Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DRUG STUDY-Magnesium Sulfate
Uploaded by
Carissa Mae Tapec Estrada80%(5)80% found this document useful (5 votes)
5K views2 pagesOriginal Title
DRUG STUDY-Magnesium sulfate
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
80%(5)80% found this document useful (5 votes)
5K views2 pagesDRUG STUDY-Magnesium Sulfate
Uploaded by
Carissa Mae Tapec EstradaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
DRUG STUDY
Name of Student Nurse: Carissa Mae T. Estrada Date:
Level/Block/Group: 2BSN-04 Hospital/Area:
Clinical Instructor: Ma’am/Mrs. Apolonia Dela Cruz
MAGNESIUM SULFATE
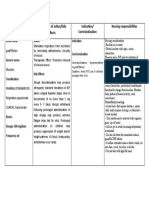
NAME OF DRUG MECHANISM CONTRAIND SIDE EFFECTS ADVERSE NURSING
OF ACTION ICATIONS EFFECTS RESPONSIBILITIES
GENERIC NAME Magnesium is Hypersensiti -heart CNS: -Magnesium levels
the second vity disturbances drowsiness, must be monitored
- Magnesium most plentiful -breathing depressed frequently by
sulfate cation of the Myocardial difficulties reflexes, flaccid checking serum
intracellular damage, -poor reflexes paralysis. levels every 6 to 8
BRAND NAME fluids. It is -confusion hours or clinically by
essential for Diabetic -weakness CV: checking patellar
- Epsom Salt the activity of coma, -flushing (warmth, hypotension, reflexes or urinary
- Sulfamag many enzyme redness, or tingly flushing, output.
systems and Heart block feeling) circulatory
CLASSIFICATION plays an -sweating collapse, - Inject I.V. bolus
important role Hypermagn -lowered blood depressed slowly to avoid
Pharmacologic with regard to esemia pressure cardiac function. respiratory or cardiac
classification: mineral/ neurochemica -feeling like you arrest.
electrolyte l transmission Hypercalce might pass out Metabolic:
and muscular mia -anxiety hypocalcemia. -Administer by
Therapeutic excitability. -cold feeling constant infusion
classification: Magnesium Administrati -extreme Respiratory: pump if possible;
anticonvulsant sulfate on during 2 drowsiness respiratory maximum infusion
reduces hours -muscle tightness paralysis rate is 150
Pregnancy risk category striated preceding or contraction, or mg/minute. Rapid
A muscle delivery for headache. Skin: drip causes feeling of
INDICATION contractions mothers diaphoresis heat.
-Prevention of seizures and blocks with
in peripheral toxemia of Other: - Test knee jerk reflex
eclampsia/preeclampsia neuromuscula pregnancy hypothermia. before each dose; if
r transmission absent, discontinue
-Constipation by reducing magnesium. Use of
acetylcholine drug beyond this
-Hypomagnesemia release at the point risks
myoneural respiratory center
-Acute nephritis junction. failure.
(pediatric patients) Additionally,
Magnesium - Monitor patient for
-Cardiac arrhythmias inhibits Ca2+ magnesium toxicity
secondary to influx through and monitor I.V.
hypomagnesemia
dihydropyridin infusion to avoid
-Soaking minor cuts or e-sensitive, circulatory overload.
bruises voltage-
DOSAGE & FREQUENCY dependent -After use in toxemic
channels. This women within 24
Preeclampsia,
accounts for hours before
Eclampsia
much of its delivery, newborn
Adult: IM/IV 4 g in 250
relaxant requires observation
mL D5W infused slowly,
action on for signs of
followed by 4–5 g IM in
vascular magnesium toxicity,
alternate buttocks q4h
smooth including
muscle. neuromuscular and
-Hypomagnesemia
respiratory
Seizures
- depression.
Adult: IM/IV Mild, 1 g
q6h for 4 doses; Severe,
-Observe newborns
250 mg/kg infused over
of mothers who
4h
received parenteral
Child: IV 20–100 mg/kg
magnesium sulfate
q4–6h prn
within a few hours of
delivery for signs of
-Laxative
toxicity, including
Adult: PO 10–15 g
respiratory and
once/d
neuromuscular
depression.
-Total Parenteral
Nutrition
-Recommended daily
Adult: IV 0.5–3 g/d
allowances of
magnesium are
obtained in a normal
-Arrhythmias.
diet. Rich sources are
Adult: give 1 to 6 g I.V.
whole-grain cereals,
over several minutes
legumes, nuts,
followed by 3- to 20-
meats, seafood, milk,
mg/minute I.V. infusion
most green leafy
for 5 to 48 hours
vegetables, and
bananas.
