Professional Documents
Culture Documents
LS10 1Pg1
Uploaded by
sinned680 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views1 pageNotochord is a strong, rod-like structure in chordates that can bend. Located just below the nerve cord that runs down the back of the animal. Chordates have a bilateral symmetry. - each half is a mirror image of the other.
Original Description:
Original Title
LS10-1Pg1
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentNotochord is a strong, rod-like structure in chordates that can bend. Located just below the nerve cord that runs down the back of the animal. Chordates have a bilateral symmetry. - each half is a mirror image of the other.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views1 pageLS10 1Pg1
Uploaded by
sinned68Notochord is a strong, rod-like structure in chordates that can bend. Located just below the nerve cord that runs down the back of the animal. Chordates have a bilateral symmetry. - each half is a mirror image of the other.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
LIFE SCIENCE 10-1 What are chordates?
OBJ: Identify the structure of chordates.
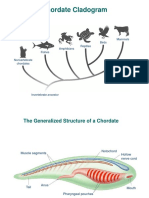
I. Phylum Chordata - fish, frogs, snakes, birds, cats, and many other
animals have had a notochord at sometime.
NOTOCHORD = strong, rod-like structure in chordates that can bend.
- it is used for support.
- it is located just below the nerve cord that runs down
the back of the animal.
CHORDATE = animal with a notochord at the sometime during its
development.
- classified in the phylum CHORDATA.
II. Other Chordate Features - hollow nerve cord.
Nerve Cord - carries messages between all the nerves in the body
and the brain.
- Chordates have paired gill slits at some point in their
development.
Gills - are used to take in oxygen dissolved in water.
III. Body Plan of Chordates - Chordates have a bilateral symmetry.
- each half is a mirror image of the other.
- Chordates have a tail at some point in their
development.
- in humans it is reduced to a tailbone.
- Chordates have many organ systems.
- closed circulatory system, made up of a heart
and many blood vessels.
- highest developed nervous system of all
animals.
III. Lancelets - In most adult chordates, the notochord is replaced by
a backbone.
- Lancelets are small, fishlike animals that keep their
notochord throughout its life.
You might also like
- Phylum Chordata TransesDocument2 pagesPhylum Chordata TransesMaribel Ramos InterinoNo ratings yet
- 7 Unikonta - Deuterostomes & ChordatesDocument5 pages7 Unikonta - Deuterostomes & ChordateskahiauNo ratings yet
- ProtochordataDocument7 pagesProtochordataricoghofarNo ratings yet
- 1 Animal DiversityDocument31 pages1 Animal DiversityAnjan Tej NayakNo ratings yet
- Intro To Chordates - PPT WeeblyDocument53 pagesIntro To Chordates - PPT Weeblyapi-375285021100% (1)
- Lab 13 Animals 2: The Evolution of VertebratesDocument25 pagesLab 13 Animals 2: The Evolution of Vertebrates13ucciNo ratings yet
- 3 - Phylum Chordata Characteristics 29.11.21Document29 pages3 - Phylum Chordata Characteristics 29.11.21Student 365No ratings yet
- Module 1 Chapters 1 and 2Document125 pagesModule 1 Chapters 1 and 2Liana Marie Castro DavidNo ratings yet
- 2 - Intro To ChordatesDocument19 pages2 - Intro To Chordatesapi-375285021No ratings yet
