 pagesBrand Name: Dilzem Generic Name: Diltiazem Indications: Angina Pectoris Includingianecunar0% (1)
- Brand Name: Diflucan Generic Name: Fluconazole Drug Classification: Antibiotics (Antifungal)Document2 pagesBrand Name: Diflucan Generic Name: Fluconazole Drug Classification: Antibiotics (Antifungal)ianecunar50% (2)
- Brand Name: Dilantin Generic Name: Phenytoin Indication: Dilantin Is IndicatedDocument4 pagesBrand Name: Dilantin Generic Name: Phenytoin Indication: Dilantin Is Indicatedianecunar100% (1)
- CelebrexDocument2 pagesCelebrexianecunarNo ratings yet
- Brand Name: Dalacin C Generic Name: Clindamycin HCL Drug ClassificationDocument2 pagesBrand Name: Dalacin C Generic Name: Clindamycin HCL Drug Classificationianecunar100% (1)
- Crest orDocument3 pagesCrest orianecunarNo ratings yet
- Co DiovanDocument2 pagesCo DiovanianecunarNo ratings yet
- Com Bi VentDocument2 pagesCom Bi VentianecunarNo ratings yet
- CoversylDocument3 pagesCoversylianecunarNo ratings yet
- Brand Name: Cozaar Generic Name: Losartan Potassium Indications: Hypetension, NephepaticallyDocument2 pagesBrand Name: Cozaar Generic Name: Losartan Potassium Indications: Hypetension, Nephepaticallyianecunar100% (1)
- Brand Name: Carnicor Generic Name: L-Carnitine Indications: Chronic Myocardia IschemiaDocument2 pagesBrand Name: Carnicor Generic Name: L-Carnitine Indications: Chronic Myocardia Ischemiaianecunar100% (1)
- Brand Name: Chloromycetin Generic Name: Chloramphenicol Indication: External Ear CanalDocument2 pagesBrand Name: Chloromycetin Generic Name: Chloramphenicol Indication: External Ear CanalianecunarNo ratings yet
- CiprobayDocument2 pagesCiprobayianecunar100% (1)
- CalpolDocument2 pagesCalpolianecunarNo ratings yet
- BiogesicDocument2 pagesBiogesicianecunarNo ratings yet
- Calcibloc ODDocument2 pagesCalcibloc ODianecunarNo ratings yet
- Brand Name: Apo-Metoprolol, Betaloc, Lopressor, Novometropol Generic Name: Metoprolol IndicationsDocument3 pagesBrand Name: Apo-Metoprolol, Betaloc, Lopressor, Novometropol Generic Name: Metoprolol IndicationsianecunarNo ratings yet
- Brand Name: Blopress Generic Name: Candesartan Indications: Management of HypertensionDocument2 pagesBrand Name: Blopress Generic Name: Candesartan Indications: Management of Hypertensionianecunar0% (2)
- AtropairDocument2 pagesAtropairianecunarNo ratings yet
- BricanylDocument4 pagesBricanylianecunarNo ratings yet
- Brand Name: Bambec Generic Name: Bambuterol HCL Indication: Bronchial AsthmaDocument2 pagesBrand Name: Bambec Generic Name: Bambuterol HCL Indication: Bronchial AsthmaianecunarNo ratings yet
- BActidolDocument2 pagesBActidolianecunar100% (3)