Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Magnesium Sulfate
Uploaded by
Ivanne HisolerCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Magnesium Sulfate
Uploaded by
Ivanne HisolerCopyright:
Available Formats
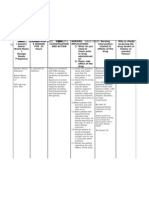
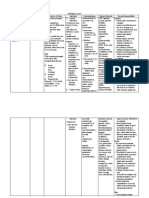
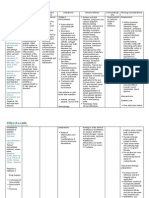
Drug Data Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Adverse Reaction Nursing Responsibilities
Generic Name Pharmacologic Cofactor of many enzyme systems General Concentrations CNS: Weakness, Before
Magnesium Class involved in neurochemical Indications - Allergy to magnesium drowsiness, dizziness, - Assess for contraindicated
Sulfate Mineral, transmission and muscular - Constipation products fainting, sweating conditions.
Electrolyte excitability; prevents or controls - Torsades de - Abdominal pain Respiratory: Decreased - Monitor knee-jerk reflex before
Trade Name seizures by locking the pointes - Nausea respiratory rate repeated parenteral administration.
Martham Therapeutic neuromuscular transmission; - Muscle stimulating - Vomiting CV: Palpitations - Give as laxative as temporary
Class attracts and retains the water in effects of barium - Acute surgical abdomen GI: Excessive bowel measure.
Minimum Dose Antiepileptic, the intestinal lumen and distends poisoning - Fecal impaction activity, perianal irritation - Reserve IV use in eclampsia for
1-2 g qH by IV Laxative; Mineral, the bowel to promote mass - Reduction of - Intestinal and biliary tract Metabolic: Magnesium life-threatening situations.
infusion electrolyte movement and relieve cerebral oedema. obstruction intoxication, - Observe the 15 rights in drug
replacement constipation. - - Hepatitis hypocalcemia with tetany administration.
Maximum Hypomagnesaemia - Myocardial damage
Dose Pregnancy Risk Pharmacokinetics - Seizures - Heart blocks During
4-6 g qH by IV Factor associated with - 2 hr preceding delivery - Give IM route by deep IM injection.
infusion A A: Following administration, 30- epilepsy, Precaution - Monitor serum magnesium levels.
B (Laxative) 50% of the dose is absorbed from glomerulonephritis - Renal insufficiency - Do not give oral MgSO4 with
Contents the small intestine. or hypothyroidism. abdominal pain, nausea, or
Magnesium D: Crosses the placenta and small - Toxemias of Drug interaction vomiting.
sulfate amounts enter the breast milk. pregnancy Drug to drug - Do not administer if knee-jerk
M: Unknown - Boils and - Potentiation of reflexes are suppressed
Availability E: Via urine and feces. carbuncles neuromuscular - Monitor bowel function.
and color blockade produced by
- Granules- 40 mEq/5 Rout Onset Peak Duratio After
g e n nondepolarizing
- Injection- 0.325, neuromuscular - Arrange to discontinue
Oral 1-2 hr unknow 3-4 hr
0.65, 1, 4 mEq/mL n relaxants administration as soon as levels are
IM 60 min unknow 3-4 hr within normal limits and desired
Routes of n
Drug to food clinical response is obtained.
IV Immedia unknow 30 min
administration - none reported - Discontinue if diarrhea or
te n
Oral cramping occurs.
Intramuscular - Arrange for dietary measures,
Drug Half Life
Intravenous exercise and environmental control
Unknown
to return to normal bowel activity.
- Report sweating, flushing, muscle
tremors or twitching, inability to
move extremities.
- Maintain urine output at a level of
100 mL every 4 hr during parenteral
administration.