- Chor DatesDocument95 pagesChor DatesKavitaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: What Are Chordates?: DeuterostomiaDocument82 pagesChapter 1: What Are Chordates?: Deuterostomiaamare aleneNo ratings yet
- A1.3b Chordata (Handout) - 2018Document3 pagesA1.3b Chordata (Handout) - 2018Wayne DayataNo ratings yet
- 29.1A Characteristics of ChordataDocument2 pages29.1A Characteristics of ChordataEirah Gabrielle RiducaNo ratings yet
- Vertebrates: Characteristics and EvolutionDocument130 pagesVertebrates: Characteristics and EvolutionNurl AinaNo ratings yet
- Chordates: Animals With Notochords and Nerve CordsDocument11 pagesChordates: Animals With Notochords and Nerve CordsMarcelle MedeirosNo ratings yet
- CH03Document34 pagesCH03BlueberryNo ratings yet
- Phylum Chordata & Vert IntroDocument22 pagesPhylum Chordata & Vert IntroFarman khanNo ratings yet
- Vetabrate NoteDocument23 pagesVetabrate NoteWong Chui SanNo ratings yet
- Comparative Vertebrate AnatomyDocument3 pagesComparative Vertebrate AnatomyDaniel KangNo ratings yet
- Invertebrates Chordata VertebratesDocument62 pagesInvertebrates Chordata VertebratesDao Ming SiNo ratings yet
- Activity 2Document4 pagesActivity 2Leopoldo ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- Comparative Anatomy Lecture Series - 1Document44 pagesComparative Anatomy Lecture Series - 1shutterspeedisfNo ratings yet
- Characters of ChordatesDocument5 pagesCharacters of ChordatesAnonymous J6r3IlQzQxNo ratings yet
- Gurumantra of Zoology Final File) - RemovedDocument11 pagesGurumantra of Zoology Final File) - RemovedShivam GuptaNo ratings yet
- Biol 1002 Exam2 NotesDocument21 pagesBiol 1002 Exam2 NotesJashayla GillespieNo ratings yet
- Klasifikasi Dan Ciri-Ciri Chordata, Klasifikasi Ciri-CiriDocument22 pagesKlasifikasi Dan Ciri-Ciri Chordata, Klasifikasi Ciri-Ciriincxx100% (2)
- Animals - Adaptations Endoskeleton, Echinoderms, Invert Chordates, VertebratesDocument9 pagesAnimals - Adaptations Endoskeleton, Echinoderms, Invert Chordates, VertebratessmedificationNo ratings yet
- What Is Morphology?Document26 pagesWhat Is Morphology?Michael Vincent P.No ratings yet
- Product Task OriginalDocument21 pagesProduct Task OriginalHeidi BrionesNo ratings yet
- ChordatesDocument43 pagesChordatesafiqah fatina zahraNo ratings yet
- Reptila To MamDocument41 pagesReptila To MamVivek BaisNo ratings yet
- Deuterostomes: Echinoderms and ChordatesDocument10 pagesDeuterostomes: Echinoderms and ChordatesFloyd SeremNo ratings yet
- Reptiles 1Document1 pageReptiles 1dddadNo ratings yet
- Science RemedialDocument3 pagesScience RemedialSalsa rsNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking On Certain Questions Concerning Comparative Anatomy of The VertebratesDocument5 pagesCritical Thinking On Certain Questions Concerning Comparative Anatomy of The VertebratesSeth Andrew SalihNo ratings yet
- BTM 111 22Document24 pagesBTM 111 22Toke SadockNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document87 pagesUnit 1Shawa DabaNo ratings yet
- UNIT-25 (Taxonomy Invertebrates and Vertebrates)Document25 pagesUNIT-25 (Taxonomy Invertebrates and Vertebrates)c r e a m p i eNo ratings yet
- 5 - Invertebrate & Vertebrate Animals - PrintDocument35 pages5 - Invertebrate & Vertebrate Animals - PrintInmaculada Campos RomeroNo ratings yet