You might also like
- Pharmacology MCQS WITH ANS (1) - CompressedDocument289 pagesPharmacology MCQS WITH ANS (1) - Compressed09Dhawal PatilNo ratings yet
- 11111a - CarbetocinDocument3 pages11111a - Carbetocinhahahahaaaaaaa0% (2)
- Cephalexin Drug StudyDocument1 pageCephalexin Drug StudyAubrey SungaNo ratings yet
- HYDRALAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE - (Apresoline)Document1 pageHYDRALAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE - (Apresoline)wen_pilNo ratings yet
- Drug Data for Oxytocin, Methergine, Hyoscine, Vitamin K and Eye Care ProphylaxisDocument4 pagesDrug Data for Oxytocin, Methergine, Hyoscine, Vitamin K and Eye Care ProphylaxisJune Dumdumaya67% (3)
- Carboprost Thromethamine Hemabate: Not To Be Given To Pregnant WomenDocument1 pageCarboprost Thromethamine Hemabate: Not To Be Given To Pregnant Womengeorgeloto12100% (2)
- Drug Study - Ascorbic AcidDocument6 pagesDrug Study - Ascorbic Acidalyssa marie salcedo100% (1)
- Health AssessmentDocument28 pagesHealth AssessmentPiyush Dutta100% (2)
- 6 MAGNESIUM SULFATE Drug StudyDocument2 pages6 MAGNESIUM SULFATE Drug StudyGwyn Rosales100% (2)
- Magnesium SulfateDocument1 pageMagnesium SulfateIvanne Hisoler67% (3)
- Methyldopa Drug StudyDocument1 pageMethyldopa Drug Studychinchin ramosNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyNica NiñoNo ratings yet
- Hydralazine Drug StudyDocument2 pagesHydralazine Drug StudyErika Robella100% (1)
- Drug Study - Calcium GluconateDocument1 pageDrug Study - Calcium GluconatemikErlhNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY-OxytocinDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY-OxytocinCarissa Mae Tapec Estrada67% (3)
- Drug Study-Nifedipine-BALLON, Karlo C.Document2 pagesDrug Study-Nifedipine-BALLON, Karlo C.Melinda Cariño Ballon100% (1)
- Drug Study: I Loilo Doctors' College College of NursingDocument6 pagesDrug Study: I Loilo Doctors' College College of NursingAudrie Allyson GabalesNo ratings yet
- Prevent bleeding and blood clots with vitamin KDocument1 pagePrevent bleeding and blood clots with vitamin KjoellaNo ratings yet
- OB Drug Study - MethylergonovineDocument2 pagesOB Drug Study - MethylergonovineJustin Ancog0% (1)
- Clonidine & Furosemide Drugs StudyDocument3 pagesClonidine & Furosemide Drugs StudyGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication/Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibilities: GenericDocument2 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication/Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibilities: GenericArian May MarcosNo ratings yet
- MethergineDocument2 pagesMethergineRoseben SomidoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study OxytocinDocument2 pagesDrug Study Oxytocinrica sebabillonesNo ratings yet
- TerbutalineDocument1 pageTerbutalineRyan Paul Balot0% (1)
- Drug Study MisoprostolDocument2 pagesDrug Study Misoprostolrica sebabillones100% (1)
- Nursing responsibilities for vitamin K administrationDocument2 pagesNursing responsibilities for vitamin K administrationelle100% (3)
- Drug Study Dopamine HCLDocument2 pagesDrug Study Dopamine HCLA.No ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY AmoxicillinDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY AmoxicillinKhylamarie VillalunaNo ratings yet
- Methyldopa: An Alpha-2 Adrenergic Agonist for HypertensionDocument4 pagesMethyldopa: An Alpha-2 Adrenergic Agonist for HypertensionJinnijinniNo ratings yet
- Midazolam Drug Study SaclotDocument1 pageMidazolam Drug Study SaclotMaybelle Cababat Saclot100% (1)
- Sample of NCP and Drug Study EPO FINAL DRUG STUDYDocument8 pagesSample of NCP and Drug Study EPO FINAL DRUG STUDYSherina BolosNo ratings yet
- ONDANSETRONDocument1 pageONDANSETRONJugen Gumba Fuentes Alquizar0% (1)
