Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Manual Mechanics
Uploaded by
Dennis CosmodOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Manual Mechanics
Uploaded by
Dennis CosmodCopyright:
Available Formats
Mechanics-branch of Physics that deals with the study of motion Branches of Mechanics: 1.
Kinematics-branch of mechanics that deals with the mathematical description of motion. This deals with the HOWs of motion. How fast? How slow? How long? How far? 2. Dynamics-branch of mechanics that deals with the reasons or explanations of motion. This deals with the WHYs of motion. Why is it moving? Why is it not moving? Types of Motion: 1. 2. 3. 4.
Linear motion- motion in a straight line; example: straight race track Circular motion- motion in a curved path or in a circle; example: fairies wheel Rotational motion-example: electric fan Vibrational motion-example: pendulum
KINEMATICS Galileo Galilie called as the founder of modern experimental science started the concept of Kinematics by describing motion in terms of times rates of change such as speed, velocity and acceleration since these three quantities involve distance and time, therefore the fundamental quantities of motion are distance, time, speed, velocity and acceleration. DISTANCE-the total length traveled DISPLACEMENT-the total length traveled plus direction Distance can be measured by any length measuring device such as rulers, tape measures and etc.
Speed is the distance traveled by a moving object per unit time. Velocity is the distance traveled by a moving object per unit time plus direction
Instantaneous Speed of a moving object is the speed at which the object is moving at any given instant. Instantaneous Velocity is instantaneous speed plus direction
You might also like
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- UntitledDocument3 pagesUntitledDennis CosmodNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Table of PenaltiesDocument64 pagesTable of PenaltiesDennis Cosmod100% (1)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- 2020-EO Amendment EO 05-005 Reorganization CIC EOCDocument4 pages2020-EO Amendment EO 05-005 Reorganization CIC EOCDennis CosmodNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- 2021-EO Reorganization CIC EOCDocument5 pages2021-EO Reorganization CIC EOCDennis CosmodNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- 2021-EO New Localized Guidelines November GCQDocument6 pages2021-EO New Localized Guidelines November GCQDennis CosmodNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- 2019-Annual Plan For PostingDocument2 pages2019-Annual Plan For PostingDennis CosmodNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Stage of Civil Cases Period Responsible Person Requirements Effects Other NotesDocument2 pagesStage of Civil Cases Period Responsible Person Requirements Effects Other NotesDennis CosmodNo ratings yet
- 2021-EO New Localized Guidelines August GCQDocument5 pages2021-EO New Localized Guidelines August GCQDennis CosmodNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- 2222 ACTIVITY-PROPOSAL-1st-Quarter-Meeting-2020Document2 pages2222 ACTIVITY-PROPOSAL-1st-Quarter-Meeting-2020Dennis CosmodNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- SWM Ordinance Final DraftDocument58 pagesSWM Ordinance Final DraftDennis CosmodNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Accomplishments Text For Board FanDocument5 pagesAccomplishments Text For Board FanDennis CosmodNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Script-Mr M2015Document5 pagesScript-Mr M2015Dennis CosmodNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Sustainable Development Goals An OverviewDocument10 pagesSustainable Development Goals An OverviewDennis CosmodNo ratings yet
- Womens Month Celebration 2017Document7 pagesWomens Month Celebration 2017Dennis Cosmod100% (4)
- Functional Statements, Objectives and Expected Results: Annual Dev't Plan 1 Jan-16 Dec-16Document4 pagesFunctional Statements, Objectives and Expected Results: Annual Dev't Plan 1 Jan-16 Dec-16Dennis CosmodNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- LYDCDocument13 pagesLYDCDennis Cosmod100% (1)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Samar State University Midterm Exams in PhysicsDocument3 pagesSamar State University Midterm Exams in PhysicsDennis CosmodNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Teachers ListDocument3 pagesTeachers ListDennis CosmodNo ratings yet
- Affidavit-Complaint: Bank Check No. Date of Check Amount Date PresentedDocument2 pagesAffidavit-Complaint: Bank Check No. Date of Check Amount Date PresentedDennis CosmodNo ratings yet
- City of Catbalogan: Office of The Mayor MessageDocument1 pageCity of Catbalogan: Office of The Mayor MessageDennis CosmodNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Judicial Affidavit-Cabada ComplainantDocument6 pagesJudicial Affidavit-Cabada ComplainantDennis CosmodNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Complaint SupportDocument4 pagesComplaint SupportDennis CosmodNo ratings yet