- Lecture 03 - Classification of ChordatesDocument26 pagesLecture 03 - Classification of Chordatesmasif gondalNo ratings yet
- Cleveland P. Hickman-Integrated Principles of Zoology, Fourteenth Edition-Mcgraw-Hill College (2007) - 511-528Document18 pagesCleveland P. Hickman-Integrated Principles of Zoology, Fourteenth Edition-Mcgraw-Hill College (2007) - 511-528tasya dhanaNo ratings yet
- 1A ChordataDocument76 pages1A ChordataDeepak ThakurNo ratings yet
- AnimaliaDocument68 pagesAnimaliaNovelynLozano-EdrosoNo ratings yet
- Invertebrate Lab 6 - Cnidarians, Hydra, Mollusks & OctopusDocument17 pagesInvertebrate Lab 6 - Cnidarians, Hydra, Mollusks & OctopusShaker MahmoodNo ratings yet
- 1.diversity of Animal LifeDocument39 pages1.diversity of Animal Lifekapil Rajputpl100% (1)
- Coral Reef OrganismsDocument3 pagesCoral Reef OrganismsNathaniel AndrewsNo ratings yet
- Phylum Chordata (Notes)Document1 pagePhylum Chordata (Notes)Kristine Claire AlberioNo ratings yet
- Discover the Diverse World of ReptilesDocument32 pagesDiscover the Diverse World of ReptilesCreate VinayNo ratings yet
- Bio 112 (Phylum Chordata) - 1Document5 pagesBio 112 (Phylum Chordata) - 1Amaan B EydreesNo ratings yet
- Project IN Science: Submitted By: Rovie Mark Y. Lopez Grade 6-Juan Luna Submitted To: Mr. Bernardino N. LibaoDocument34 pagesProject IN Science: Submitted By: Rovie Mark Y. Lopez Grade 6-Juan Luna Submitted To: Mr. Bernardino N. LibaoAlexanderLopezNebresNo ratings yet
- National Curriculum English Version: Knowledge Based Questions and Comprehensive QuestionsDocument7 pagesNational Curriculum English Version: Knowledge Based Questions and Comprehensive QuestionsStephenCovey100% (1)
- BIO 35 Chapter 2 - Nerve PhysiologyDocument14 pagesBIO 35 Chapter 2 - Nerve PhysiologyJake EverettNo ratings yet
- Protostome EvolDocument14 pagesProtostome EvolFiixaa B OlqabaaNo ratings yet
- VertebratesDocument8 pagesVertebratesfeya ayefNo ratings yet
- Animals 1Document2 pagesAnimals 1alxndrasenalesNo ratings yet
- LS10 5Pg1Document1 pageLS10 5Pg1sinned68No ratings yet
- Chordate Evolution from InvertebratesDocument203 pagesChordate Evolution from InvertebratesYhan Brotamonte BoneoNo ratings yet
- ChordataDocument28 pagesChordatatinchu guptaNo ratings yet
- Vert 1Document18 pagesVert 1Shaker MahmoodNo ratings yet
- The Book of Shells: Containing the Classes Mollusca, Conchifera, Cirrhipeda, Annulata, and CrustaceaFrom EverandThe Book of Shells: Containing the Classes Mollusca, Conchifera, Cirrhipeda, Annulata, and CrustaceaNo ratings yet
- Offensve Line Blocking ProgressionDocument9 pagesOffensve Line Blocking Progressionsinned68No ratings yet
- East Los Angeles College Pass ProtectionDocument15 pagesEast Los Angeles College Pass Protectionsinned68No ratings yet
- LS10 7Pg1Document1 pageLS10 7Pg1sinned68No ratings yet
- LS10 5Pg2ClozeDocument1 pageLS10 5Pg2Clozesinned68No ratings yet
- LS10 8Document1 pageLS10 8sinned68No ratings yet
- LS10 5Pg2Document1 pageLS10 5Pg2sinned68No ratings yet
- LS10 7Pg2Document1 pageLS10 7Pg2sinned68No ratings yet
- Laguna Hills El Toro Capo Valley Woodbridge: Pacifica Newport Harbor Irvine UniversityDocument1 pageLaguna Hills El Toro Capo Valley Woodbridge: Pacifica Newport Harbor Irvine Universitysinned68No ratings yet