- Calcium Gluconate Drug StudyDocument1 pageCalcium Gluconate Drug StudyMichael Baylon DueñasNo ratings yet
- Drug Study PethidineDocument2 pagesDrug Study Pethidinerica sebabillonesNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY-LidocaineDocument3 pagesDRUG STUDY-LidocaineCarissa Mae Tapec Estrada100% (1)
- Drug Study On MAGNESIUM SULFATEDocument6 pagesDrug Study On MAGNESIUM SULFATEshadow gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Glyburide Mechanism of Action, Side Effects and Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesGlyburide Mechanism of Action, Side Effects and Nursing Responsibilitiesanne marieNo ratings yet
- Trandate (Labetalol)Document3 pagesTrandate (Labetalol)ENo ratings yet
- Methyldopa Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMethyldopa Drug StudyBea Dela Cena100% (1)
- WVSU Nursing Drug Study OxytocinDocument3 pagesWVSU Nursing Drug Study OxytocinJulie MayNo ratings yet
- Drug Study DexamethasoneDocument4 pagesDrug Study Dexamethasoneamal abdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- Nifedipine Drug StudyDocument3 pagesNifedipine Drug StudyCrystal Queen MarquezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - LevothyroxineDocument1 pageDrug Study - LevothyroxineCarla Tongson Maravilla100% (1)
- DS HydralazineDocument3 pagesDS HydralazineGe LoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Valerie V. Villanueva BN3-CDocument1 pageDrug Study: Valerie V. Villanueva BN3-CValerie VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- PaclitaxelDocument3 pagesPaclitaxelGwyn Rosales100% (1)
- Drug Mechanism of Action/side Effects Indication/ Contraindication Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument1 pageDrug Mechanism of Action/side Effects Indication/ Contraindication Nursing ResponsibilitiesSheryhan Tahir BayleNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Amoxicillin Mechanism and Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument3 pagesDrug Study: Amoxicillin Mechanism and Nursing ResponsibilitiesKrzia TehNo ratings yet
- Drug Sudy Format MethyldopaDocument3 pagesDrug Sudy Format MethyldopaBianca Marithè RejanoNo ratings yet
- Methyldopa Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMethyldopa Drug Studymilkv100% (14)
- CaptoprilDocument2 pagesCaptoprilJohn Louie EscardaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Amoxicillin PDFDocument4 pagesDrug Study Amoxicillin PDFMc SantosNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Effects and Nursing ConsiderationsDocument2 pagesDrug Study Effects and Nursing ConsiderationsCelline Isabelle ReyesNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyBrix John PortellanoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: ChlorthalidoneDocument2 pagesDrug Study: ChlorthalidoneLIEZEL GRACE VELAYONo ratings yet
- Drug Study SalbutamolDocument2 pagesDrug Study Salbutamolprince gonzales100% (1)
- Acyclovir Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComDocument3 pagesAcyclovir Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComJanaica JuanNo ratings yet
- Ferrous Sulfate Supplement GuideDocument1 pageFerrous Sulfate Supplement GuidezjoshuacNo ratings yet
- Drug Study LabetalolDocument2 pagesDrug Study LabetalolJanzelvine Lee MontenegroNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Nursing DepartmentDocument1 pageDrug Study: Nursing Departmentgiselle chloe100% (1)
- MENDOZA, Francis Luigi C. - DRUG STUDY MAGNESIUM SULFATEDocument2 pagesMENDOZA, Francis Luigi C. - DRUG STUDY MAGNESIUM SULFATEbaka esh toNo ratings yet
- Drug Study-MsGO4 (A)Document3 pagesDrug Study-MsGO4 (A)Ronel ResurricionNo ratings yet
- Health Declaration Form: (Buong Pangalan) (Petsa) (Oras) (Kasa/ukuyang Tirahan) : (Numero NG Telepono)Document2 pagesHealth Declaration Form: (Buong Pangalan) (Petsa) (Oras) (Kasa/ukuyang Tirahan) : (Numero NG Telepono)Carissa Mae Tapec EstradaNo ratings yet