Source: Source: Source: Source: Source: Source: Source:
Karch, Amy: 2009 http://mims.com.ph/, http://mims.com.ph/, Karch, Amy: 2009 http://mims.com.ph/ Karch, Amy: 2009 Lippincott’s Karch, Amy: 2009 Lippincott’s Karch, Amy: 2009 Lippincott’s Nursing Drug
Lippincott’s Nursing Karch, Amy: 2009 Lippincott’s Nursing Drug Guide, pp. 724-725 Nursing Drug Guide, pp. 724- Nursing Drug Guide, p. 725 Guide, pp. 725-726
Drug Guide, p. 724 Lippincott’s Nursing 725
Drug Guide, pp. 724
You might also like
- 6 MAGNESIUM SULFATE Drug StudyDocument2 pages6 MAGNESIUM SULFATE Drug StudyGwyn Rosales100% (2)
- DRUG STUDY-Magnesium SulfateDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY-Magnesium SulfateCarissa Mae Tapec Estrada80% (5)
- Salazar Colleges of Science and Institute of TechnologyDocument2 pagesSalazar Colleges of Science and Institute of TechnologyMark Keem Escuadro100% (3)
- Magnesium SulfateDocument2 pagesMagnesium SulfateCecilia Cenas Bendol100% (2)
- Drug Study - Nifedipine PODocument1 pageDrug Study - Nifedipine POJet BautistaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study On CARBOPROSTDocument4 pagesDrug Study On CARBOPROSTshadow gonzalez100% (1)
- Methyldopa Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMethyldopa Drug StudyBea Dela Cena100% (1)
- HydralazineDocument2 pagesHydralazineShermayne Mallapre HernandezNo ratings yet
- Labetalol Hydro ChlorideDocument3 pagesLabetalol Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941100% (1)
- Clinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsDocument3 pagesClinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsENo ratings yet
- Methergine Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMethergine Drug StudycuakialyannaNo ratings yet
- Calcium Gluconate Drug SummDocument1 pageCalcium Gluconate Drug SummWarren100% (2)
- Methyldopa Drug StudyDocument1 pageMethyldopa Drug Studychinchin ramosNo ratings yet
- Carboprost 1Document3 pagesCarboprost 1angerson5100% (1)
- 11111a - CarbetocinDocument3 pages11111a - Carbetocinhahahahaaaaaaa0% (2)
- PHENYLEPHRINEDocument3 pagesPHENYLEPHRINERoger Jr PumarenNo ratings yet
- Magnesium Sulfate Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMagnesium Sulfate Drug StudyMaan Molinyawe81% (16)
- Ketorolac and NalbuphineDocument4 pagesKetorolac and NalbuphineMaureen Campos-PineraNo ratings yet
- OfloxacinDocument2 pagesOfloxacinCarla Arciaga100% (1)
- MethergineDocument2 pagesMethergineKureaa Oh100% (1)
- Methergine Drug StudyDocument3 pagesMethergine Drug StudyjoshNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Number 3 Repro.,respi and GastrointestinalDocument64 pagesDrug Study Number 3 Repro.,respi and Gastrointestinaljamaica cabrigaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyYaniiee DeFiestaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Calcium GluconateDocument1 pageDrug Study - Calcium GluconatemikErlhNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: College of NursingDocument3 pagesDrug Study: College of NursingJulie MayNo ratings yet
- Drug Study OxytocinDocument1 pageDrug Study OxytocinGil GanibanNo ratings yet
- IsoxsuprineDocument1 pageIsoxsuprineAndrean EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Labetalol Hydro ChlorideDocument6 pagesDrug Study: Labetalol Hydro ChlorideMark ToxNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AmpicillinDocument6 pagesDrug Study AmpicillinDgjj Compuiter100% (1)
- Drug Study CytotecDocument2 pagesDrug Study CytotecLuige Avila60% (10)
- Drug Study PethidineDocument2 pagesDrug Study Pethidinerica sebabillonesNo ratings yet
- Calcium Gluconate Drug StudyDocument2 pagesCalcium Gluconate Drug StudyErika ManubayNo ratings yet
- Naloxone and Benzylpenicillin DRUG STUDYDocument3 pagesNaloxone and Benzylpenicillin DRUG STUDYNasrah N. Musa100% (3)
- A Drug Study On Evening Primrose OilDocument5 pagesA Drug Study On Evening Primrose OilAlexis Khalyl Y. MontejoNo ratings yet
- MethergineDocument2 pagesMethergineJulie May33% (3)
- Ferrous Sulfate: o o o o o o oDocument5 pagesFerrous Sulfate: o o o o o o oLelanie Japitana100% (1)
- Drug Study - Cefazolin DoxycyclineDocument2 pagesDrug Study - Cefazolin DoxycyclineDan Dan Soi T50% (2)