- LS10 7Pg2ClozeDocument1 pageLS10 7Pg2Clozesinned68No ratings yet
- LS10 7Pg1ClozeDocument1 pageLS10 7Pg1Clozesinned68No ratings yet
- LS10 6Document1 pageLS10 6sinned68No ratings yet
- LS10 6clozeDocument1 pageLS10 6clozesinned68No ratings yet
- LS10 5Pg1Document1 pageLS10 5Pg1sinned68No ratings yet
- LS10 5Pg1Document1 pageLS10 5Pg1sinned68No ratings yet
- LS10 1Pg2ClozeDocument1 pageLS10 1Pg2Clozesinned68No ratings yet
- LS10 4Document1 pageLS10 4sinned68No ratings yet
- LS10 1Pg2Document1 pageLS10 1Pg2sinned68No ratings yet
- LS10 4clozeDocument1 pageLS10 4clozesinned68No ratings yet
- LS10 1Pg1ClozeDocument1 pageLS10 1Pg1Clozesinned68No ratings yet
- LS9 10clozeDocument1 pageLS9 10clozesinned68No ratings yet
- LS9 8ClozePg2Document1 pageLS9 8ClozePg2sinned68No ratings yet
- LS9 10Document1 pageLS9 10sinned68No ratings yet
- LS9 8Document1 pageLS9 8sinned68No ratings yet
- LS9 9clozeDocument1 pageLS9 9clozesinned68No ratings yet
- LS9 8ClozePg1Document1 pageLS9 8ClozePg1sinned68No ratings yet
- LIFE SCIENCE 9-6 What Are Echinoderms?: OBJ: List Common Characteristics of Echinoderms. Name Some EchinodermsDocument1 pageLIFE SCIENCE 9-6 What Are Echinoderms?: OBJ: List Common Characteristics of Echinoderms. Name Some Echinodermssinned68No ratings yet
- LS9 9Document1 pageLS9 9sinned68No ratings yet
- LS9 7clozeDocument1 pageLS9 7clozesinned68No ratings yet
- LS9 7Document1 pageLS9 7sinned68No ratings yet
- Toyota TPMDocument23 pagesToyota TPMchteo1976No ratings yet
- Mar 2021Document2 pagesMar 2021TanNo ratings yet
- MASM Tutorial PDFDocument10 pagesMASM Tutorial PDFShashankDwivediNo ratings yet
- V-AMP3: User ManualDocument19 pagesV-AMP3: User Manualnutmeg_kickerNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Lymphatic System and Body DefensesDocument10 pagesLesson 3 Lymphatic System and Body DefensesJulio De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- 13 Years of Unremitting Tracking of Chinese Scientists To Find The Source of SARS Virus - NewsDocument14 pages13 Years of Unremitting Tracking of Chinese Scientists To Find The Source of SARS Virus - NewsWillSmathNo ratings yet
- Managment Information Question BankDocument302 pagesManagment Information Question BankLuca Papasizza100% (2)
- 2006 - Bykovskii - JPP22 (6) Continuous Spin DetonationsDocument13 pages2006 - Bykovskii - JPP22 (6) Continuous Spin DetonationsLiwei zhangNo ratings yet
- Limiting and Excess Reactants Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesLimiting and Excess Reactants Lesson Planapi-316338270100% (3)
- Fuzzy Logic - Wikipedia PDFDocument69 pagesFuzzy Logic - Wikipedia PDFannie joseNo ratings yet
- Vdoc - Pub Parrys Valuation and Investment TablesDocument551 pagesVdoc - Pub Parrys Valuation and Investment TablesWan Rosman100% (1)
- Proceedings of The 2012 PNLG Forum: General AssemblyDocument64 pagesProceedings of The 2012 PNLG Forum: General AssemblyPEMSEA (Partnerships in Environmental Management for the Seas of East Asia)No ratings yet
