Professional Documents
Culture Documents
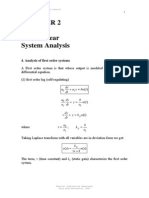
Overdamped, Underdamped, Critically damped and Undamped system responses
Uploaded by
aripratnaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Overdamped, Underdamped, Critically damped and Undamped system responses
Uploaded by
aripratnaCopyright:
Available Formats
Overdamped, Underdamped, Critically damped and Undamped responses
Overdamped Two real unequal poles Underdamped Two complex poles Undamped Two imaginary poles Critically damped Two real equal poles
c(t ) = K1e 1t + K 2 e 2t c(t ) = Ae d t cos(d t + ) c(t ) = A cos(n t + ) c(t ) = K1e 1t + K 2 te 1t
= tan -1
Im g Re
Example
For each plant, solve for the natural frequency and damping ratio
Effect of adding an additional pole
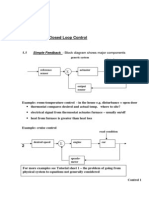
If the system has two or more poles or with zeros, it may be approximated as a second-order system that has two complex dominant poles. If the approximation can justified, secondorder formulae can be applied.
Component responses of a three-pole system: a. pole plot; b. component responses: nondominant pole is near dominant second-order pair (Case I), far from the pair (Case II), and at infinity (Case III)
Cases
Dominant poles?
Step responses of system T1(s), system T2(s), and system T3(s)
Validity of 2nd order approx.
In general, if the additional pole is five times or more further away to the left on the s-plane than the real part of the complex dominant pole, a second order approximation is valid. The 2nd order approximation is valid for T2(s) and not for T3(s).
Example
Determine the validity of a 2nd order approx for these 2 TFs
G(s) = G(s) =
700
( s + 15 ) ( s 2 + 4s + 100 )
360
( s + 4 ) ( s 2 + 2s + 90 )
Validity test
System response with an additional zero (first order)
Recall: The poles and zeros generate the amplitudes for both the forced and natural response.
C ( s) = A= B=
Without the zeros the amplitudes for both the forced and natural response.
C ( s) = A= B= 1 A B = + s ( s + 5) s s + 5 1 lim = 1 5
(s + 2)
s ( s + 5)
A B + s s+5
lim = s s5 5 2 3 5t c (t ) = + e 5 5
( s + 2) 2 lim = ( s + 5 ) s 0 5 ( s + 2) 3
( s + 5 ) s 0
1 1 lim = 5 s s 5 1 1 c (t ) = e5 t 5 5
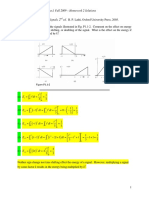
Effect of adding a zero to a two-pole system
Step response of a nonminimum -phase system
Zero on the right hand side of the splane
Step response of the nonminimum-phase network (c(t)) and normalized step response of an equivalent network without the zero
You might also like
- Control Systems Formula SheetDocument12 pagesControl Systems Formula SheetliamhrNo ratings yet
- Ch-5 Time Res WebpageDocument48 pagesCh-5 Time Res WebpageTushar GuptaNo ratings yet
- M 61 Vulcan CannonDocument6 pagesM 61 Vulcan CannonaripratnaNo ratings yet
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Time Response AnalysisDocument151 pagesTime Response AnalysisTushar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Signal System ObjectiveDocument82 pagesSignal System ObjectiveNitin Kathuria100% (3)
- Chapter 2.2 Response Ist Order SystemsDocument30 pagesChapter 2.2 Response Ist Order SystemsSyed AliNo ratings yet
- Unit-Step Response:: 1 First Order SystemsDocument2 pagesUnit-Step Response:: 1 First Order SystemsNatalie ChehraziNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 System IInd Order ResponsesDocument38 pagesChapter 2 System IInd Order ResponsesAli AhmadNo ratings yet
- Signals and Systems QuestionsDocument16 pagesSignals and Systems QuestionsVishal KumarNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Signals & SystemsDocument48 pagesSignals & SystemsailamrudhulaNo ratings yet
- Transient Response Analysis: Test Signals: Impulse Step Ramp Sin And/or CosDocument38 pagesTransient Response Analysis: Test Signals: Impulse Step Ramp Sin And/or Cosomar9aNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: Time Response, Part 3: Systems With Additional Poles or ZeroesDocument10 pagesUnit 3: Time Response, Part 3: Systems With Additional Poles or ZeroesNikhil PanikkarNo ratings yet