- Group Presentation RubricDocument1 pageGroup Presentation RubricCarissa Mae Tapec EstradaNo ratings yet
- PHINMA University of Pangasinan Syllabus: Pen Code Credit PEN Subject Title Prerequisite A. Subject DescriptionDocument2 pagesPHINMA University of Pangasinan Syllabus: Pen Code Credit PEN Subject Title Prerequisite A. Subject DescriptionCarissa Mae Tapec EstradaNo ratings yet
- Carissa Estrada Activity No. 9 EnzymesDocument3 pagesCarissa Estrada Activity No. 9 EnzymesCarissa Mae Tapec EstradaNo ratings yet
- Caring For Patients Who Refuse Blood A Guide To Good Practice PDFDocument40 pagesCaring For Patients Who Refuse Blood A Guide To Good Practice PDFSpop SevenNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Chapter1notesDocument6 pagesAnaphy Chapter1notesCarissa Mae Tapec EstradaNo ratings yet
- The Five Pillars of Islamic BeliefsDocument3 pagesThe Five Pillars of Islamic BeliefsCarissa Mae Tapec EstradaNo ratings yet
- NUTRITION NOTESDocument10 pagesNUTRITION NOTESCarissa Mae Tapec EstradaNo ratings yet
- Mat152 Final Quiz Set CDocument2 pagesMat152 Final Quiz Set CCarissa Mae Tapec EstradaNo ratings yet
- Letter of Explaination 1Document1 pageLetter of Explaination 1Carissa Mae Tapec EstradaNo ratings yet
- Gen 002 Midterm Performance TaskDocument2 pagesGen 002 Midterm Performance TaskCarissa Mae Tapec EstradaNo ratings yet
- Stress SssssDocument1 pageStress SssssCarissa Mae Tapec EstradaNo ratings yet
- Caring For Patients Who Refuse Blood A Guide To Good Practice PDFDocument40 pagesCaring For Patients Who Refuse Blood A Guide To Good Practice PDFSpop SevenNo ratings yet
- PersuasiveDocument2 pagesPersuasiveCarissa Mae Tapec EstradaNo ratings yet
- Gen 017 Lesson 9Document4 pagesGen 017 Lesson 9Carissa Mae Tapec EstradaNo ratings yet
- Family Planning GATHER APPROACH CounselingDocument3 pagesFamily Planning GATHER APPROACH CounselingCarissa Mae Tapec EstradaNo ratings yet
- Analgesia For Forceps DeliveryDocument2 pagesAnalgesia For Forceps DeliveryCarissa Mae Tapec EstradaNo ratings yet
- Anti AbortionDocument1 pageAnti AbortionCarissa Mae Tapec EstradaNo ratings yet
- Gen 017 - Lesson 8Document3 pagesGen 017 - Lesson 8Carissa Mae Tapec EstradaNo ratings yet
- Day 8 Pharma RationaleDocument1 pageDay 8 Pharma RationaleCarissa Mae Tapec EstradaNo ratings yet
- Interview With A Community Health Nurse: MissDocument4 pagesInterview With A Community Health Nurse: MissCarissa Mae Tapec EstradaNo ratings yet
- Essay Quiz 2 2. What Activity, Really Affects Your Condition This Midst of PandemicDocument1 pageEssay Quiz 2 2. What Activity, Really Affects Your Condition This Midst of PandemicCarissa Mae Tapec EstradaNo ratings yet
- THE Florida State University College OF Medicine: Complete History Checklist Clinical Skills Course MS1-3Document5 pagesTHE Florida State University College OF Medicine: Complete History Checklist Clinical Skills Course MS1-3mj Canilang100% (1)
- Gen 017 - Lesson 8Document3 pagesGen 017 - Lesson 8Carissa Mae Tapec EstradaNo ratings yet
- NCP VacuumDocument5 pagesNCP VacuumCarissa Mae Tapec EstradaNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 - Module 3Document2 pagesActivity 2 - Module 3Carissa Mae Tapec EstradaNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY-OxytocinDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY-OxytocinCarissa Mae Tapec Estrada67% (3)
- Gen 017 - Lesson 8Document3 pagesGen 017 - Lesson 8Carissa Mae Tapec EstradaNo ratings yet
- Gen 017 Lesson 9Document4 pagesGen 017 Lesson 9Carissa Mae Tapec EstradaNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY-LidocaineDocument3 pagesDRUG STUDY-LidocaineCarissa Mae Tapec Estrada100% (1)
- The Pathogenesis of The Diabetic Foot UlcerDocument29 pagesThe Pathogenesis of The Diabetic Foot UlcernyuwwchocolavaNo ratings yet