- Fentanyl Citrate Drug StudyDocument1 pageFentanyl Citrate Drug StudyArthur Christopher CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Drug Study-Nifedipine-BALLON, Karlo C.Document2 pagesDrug Study-Nifedipine-BALLON, Karlo C.Melinda Cariño Ballon100% (1)
- Ceftriaxone, Misoprostol, OxytocinDocument4 pagesCeftriaxone, Misoprostol, OxytocinKrizia Bonilla100% (1)
- DRUG STUDY Amoxicillin PDFDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY Amoxicillin PDFMc SantosNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument13 pagesDrug StudyGi Ey ElNo ratings yet
- Midazolam Drug Study SaclotDocument1 pageMidazolam Drug Study SaclotMaybelle Cababat SaclotNo ratings yet
- Carboprost TromethamineDocument2 pagesCarboprost TromethamineDeathDefying DonutNo ratings yet
- MedroxyprogesteroneDocument5 pagesMedroxyprogesteroneunkown userNo ratings yet
- Hydralazine Drug StudyDocument2 pagesHydralazine Drug StudyErika Robella100% (1)
- Pharmacologic: Systemic Administration AssessmentDocument3 pagesPharmacologic: Systemic Administration Assessmentitsmeaya100% (1)
- Betamethasone (Drug Study)Document4 pagesBetamethasone (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888100% (1)
- Drug Study MgSO4Document1 pageDrug Study MgSO4Brigette Quirante100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyROCHELLE DALIWAN100% (1)
- DS HydralazineDocument3 pagesDS HydralazineGe LoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study OxytocinDocument2 pagesDrug Study Oxytocinpjcolita100% (1)
- Methergine Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMethergine Drug StudyJj Delacruz0% (1)
- ORDocument7 pagesORMay EvelynNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Delivery RoomDocument7 pagesDrug Study Delivery RoomkhleeoNo ratings yet
- Myasthenia Gravis, Megacolon and Narrow Angle Glaucoma, Hypersensitivity To HNBB and Other Components of The ProductDocument3 pagesMyasthenia Gravis, Megacolon and Narrow Angle Glaucoma, Hypersensitivity To HNBB and Other Components of The ProductGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- MetoclopramideDocument1 pageMetoclopramideIvanne Hisoler89% (27)
- Magnesium SulfateDocument2 pagesMagnesium SulfateGwyn Rosales100% (1)
- Drugstudy 3Document1 pageDrugstudy 3Lorlyn OrehuelaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MetoclopramideDocument2 pagesDrug Study Metoclopramiderica sebabillones100% (1)
- Daily Assignment PlanDocument2 pagesDaily Assignment PlanIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Land Titles Cases (6.21.14)Document31 pagesLand Titles Cases (6.21.14)Ivanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Lumantas MD v. CalapizDocument2 pagesLumantas MD v. CalapizIvanne Hisoler100% (1)
- Persons - Midterms NotesDocument23 pagesPersons - Midterms NotesEvina Michaela LupangoNo ratings yet
- Contract of Lease (Motor Vehicle)Document3 pagesContract of Lease (Motor Vehicle)Ivanne Hisoler71% (7)
- Republic vs. Castellvi DigestDocument1 pageRepublic vs. Castellvi DigestIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Case Digest (QC v. Ericta)Document1 pageCase Digest (QC v. Ericta)Ivanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- OxytocinDocument1 pageOxytocinIvanne Hisoler100% (7)
- Eminent Domain Case DigestsDocument18 pagesEminent Domain Case DigestsIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Penicillin G BenzathineDocument1 pagePenicillin G BenzathineIvanne Hisoler100% (7)
- MethotrexateDocument2 pagesMethotrexateIvanne Hisoler83% (6)
- Promethazine HCLDocument2 pagesPromethazine HCLIvanne Hisoler100% (8)
- Terbutaline SulfateDocument1 pageTerbutaline SulfateIvanne Hisoler100% (2)
- MetoclopramideDocument1 pageMetoclopramideIvanne Hisoler89% (27)
- DroperidolDocument1 pageDroperidolIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- HydralazineDocument1 pageHydralazineIvanne Hisoler75% (8)
- FurosemideDocument2 pagesFurosemideIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- MethadoneDocument2 pagesMethadoneIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- DisulfiramDocument1 pageDisulfiramIvanne Hisoler100% (1)
- HydrocortisoneDocument2 pagesHydrocortisoneIvanne Hisoler100% (15)
