Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Potpot Pneumonics
Uploaded by
webang0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
292 views3 pagesEach letter stands for a key sign or symptom of serum sickness. HYPOCALCEMIA "CATS" C - Convulsions a - Arrhythmias T - Tetany S - Spasms and stridor.
Original Description:
Original Title
potpot pneumonics
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentEach letter stands for a key sign or symptom of serum sickness. HYPOCALCEMIA "CATS" C - Convulsions a - Arrhythmias T - Tetany S - Spasms and stridor.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
292 views3 pagesPotpot Pneumonics
Uploaded by
webangEach letter stands for a key sign or symptom of serum sickness. HYPOCALCEMIA "CATS" C - Convulsions a - Arrhythmias T - Tetany S - Spasms and stridor.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
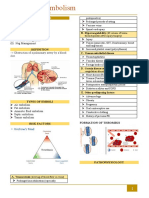
HYPERNATREMIA Hyperkalemia HYPERKALEMIA Causes of
Increased Serum K+
"You Are Fried" Signs & Symptoms Increased
Serum K+ “Machine"
F - Fever (low), flushed skin MURDER M - Medications - ACE inhibitors,
R - Restless (irritable) NSAIDS
I - Increased fluid retention & M - Muscle weakness A - Acidosis - Metabolic and respiratory
increased BP U - Urine, oliguria, anuria C - Cellular destruction - Burns,
E - Edema (peripheral and pitting) R- Respiratory distress traumatic injury
D - Decreased urinary output, dry D - Decreased cardiac H – Hypoaldosteronism/
mouth contractility hemolysis
E - ECG changes I - Intake - Excessive
Can also use this one: R - Reflexes, hyperreflexia, N - Nephrons, renal failure
SALT or areflexia (flaccid) E - Excretion - Impaired
S = Skin flushed
A = Agitation
L = Low-grade fever
T = Thirst
HYPOCALCEMIA Sx’s minor bleeding: . "HOOK" for serum sickness:
“CATS” BEEP each letter stands for a key sign
or symptom of serum sickness.
C - Convulsions B: Bleeding gums
A- Arrhythmias E: Ecchymoses (bruises) F: Fever
T - Tetany E: Epistaxis (nosebleed) A: Arthralgias
S - Spasms and stridor P: Petechiae (tiny purplish R: Rash
spots) M: Malaise
Cancer Assessment ABG's: Respiratory depression
CAUTION inducing drugs
ROME "STOP breathing":
C: Change in bowel/ bladder Sedatives and hypnotics
habits Respiratory Opposite Trimethoprim
A: A sore that doesn’t heal Metabolic Equal Opiates
U: Unusual bleeding or discharge Polymyxins
T: Thickening or lump
I: Indigestion or difficulty
swallowing
O: Obvious changes in a wart or
mole
N: Nagging cough or hoarseness.
COPD: Croup: symptoms Neonatal resuscitation:
blue bloater vs. pink puffer diseases 3 S's: successive steps
"Do What Pediatricians Say To, Or
emPhysema has letter P (and not Stridor Be Inviting Costly Malpractice"
B) so Pink Puffer. Subglottic swelling
chronic Bronchitis has letter B Seal-bark cough Drying
(and not P) so Blue Bloater. Warming
Positioning
Suctioning
Tactile stimulation
Oxygen
Bagging
Intubate endotracheally
Chest compressions
Medications
Asthma acute attack: Pneumonia: risk factors Asthma: management of acute
5 life threatening signs SHOCK: INSPIRATION: severe
Immunosuppression “O-SHIT”
Silent chest Neoplasia
Hypotension Secretion retention O- oxygen (high dose: >60%)
One third of best/predicted PFR Pulmonary oedema S- salbutamol (5mg via oxygen-driven
Cyanosis Impaired alveolar nebuliser)
Konfusion macrophages H- Hydrocortisone (or prednisolone)
RTI (prior) I - Ipratropium bromide (if life
threatening)
Antibiotics & cytotoxics T- theophylline (or preferably
Tracheal instrumentation aminophylline-if life threatening
IV dug abuse
Other (general debility,
immobility)
Neurologic impairment of
cough reflex, (eg NMJ
disorders)
RDS -Respiratory distress syndrome in Lung cancer: main sites for distant Pneumothorax: sx
infants: major risk factors PCD metastases BLAB: P-THORAX:
(Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia, a Bone
cause of Respiratory distress Liver Pleuretic pain