- IB - Biocompatibility and Therapeutic Evaluation of Magnetic Liposomes Designed For Self-Controlled Cancer Hyperthermia and ChemotherapyDocument11 pagesIB - Biocompatibility and Therapeutic Evaluation of Magnetic Liposomes Designed For Self-Controlled Cancer Hyperthermia and ChemotherapyManash GogoiNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test in TLE 8 - 2nd QuarterDocument31 pagesDiagnostic Test in TLE 8 - 2nd QuarterRowel NillasNo ratings yet
- FINAL Biodiversity Baseline KNI-Pomalaa - 06!03!2023Document88 pagesFINAL Biodiversity Baseline KNI-Pomalaa - 06!03!2023lee alexphoneNo ratings yet
- NCMB 418 Midterm ReviewerDocument13 pagesNCMB 418 Midterm ReviewerMARIA KYLA PAMANo ratings yet
- Unit h420 01 Biological Processes Sample Assessment MaterialsDocument48 pagesUnit h420 01 Biological Processes Sample Assessment MaterialsGozde Ozan BayraktarNo ratings yet
- Day 37 - Daily MCQ Workout - 40 Revision MCQsDocument5 pagesDay 37 - Daily MCQ Workout - 40 Revision MCQsBobbyNo ratings yet
- Cultivation of Fruitbodies and SclerotiaDocument4 pagesCultivation of Fruitbodies and SclerotiaEsporas De MexicoNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy & NeurophysiologyDocument5 pagesNeuroanatomy & NeurophysiologyTahir AhmadNo ratings yet
- Biological Treatment of Palm Oil Mill Effluent (Pome) Using An Up-Flow Anaerobic SludgeDocument53 pagesBiological Treatment of Palm Oil Mill Effluent (Pome) Using An Up-Flow Anaerobic SludgeJim ChongNo ratings yet
- The Biomedical Engineering Handbook: Second EditionDocument13 pagesThe Biomedical Engineering Handbook: Second EditionEng-Mugahed AlmansorNo ratings yet
- Identificación PolygonumDocument8 pagesIdentificación PolygonumvalentinaNo ratings yet
- Blood Bank Quality ProgramDocument28 pagesBlood Bank Quality ProgramMohamed Elmasry100% (1)
- Giant Cell Tumor - CompleteDocument35 pagesGiant Cell Tumor - CompletewildanmalikNo ratings yet
- Body Fluids & ElectrolytesDocument26 pagesBody Fluids & ElectrolytesMohamad Zekry Zuhairy100% (1)
- ESE200 Online TextbookDocument594 pagesESE200 Online TextbookSuren UlaganathanNo ratings yet
- Future Developments in BiosensorsDocument6 pagesFuture Developments in BiosensorsJigyasu JunejaNo ratings yet
- PERDEV ReviewerDocument5 pagesPERDEV ReviewerKrystian BonghanoyNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 March 30 Biology Chapter 1 Reproduction in OrganismsDocument6 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 12 March 30 Biology Chapter 1 Reproduction in Organismstechno indiaNo ratings yet
- Patient Centered Medicineresident ปี 1 พศ. 57 BenjapornDocument45 pagesPatient Centered Medicineresident ปี 1 พศ. 57 BenjapornPao RattanawanNo ratings yet
- 1.02 General Pathology - Cellular Pathology (Part 2) - Dr. Abelardo AleraDocument7 pages1.02 General Pathology - Cellular Pathology (Part 2) - Dr. Abelardo AleraCherry RahimaNo ratings yet
- Fotosintesis 1213Document25 pagesFotosintesis 1213scanny16No ratings yet
- The Typification and Status of Phymatolithon Corallinaceae RhodophytaDocument27 pagesThe Typification and Status of Phymatolithon Corallinaceae RhodophytaJamesNo ratings yet
- Regenerative Medicine and Tissue Engineering - Cells and BiomaterialsDocument602 pagesRegenerative Medicine and Tissue Engineering - Cells and BiomaterialsMarlena RindasuNo ratings yet
- Gustafsson 2017Document443 pagesGustafsson 2017Shennovy MarllonNo ratings yet
- Hematologic EffectsDocument8 pagesHematologic EffectsGiralph NikkoNo ratings yet
- Anti-H PyloripaperDocument10 pagesAnti-H PyloripaperLeandro DouglasNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology COVID-19 (SARS-Cov-2) RT-PCR: 80994699 Mr.I C SharmaDocument1 pageMolecular Biology COVID-19 (SARS-Cov-2) RT-PCR: 80994699 Mr.I C SharmaMohd YasarNo ratings yet