- 16letter Tribu K Excuse LetterDocument4 pages16letter Tribu K Excuse LetterDennis CosmodNo ratings yet
- Judicial Affidavit RobberyDocument3 pagesJudicial Affidavit RobberyDennis Cosmod80% (35)
- Civil Service Form NoDocument4 pagesCivil Service Form NoDennis CosmodNo ratings yet
- Asia Pacific Conference-Programme GuidelineDocument3 pagesAsia Pacific Conference-Programme GuidelineDennis CosmodNo ratings yet
- 15speech Children MonthDocument3 pages15speech Children MonthDennis CosmodNo ratings yet
- Judicial Affidavit-Attempted Homicide AccusedDocument4 pagesJudicial Affidavit-Attempted Homicide AccusedDennis Cosmod70% (20)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Calculation of The Flight Characteristics of The Aircraft, An-225Document15 pagesCalculation of The Flight Characteristics of The Aircraft, An-225Mohamed Sherif Ahmed SolimanNo ratings yet
- Flow of Compressible Fluids - UnlockedDocument32 pagesFlow of Compressible Fluids - UnlockedBianca BayumbonNo ratings yet
- 3 Aperture-Shared - Millimeter-Wave - Sub-6 - GHZ - Dual-Band - Antenna - Hybridizing - FabryProt - Cavity - and - Fresnel - Zone - PlateDocument12 pages3 Aperture-Shared - Millimeter-Wave - Sub-6 - GHZ - Dual-Band - Antenna - Hybridizing - FabryProt - Cavity - and - Fresnel - Zone - PlateAnuj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Dynamics: Vector Mechanics For EngineersDocument32 pagesDynamics: Vector Mechanics For EngineersMadhulaalasa KurmaNo ratings yet
- Wave WorksheetDocument11 pagesWave WorksheetShigenobu MiñozaNo ratings yet
- GravitationDocument3 pagesGravitationshweta SharmaNo ratings yet
- Circular Orbits Under Central Forces in Special Relativity: August 2004Document8 pagesCircular Orbits Under Central Forces in Special Relativity: August 2004Vishal NarnauliaNo ratings yet
- Exam I: Turabo University School of Engineering Department of Mechanical Engineering MEEN 621 Boundary LayersDocument2 pagesExam I: Turabo University School of Engineering Department of Mechanical Engineering MEEN 621 Boundary LayersJoseph O. Camacho IrizarryNo ratings yet
- Boundary LayerDocument8 pagesBoundary LayerVenkatarao ChukkaNo ratings yet
- Homework 6Document5 pagesHomework 6Stephen RandallNo ratings yet
- Radio Wave Propagation1Document21 pagesRadio Wave Propagation1Kenth Salcedo SallegueNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Experiment 204: Torque: Second Condition of Equilibrium: Result and DiscussionDocument5 pagesExperiment 204: Torque: Second Condition of Equilibrium: Result and DiscussionDave Vendivil SambranoNo ratings yet
- 02A - Modul A+ Fizik Tg4Document22 pages02A - Modul A+ Fizik Tg4Marry Jane100% (4)
- CE222 Problem Set 2Document12 pagesCE222 Problem Set 2Mehmet ArasNo ratings yet
- EGM3401 Funwork 8Document4 pagesEGM3401 Funwork 8Jerome SiegelNo ratings yet
- By Ian Stewart: Nature's Numbers: The Unreal Reality of Mathematical ImaginationDocument4 pagesBy Ian Stewart: Nature's Numbers: The Unreal Reality of Mathematical ImaginationZoe Dominique Gudio100% (1)
- Studies On Shock Waves Produced by Reddy TubeDocument7 pagesStudies On Shock Waves Produced by Reddy TubeSai DhruvNo ratings yet
- ISV SM Ch10Document69 pagesISV SM Ch10손은결No ratings yet
- 9-Physics-Practice Questions emDocument34 pages9-Physics-Practice Questions emmahaboob kpNo ratings yet
- Review of Linear Mechanism of Wave Emergence From Vortices in Smooth Shear FlowsDocument7 pagesReview of Linear Mechanism of Wave Emergence From Vortices in Smooth Shear FlowsJOAQUIM P JOSSYNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Transmission of Motion by Direct ContactDocument16 pagesChapter 6 - Transmission of Motion by Direct ContactRona Mae BeldadNo ratings yet
- MIT2 25F13 EquationSheetDocument2 pagesMIT2 25F13 EquationSheetMauricio Andrés Gutiérrez BravoNo ratings yet
- Physics Notes Work Done, Energy, PowerDocument5 pagesPhysics Notes Work Done, Energy, PowerJennieNo ratings yet
- Phys101 Lecture 6 Circular Motion: Key PointsDocument11 pagesPhys101 Lecture 6 Circular Motion: Key PointsJoby Jobzz SebellinoNo ratings yet
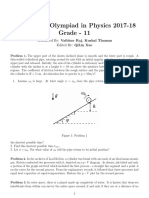
- All Russian Olympiad in Physics 2017-18 Grade - 11: Translated By: Vaibhav Raj, Kushal Thaman Edited By: Qilin XueDocument3 pagesAll Russian Olympiad in Physics 2017-18 Grade - 11: Translated By: Vaibhav Raj, Kushal Thaman Edited By: Qilin XueNitin SharmaNo ratings yet
- 1.053J/2.003J Dynamics and Control I Fall 2007 Exam 1: 24 October, 2007Document4 pages1.053J/2.003J Dynamics and Control I Fall 2007 Exam 1: 24 October, 2007Vaibhav GuptaNo ratings yet
- 4.newton's Law of MotionDocument29 pages4.newton's Law of MotionHo Fung ChowNo ratings yet
- Acoustics Lecture 1Document21 pagesAcoustics Lecture 1Alejandro Romero BallestasNo ratings yet
- Numerical Investigation of The Turbulent Cross Flow and Heat Transfer in A Wall Bounded Tube Bundles - LiDocument13 pagesNumerical Investigation of The Turbulent Cross Flow and Heat Transfer in A Wall Bounded Tube Bundles - LiMeshal Al-mutairiNo ratings yet
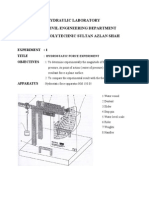
- CC501 - Lab - 1 HydraulicDocument11 pagesCC501 - Lab - 1 HydraulicMuhammad Azizul100% (1)