syndrome): Adrenals Trachea deviation
Prematurity Brain Hyperresonance
Cesarean section Onset sudden
Diabetic mother Reduced breath sounds (&
dypsnea)
Absent fremitus
X-ray shows collapse
Bronchi: which one is more Beta-1 vs Beta-2 receptor Wheezing: causes ASTHMA:
vertical location Asthma
"Inhale a bite, goes down the "You have 1 heart and 2 Small airways disease
right" lungs": Tracheal obstruction
Inhaled objects more likely to Beta-1 are therefore primarily Heart failure
lodge in right bronchus, since it is on heart. Mastocytosis or carcinoid
the one that is more vertical. Beta-2 primarily on lungs. Anaphylaxis or allergy
Shortness of breath: short Respiratory co anaesthesia: Dyspnea: differential
differential AAAA PPPP: patients at risk COUPLES: 3A's: Three Airways: Airway
obstruction, Anaphylaxis, Asthma
Airway obstruction COPD 3P's: Three Pulmonary's:
Angina Obese Pneumothorax, PE, Pulmonary edema
Anxiety Upper abdominal surgery 3C's: Three Cardiacs: Cardiogenic
Asthma Prolonged bed rest pulmonary edema, Cardiac ischemia,
Pneumonia Long surgery Cardiac tamponade
3M's: Three Metabolics: (DOC) DKA,
Pneumothorax Elderly Organophosphates, Carbon monoxide
Pulmonary Edema Smokers poisoning
Pulmonary Embolus
TB: antibiotics used Ascultation: crackles (rales) treat viral respiratory
drugs to
STRIPE: "PEBbles": infections "You'd get a respiratory
infection if you shoot an ARO (arrow)
STreptomycin Pneumonia laced with viruses into the lungs":
Rifampicin Edema of lung ARO:
Isoniazid Bronchiti Amantadine
Pyrizinamide Rimantadine
Ethambutol Oseltamivir
Pulmonary edema: tx Kubler-Ross dying process:
MAD DOG stages
"Death Always Brings Great
Morphine Acceptance":
Aminophylline
Digitalis Denial
Diuretics Anger
Oxygen Bargaining
GGases in blood (ABG's) Grieving
Acceptance
You might also like
- Medicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtFrom EverandMedicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- MnemonicsDocument10 pagesMnemonicsRichard GarciaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Advanced Life Support: I. PALS System Approach AlgorithmDocument19 pagesPediatric Advanced Life Support: I. PALS System Approach AlgorithmIsabel Castillo100% (1)
- Mnemonics for Medical ConditionsDocument4 pagesMnemonics for Medical ConditionsLheidaniel MMM.100% (1)
- MnemonicsDocument4 pagesMnemonicsKarol Delagana67% (3)
- Dyspnoea Ddx/Associated Features Body System/key Qs AcuteDocument4 pagesDyspnoea Ddx/Associated Features Body System/key Qs Acutedragtoss2No ratings yet
- MnemonicsDocument23 pagesMnemonicsJot grewalNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Disorders Guide for Care and ManagementDocument40 pagesRespiratory Disorders Guide for Care and Managementanabbondad2932No ratings yet
- Active learning tips and techniquesDocument19 pagesActive learning tips and techniquesSontoshMBsmmuNo ratings yet
- Shortness of Breath: ER Perspective Shaesta TabassumDocument46 pagesShortness of Breath: ER Perspective Shaesta TabassumAjay DherwaniNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Conditions ChartDocument1 pageRespiratory Conditions ChartAmanda MuchaNo ratings yet
- RespiratoryDocument7 pagesRespiratoryThomas KearneyNo ratings yet
- DyspneaDocument21 pagesDyspneaMahboob AlamNo ratings yet
- Asthma-1Document79 pagesAsthma-1DanishMandiNo ratings yet
- What To Ask:: Infection (LRTI)Document11 pagesWhat To Ask:: Infection (LRTI)habbouraNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Examination - Protected 1Document4 pagesRespiratory Examination - Protected 1anirudh811100% (1)
- NCM 112-Mod3Document19 pagesNCM 112-Mod3Samantha BolanteNo ratings yet
- COPD Exacerbation and Asthma DiagnosisDocument11 pagesCOPD Exacerbation and Asthma DiagnosisCalingalan Hussin CaluangNo ratings yet
- Mnemonics For Medical PGEntranceDocument145 pagesMnemonics For Medical PGEntranceCharan RebelNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Study GuideDocument5 pagesPneumonia Study GuideMartha Marty BalintNo ratings yet