- Ward A. Thompson v. City of Lawrence, Kansas Ron Olin, Chief of Police Jerry Wells, District Attorney Frank Diehl, David Davis, Kevin Harmon, Mike Hall, Ray Urbanek, Jim Miller, Bob Williams, Craig Shanks, John Lewis, Jack Cross, Catherine Kelley, Dan Ward, James Haller, Dave Hubbell and Matilda Woody, Frances S. Wisdom v. City of Lawrence, Kansas Ron Olin, Chief of Police David Davis, Mike Hall, Jim Miller, Bob Williams, Craig Shanks, John L. Lewis, Jack Cross, Kevin Harmon, Catherine Kelley, Dan Ward and James Haller, Jr., 58 F.3d 1511, 10th Cir. (1995)Document8 pagesWard A. Thompson v. City of Lawrence, Kansas Ron Olin, Chief of Police Jerry Wells, District Attorney Frank Diehl, David Davis, Kevin Harmon, Mike Hall, Ray Urbanek, Jim Miller, Bob Williams, Craig Shanks, John Lewis, Jack Cross, Catherine Kelley, Dan Ward, James Haller, Dave Hubbell and Matilda Woody, Frances S. Wisdom v. City of Lawrence, Kansas Ron Olin, Chief of Police David Davis, Mike Hall, Jim Miller, Bob Williams, Craig Shanks, John L. Lewis, Jack Cross, Kevin Harmon, Catherine Kelley, Dan Ward and James Haller, Jr., 58 F.3d 1511, 10th Cir. (1995)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Geller (LonginusRhetoric'sCure)Document27 pagesGeller (LonginusRhetoric'sCure)Miguel AntónioNo ratings yet
- EDU101 Solution FileDocument2 pagesEDU101 Solution FileTahaNo ratings yet
- Enneagram Type-2Document18 pagesEnneagram Type-2pundirNo ratings yet
- Student Teaching Edtpa Lesson Plan TemplateDocument7 pagesStudent Teaching Edtpa Lesson Plan Templateapi-3531253350% (1)
- 20 Reasons Composers Fail 2019 Reprint PDFDocument30 pages20 Reasons Composers Fail 2019 Reprint PDFAlejandroNo ratings yet
- Understanding electromagnetic waves and radioactivityDocument7 pagesUnderstanding electromagnetic waves and radioactivityJayesh VermaNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Compliance ATF F 5330 20Document2 pagesCertificate of Compliance ATF F 5330 20Jojo Aboyme CorcillesNo ratings yet
- Write The Missing Words of The Verb To Be (Affirmative Form)Document1 pageWrite The Missing Words of The Verb To Be (Affirmative Form)Daa NnaNo ratings yet
- Vaccination Consent Form: Tetanus, Diphtheria / Inactivated Polio Vaccine (DTP) & Meningococcal ACWY (Men ACWY)Document2 pagesVaccination Consent Form: Tetanus, Diphtheria / Inactivated Polio Vaccine (DTP) & Meningococcal ACWY (Men ACWY)meghaliNo ratings yet
- 2015 Masonry Codes and Specifications Compilation, MCAA StoreDocument1 page2015 Masonry Codes and Specifications Compilation, MCAA StoreMuhammad MurtazaNo ratings yet
- The Revival Strategies of Vespa Scooter in IndiaDocument4 pagesThe Revival Strategies of Vespa Scooter in IndiaJagatheeswari SelviNo ratings yet
- Text Detection and Recognition in Raw Image Dataset of Seven Segment Digital Energy Meter DisplayDocument11 pagesText Detection and Recognition in Raw Image Dataset of Seven Segment Digital Energy Meter DisplaykkarthiksNo ratings yet
- Compatibility Testing: Week 5Document33 pagesCompatibility Testing: Week 5Bridgette100% (1)
- Creating Early Learning Environments PDFDocument25 pagesCreating Early Learning Environments PDFkrisnahNo ratings yet
- CH1 Ncert 11th BiologyDocument18 pagesCH1 Ncert 11th Biologysomnathsharma777No ratings yet
- Summer Training Report at Bikanervala FoodsDocument21 pagesSummer Training Report at Bikanervala FoodsVanshika Srivastava 17IFT017100% (1)
- It - Unit 14 - Assignment 2 1Document8 pagesIt - Unit 14 - Assignment 2 1api-669143014No ratings yet