- AME455 - Midterm Exam 02 - 03/11/11Document7 pagesAME455 - Midterm Exam 02 - 03/11/11Cam VintatNo ratings yet
- CONTROL SYSTEMS ENGINEERING TUTORIALDocument5 pagesCONTROL SYSTEMS ENGINEERING TUTORIALcataiceNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 6: Transient ResponseDocument19 pagesLecture - 6: Transient ResponseSakib RushdiNo ratings yet
- Precision Measurement & Control RevisionDocument8 pagesPrecision Measurement & Control RevisionEleanor McCutcheonNo ratings yet
- 2.004 Dynamics and Control Ii: Mit OpencoursewareDocument9 pages2.004 Dynamics and Control Ii: Mit OpencoursewareDavid VidalesNo ratings yet
- 01 Review of Closed Loop ControlDocument17 pages01 Review of Closed Loop ControlferrarivcaNo ratings yet
- General Forced Response: P T N B P T N A A T FDocument11 pagesGeneral Forced Response: P T N B P T N A A T FSathish Kumar SNo ratings yet
- Manolis KoliopoulosDocument58 pagesManolis KoliopoulosSushil MundelNo ratings yet
- ECE633 Signals and Systems I, Fall 2009 - Homework 2 SolutionsDocument13 pagesECE633 Signals and Systems I, Fall 2009 - Homework 2 SolutionsGabrielPopoola13100% (2)
- Chap02b.advanced Process Control PDFDocument15 pagesChap02b.advanced Process Control PDFAnthony PattersonNo ratings yet
- HW3 Solutions2printDocument6 pagesHW3 Solutions2printයෙදුම් KarunarathnaNo ratings yet
- Lec 5Document31 pagesLec 5adasdsdadNo ratings yet
- Process Dynamics and Control Seborg 2nd Ch06 PDFDocument43 pagesProcess Dynamics and Control Seborg 2nd Ch06 PDFRon PascualNo ratings yet
- ECE633F09 HW2solutionsDocument13 pagesECE633F09 HW2solutionsAnonymous xuEZu5KyNo ratings yet
- SignalsDocument3 pagesSignalsBerentoNo ratings yet
- Time Respons: Dasar Sistem KontrolDocument13 pagesTime Respons: Dasar Sistem KontrolitmyNo ratings yet
- Notes LT3Document12 pagesNotes LT3veteron56No ratings yet
- System PrototypesDocument29 pagesSystem PrototypesYgor AguiarNo ratings yet
- MEM1833 Topic 3 State Space Realizations HANDOUTDocument27 pagesMEM1833 Topic 3 State Space Realizations HANDOUTHasrulnizam HashimNo ratings yet
- (408177384) FinalExam SolutionDocument8 pages(408177384) FinalExam SolutionNikolay Ysayaka HatakeNo ratings yet
- Serv - Chula.ac - TH Tarporn 487 HandOut DynamicCDocument38 pagesServ - Chula.ac - TH Tarporn 487 HandOut DynamicCAaditya RoyNo ratings yet
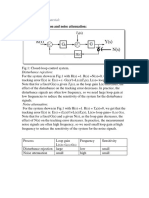
- Disturbance Rejection and Noise Attenuation:: Control 1, Second MaterialDocument5 pagesDisturbance Rejection and Noise Attenuation:: Control 1, Second MaterialKaram AlmasriNo ratings yet
- Automatic Control (ME-1401) : A B C DDocument2 pagesAutomatic Control (ME-1401) : A B C DMehroos AliNo ratings yet
- Capitulo 3 (Ackermanf)Document20 pagesCapitulo 3 (Ackermanf)Gabyta XikitaaNo ratings yet
- Lab # 7 Control SystemDocument15 pagesLab # 7 Control SystemZabeehullahmiakhailNo ratings yet
- Revision of Fourier SeriesDocument37 pagesRevision of Fourier SeriesGeorges YoussefNo ratings yet
- Modelling Second Order Systems and Examples: CL-417 Process Control Prof. Kannan M. MoudgalyaDocument29 pagesModelling Second Order Systems and Examples: CL-417 Process Control Prof. Kannan M. MoudgalyaVivekNo ratings yet
- Respostas Controle de Sistemas Dinâmicos - OgathaDocument3 pagesRespostas Controle de Sistemas Dinâmicos - OgathaCarlitos FerNo ratings yet
- Files-3-Handouts Solved Problems Chapter 3 Mechanical Systems PDFDocument7 pagesFiles-3-Handouts Solved Problems Chapter 3 Mechanical Systems PDFHemanta DikshitNo ratings yet
- Control Systems Lecture04: Transfer Functions and Poles & ZerosDocument53 pagesControl Systems Lecture04: Transfer Functions and Poles & Zerosxtito2No ratings yet
- EI - 301 Control Systems End-Sem Question Paper Nov' 2013Document1 pageEI - 301 Control Systems End-Sem Question Paper Nov' 2013lalusebanNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Behavior of More General SystemsDocument32 pagesDynamic Behavior of More General Systemsjasonbkyle9108No ratings yet