- Pathognomonic SignsDocument11 pagesPathognomonic Signscheskahortelano08No ratings yet
- Mnemonics - ClinicalDocument16 pagesMnemonics - Clinicalkavidi100% (1)
- Approach To DyspneaDocument9 pagesApproach To DyspneaMuhammad LukmanNo ratings yet
- Nursing MnemonicsDocument73 pagesNursing MnemonicsJemy Lorane Temporal100% (4)
- Pediatric Hematooncology Alarm SymptomsDocument22 pagesPediatric Hematooncology Alarm SymptomsMuhammad ArifNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Embolism TransesDocument4 pagesPulmonary Embolism TransesKdamnzNo ratings yet
- Short List of Really Good MnemonicsDocument4 pagesShort List of Really Good MnemonicstipletonNo ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: PGI Ponferrado/ PGI Salita/ PGI MondeloDocument31 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: PGI Ponferrado/ PGI Salita/ PGI MondeloMark Angelo PonferradoNo ratings yet
- Essential Basics of General Medicine Faculty of Dentistry Cairo UniversityDocument104 pagesEssential Basics of General Medicine Faculty of Dentistry Cairo Universitybavly waidyNo ratings yet
- Neuro DisordersDocument13 pagesNeuro DisordersMicz Celiz100% (3)
- DyspnoeaDocument1 pageDyspnoeaShubham TarapureNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Anaphylaxis: Pediatric Stage Faculty of Medicine Christian University of Indonesia 23 September - 16 NovemberDocument34 pagesPediatric Anaphylaxis: Pediatric Stage Faculty of Medicine Christian University of Indonesia 23 September - 16 NovemberNovelia CarolinNo ratings yet
- Pediatric NursingDocument14 pagesPediatric NursingJoanne PaulineNo ratings yet
- Dyspnea - DR AllenDocument50 pagesDyspnea - DR AllenalmiraerickaiNo ratings yet
- Sample Medical Guidelines: Respiratory DistressDocument2 pagesSample Medical Guidelines: Respiratory DistressLea RonaldoNo ratings yet
- Emergency 范围Document43 pagesEmergency 范围Wei Chian BTCM19C KhorNo ratings yet
- Increased Intracranial Pressure and Seizure Feb 14Document2 pagesIncreased Intracranial Pressure and Seizure Feb 14anime listNo ratings yet
- Respiratory EmergenciesDocument21 pagesRespiratory EmergenciesMohamed Anas SayedNo ratings yet
- Mnemonics For NursesDocument29 pagesMnemonics For Nursesashdmb217100% (2)
- Cardiology: C B: A V L U: J 2019Document20 pagesCardiology: C B: A V L U: J 2019Owen AgnewNo ratings yet
- Asthma DX Article 1Document16 pagesAsthma DX Article 1Pat Caz SarNo ratings yet
- Mnemonic DeviceDocument12 pagesMnemonic DeviceJonathan ObañaNo ratings yet
- 2023 UsDocument10 pages2023 UswisgeorgekwokNo ratings yet
- COPD Case Presentation on 78-Year-Old FemaleDocument15 pagesCOPD Case Presentation on 78-Year-Old FemaleCalingalan Hussin CaluangNo ratings yet
- Word AssociationDocument27 pagesWord AssociationMilan Kolovrat100% (1)
- Pneumonias (PNAs) CAP HAP VAPDocument37 pagesPneumonias (PNAs) CAP HAP VAPaniqahmed6565No ratings yet
- PBL 2nd Sem Scenario 1Document164 pagesPBL 2nd Sem Scenario 1stephaniecaronan15No ratings yet
- 10) Dyspnea Nov 2016 PDFDocument99 pages10) Dyspnea Nov 2016 PDFGopala HariNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology Notes for Medical StudentsFrom EverandEndocrinology Notes for Medical StudentsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Anaphylaxis: A Practical GuideFrom EverandAnaphylaxis: A Practical GuideAnne K. EllisNo ratings yet
- Mnemonics for Medicine: Differential Diagnoses and Other PearlsFrom EverandMnemonics for Medicine: Differential Diagnoses and Other PearlsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Syncope, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesFrom EverandSyncope, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesNo ratings yet
- COPD TextbookDocument10 pagesCOPD Textbooknob2011nobNo ratings yet