- DactinomycinDocument1 pageDactinomycinIvanne Hisoler0% (2)
- Dopamine HCLDocument1 pageDopamine HCLIvanne Hisoler100% (3)
- AmpicillinDocument1 pageAmpicillinIvanne Hisoler100% (1)
- DiazepamDocument1 pageDiazepamIvanne Hisoler71% (7)
- DigoxinDocument1 pageDigoxinIvanne Hisoler100% (3)
- Revision Notes CH 3 Human Strengths and Meeting Life ChallengesDocument8 pagesRevision Notes CH 3 Human Strengths and Meeting Life ChallengesFuljhuri BasuNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Assessment For Clinicians 3rd EditionDocument298 pagesCognitive Assessment For Clinicians 3rd EditionInes Strenja Linić100% (3)
- Slide Eritroderma 2Document7 pagesSlide Eritroderma 2Anonymous QqGJk2jK5No ratings yet
- Endoscopic Endonasal and Transorbital Routes To The Petrous Apex: Anatomic Comparative Study of Two PathwaysDocument13 pagesEndoscopic Endonasal and Transorbital Routes To The Petrous Apex: Anatomic Comparative Study of Two Pathwaysgabriele1977No ratings yet
- Patho Week 3Document4 pagesPatho Week 3Lin LanNo ratings yet
- Essential Newborn CareDocument5 pagesEssential Newborn CareJig PirameNo ratings yet
- The Difficult or Failed Airway: Pat Melanson, MDDocument28 pagesThe Difficult or Failed Airway: Pat Melanson, MDMinorC3No ratings yet
- Vertebrate RespirationDocument19 pagesVertebrate RespirationOSCAR JOSHUA PAYAWALNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument25 pagesCirculatory SystemadnanNo ratings yet
- Sas 06Document4 pagesSas 06Keziah Kish Torres GilNo ratings yet
- Phylums and TaxonomyDocument9 pagesPhylums and TaxonomyNatNo ratings yet
- Huberman Lab NotesDocument152 pagesHuberman Lab Notescan dagidir80% (5)
- Cirugia Periodontal Manejo Recesiones Gingivales en 1 o Mas DiengtesDocument21 pagesCirugia Periodontal Manejo Recesiones Gingivales en 1 o Mas DiengtesAlejandro MorenoNo ratings yet
- Biológia Angol Nyelven: Emelt Szintű Írásbeli Érettségi VizsgaDocument7 pagesBiológia Angol Nyelven: Emelt Szintű Írásbeli Érettségi VizsgaDsanNo ratings yet
- 2010 05 25 0848472010 - CaluscusinDocument50 pages2010 05 25 0848472010 - CaluscusinAchmad Deddy FatoniNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument27 pagesRespiratory Systemapi-210569514No ratings yet
- Type 1 Diabetes Pathogenesis Genetics and ImmunotherapyDocument670 pagesType 1 Diabetes Pathogenesis Genetics and ImmunotherapyMihaela PurcaruNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Distention inDocument45 pagesAbdominal Distention inArif Rahman DmNo ratings yet
- Philips Heartstart XL Plus Defibrillator ManualDocument235 pagesPhilips Heartstart XL Plus Defibrillator ManualvikasNo ratings yet
- (Chapter 1 and 2) : Anaphy Quiz Reviewer (Chapters 1-3)Document20 pages(Chapter 1 and 2) : Anaphy Quiz Reviewer (Chapters 1-3)Mariam GamosNo ratings yet
- GP1 2002Document95 pagesGP1 2002ManoloNo ratings yet
- Fragrance With Antiaging Benefits: Naturals-Driven Functionality For Added ValueDocument6 pagesFragrance With Antiaging Benefits: Naturals-Driven Functionality For Added Valuejasminai_17No ratings yet
- ESR Tantra and The Limits of Female PoteDocument28 pagesESR Tantra and The Limits of Female PotePILAR RUTH LOPEZ DE LA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Lecture PharynxDocument28 pagesLecture PharynxHoor AlnabhaniNo ratings yet
- Radiologi SinusitisDocument42 pagesRadiologi SinusitisMonic GultomNo ratings yet
- Closed Fractures of The Tibial Diaphysis: David L. Rothberg, MD Erik N. Kubiak, MDDocument64 pagesClosed Fractures of The Tibial Diaphysis: David L. Rothberg, MD Erik N. Kubiak, MDtilahunthmNo ratings yet
- Modified Cumulative Illness Rating Scale: Each System Is Rated As FollowsDocument1 pageModified Cumulative Illness Rating Scale: Each System Is Rated As FollowsFabi kNo ratings yet
- 3-CVS-Valvular Diseases-Prof. Magdy-Student-Final (Compatibility Mode)Document11 pages3-CVS-Valvular Diseases-Prof. Magdy-Student-Final (Compatibility Mode)أميرةNo ratings yet
- Medical Entrance AIPMT PapersDocument15 pagesMedical Entrance AIPMT Paperssumit kumar0% (1)
- Solutions (Cellullar Biophysics - Vol 1 - Trasport) WeissDocument173 pagesSolutions (Cellullar Biophysics - Vol 1 - Trasport) WeissErick100% (1)