- Time Domain Analysis of 1st Order SystemsDocument19 pagesTime Domain Analysis of 1st Order SystemsIslam SaqrNo ratings yet
- Econometrics Chapter 9 Exercise SolutionsDocument34 pagesEconometrics Chapter 9 Exercise SolutionsreloadedmemoryNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics Questions and AnswersDocument9 pagesEngineering Mathematics Questions and AnswersZaky Muzaffar100% (1)
- Class Test - 2016: Electrical EngineeringDocument9 pagesClass Test - 2016: Electrical EngineeringarunNo ratings yet
- 4 SecondOrderDocument9 pages4 SecondOrderThinseepNo ratings yet
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- The Plasma Dispersion Function: The Hilbert Transform of the GaussianFrom EverandThe Plasma Dispersion Function: The Hilbert Transform of the GaussianRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Introductory Differential Equations: with Boundary Value Problems, Student Solutions Manual (e-only)From EverandIntroductory Differential Equations: with Boundary Value Problems, Student Solutions Manual (e-only)No ratings yet
- Commensurabilities among Lattices in PU (1,n). (AM-132), Volume 132From EverandCommensurabilities among Lattices in PU (1,n). (AM-132), Volume 132No ratings yet
- Darwin's Second History of WarDocument1 pageDarwin's Second History of WararipratnaNo ratings yet
- List of PapersDocument9 pagesList of PapersaripratnaNo ratings yet
- To Propellants and Pyrotechnics (Page. 149) - Cambridge: Royal Society ofDocument1 pageTo Propellants and Pyrotechnics (Page. 149) - Cambridge: Royal Society ofaripratnaNo ratings yet
- Time AnalysisDocument15 pagesTime AnalysisaripratnaNo ratings yet
- Jou Kowski AirfoilDocument3 pagesJou Kowski AirfoilaripratnaNo ratings yet
- Harga Spare Part Revo 110Document11 pagesHarga Spare Part Revo 110imran_machazzartNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics: BASIR, ST., M.Eng., M.SCDocument10 pagesFluid Mechanics: BASIR, ST., M.Eng., M.SCaripratnaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics: BASIR, ST., M.Eng., M.SCDocument10 pagesFluid Mechanics: BASIR, ST., M.Eng., M.SCaripratnaNo ratings yet
- Email IpDocument1 pageEmail IparipratnaNo ratings yet
- Cover Kaset Pak KarsenoDocument3 pagesCover Kaset Pak KarsenoaripratnaNo ratings yet
- Normal Adjective & Icebreaker Technology: Selasa, 8 Mei 2012 Jam 19.00 S/D Selesai Ruang ABD 7 Presented by Aes SttaDocument1 pageNormal Adjective & Icebreaker Technology: Selasa, 8 Mei 2012 Jam 19.00 S/D Selesai Ruang ABD 7 Presented by Aes SttaaripratnaNo ratings yet
- CookDocument2 pagesCookaripratnaNo ratings yet
- Tugas Dinamikka Terbang EditDocument2 pagesTugas Dinamikka Terbang EditaripratnaNo ratings yet
- Lateral Control Analysis of AircraftDocument16 pagesLateral Control Analysis of AircraftaripratnaNo ratings yet
- Ringkasan ManufakturDocument6 pagesRingkasan ManufakturaripratnaNo ratings yet
- Research on Biojet Fuel Blended with Jet A-1 in Aircraft EnginesDocument1 pageResearch on Biojet Fuel Blended with Jet A-1 in Aircraft EnginesaripratnaNo ratings yet
- CookDocument2 pagesCookaripratnaNo ratings yet
- Iskandar Muda International AirportDocument1 pageIskandar Muda International AirportaripratnaNo ratings yet
- Professional: CAHAYA TRANSPORT - Rental Mobil Siaga 24 JamDocument1 pageProfessional: CAHAYA TRANSPORT - Rental Mobil Siaga 24 JamaripratnaNo ratings yet
- Psikotes NomorDocument1 pagePsikotes NomoraripratnaNo ratings yet
- Trace EmailDocument2 pagesTrace EmailaripratnaNo ratings yet
- CookDocument2 pagesCookaripratnaNo ratings yet
- CookDocument2 pagesCookaripratnaNo ratings yet
- CookDocument2 pagesCookaripratnaNo ratings yet
- CookDocument2 pagesCookaripratnaNo ratings yet
- Soal Un SMP Bhs. InggrisDocument11 pagesSoal Un SMP Bhs. Inggrissuper_ihno50% (2)
- Triple PythagorasDocument1 pageTriple PythagorasaripratnaNo ratings yet
- CookDocument2 pagesCookaripratnaNo ratings yet





















































![Mathematical Tables: Tables of in G [z] for Complex Argument](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/282615796/149x198/febb728e8d/1699542561?v=1)