- Conclusions From NAS Report The Health Effects of Cannabis and Cannabinoids ConclusionsDocument6 pagesConclusions From NAS Report The Health Effects of Cannabis and Cannabinoids ConclusionsPBS NewsHourNo ratings yet
- Faraz Pearls For MRCPDocument223 pagesFaraz Pearls For MRCPSyed Ali Akbar86% (14)
- Pne67!2!08pozzi ReviewDocument10 pagesPne67!2!08pozzi ReviewmunirdayaniNo ratings yet
- Agnihotra Reduces Air Pollution by 51-65% According to Lab StudyDocument13 pagesAgnihotra Reduces Air Pollution by 51-65% According to Lab StudyLalit MishraNo ratings yet
- Post TestDocument11 pagesPost TestDemuel Dee L. BertoNo ratings yet
- Quality of Life: Concept and Definition: COPD: Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseDocument10 pagesQuality of Life: Concept and Definition: COPD: Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseKaren SanchezNo ratings yet
- Dangers of Mainstream SmokeDocument3 pagesDangers of Mainstream SmokeBrandon RomeroNo ratings yet
- Differential DiagnosisDocument10 pagesDifferential DiagnosisRhaffy Bearneza RapaconNo ratings yet
- 4a's LESSON PLAN FOR GRADE 8 - HealthDocument2 pages4a's LESSON PLAN FOR GRADE 8 - HealthDremie Works100% (1)
- Myocardial Infarction Covid Heart Failure Quiz RLE 5-6-2021Document58 pagesMyocardial Infarction Covid Heart Failure Quiz RLE 5-6-2021MuhyeeSalaIdjadNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - Respiratory SystemDocument8 pagesWorksheet - Respiratory SystemDhen MarcNo ratings yet
- Syllabus IIIDocument85 pagesSyllabus IIIAsħîŞĥLøÝå100% (1)
- Auto PEEPDocument9 pagesAuto PEEPJoãoBrasil100% (1)
- Pulmon Ology MCQ SDocument280 pagesPulmon Ology MCQ SSai ShankerNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Discussion Board ActivityDocument2 pagesWeek 2 Discussion Board ActivityWekesa EvansNo ratings yet
- (Oxy) Med-Surg Checklist With RationaleDocument13 pages(Oxy) Med-Surg Checklist With RationaleUri Perez MontedeRamos100% (1)
- How lifestyle diseases are causedDocument3 pagesHow lifestyle diseases are causedKristine AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Moretti 2007Document10 pagesMoretti 2007Dewi SariNo ratings yet
- BIOC3364 - 2021 Lecture Notes AsthmaDocument26 pagesBIOC3364 - 2021 Lecture Notes AsthmachrystalNo ratings yet
- Instruction: Select The Correct Answer For Each of The Following Questions. Mark Only One Answer byDocument7 pagesInstruction: Select The Correct Answer For Each of The Following Questions. Mark Only One Answer byEden Marie FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Respi ReviewerDocument5 pagesRespi ReviewerDianne Erika MeguinesNo ratings yet
- Leader's Guide Drug Addiction and Basic Counselling SkillsDocument193 pagesLeader's Guide Drug Addiction and Basic Counselling SkillsHarsh RathoreNo ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Case Presentation OnDocument95 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Case Presentation OnJunery Bagunas100% (2)
- What is COPD? Understanding Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseDocument9 pagesWhat is COPD? Understanding Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseasemartha kurniaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 29: Nursing Management: Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases Test BankDocument15 pagesChapter 29: Nursing Management: Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases Test BankBriseidaSolisNo ratings yet
- 9-St-George Respiratory Questionnaire ManualDocument17 pages9-St-George Respiratory Questionnaire ManualastreedewiNo ratings yet
- Assessment Questions (Assessment Criteria)Document2 pagesAssessment Questions (Assessment Criteria)sujanaNo ratings yet
- April 2018 Question 1 C: View RationaleDocument6 pagesApril 2018 Question 1 C: View RationaleJohannah DianeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 and Chapter 2, Related Literature GROUP 5Document11 pagesChapter 1 and Chapter 2, Related Literature GROUP 5Alcaraz Paul JoshuaNo ratings yet