Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Muscles Sci
Uploaded by
prameeta0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
224 views1 pageBiceps and triceps (antagonistic) act in opposite ways, when one contracts, the other relaxes. Ciliary muscles constrict (less light enters into eye) radial muscles relax (allows length of muscle to return to its original length, decreases diameter)
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentBiceps and triceps (antagonistic) act in opposite ways, when one contracts, the other relaxes. Ciliary muscles constrict (less light enters into eye) radial muscles relax (allows length of muscle to return to its original length, decreases diameter)
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
224 views1 pageMuscles Sci
Uploaded by
prameetaBiceps and triceps (antagonistic) act in opposite ways, when one contracts, the other relaxes. Ciliary muscles constrict (less light enters into eye) radial muscles relax (allows length of muscle to return to its original length, decreases diameter)
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
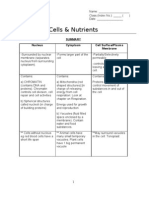
Muscles
Revision Summary
Action of muscles
Muscles undergo:
- Contraction which shortens the length of the muscle, increases diameter
- Relaxation which allows length of muscle to return to its original length,
decreases diameter
Antagonistic muscles: Present in pairs and act in opposite ways, when one contracts,
the other relaxes. Having muscles in pairs enable a reversal of the action (as muscles
can only contract and relax and one set brings about 1 action).
Action & Muscle Action Effect
Arm movement: Contraction of biceps Forearm pulled upwards
Attached to the skeleton: (Relaxation of triceps)
Skeletal
Biceps and triceps Contraction of triceps Forearm pulled down
(antagonistic) (Relaxation of biceps)
Knee jerk reflex: Contraction of upper thigh muscle Lower leg kicks upwards
Upper thigh muscle
Peristalsis: Circular muscle Contraction of circular muscle Narrows lumen of gut, pushes
and longitudinal muscle in gut (Relaxation of longitudinal muscle) food forward
wall (antagonistic)
Gut
Contraction of longitudinal muscle Shortens length of gut (widens
(Relaxation of circular muscle) lumen of gut), pulls food forward,
allows food to move forward
Accomodation: Contraction of ciliary muscles Elastic lens becomes thicker,
Cilary muscles attached to (Slackens pull of ligaments on more convex, refracts light rays
lens via suspensory lens) from nearby object
ligaments (ligaments are Relaxation of ciliary muscles Elastic lens becomes thinner, less
passive, they cannot (Increases upll of ligaments on convex, refracts light rays from
Eye
contract/relax) lens) faraway object
Entry of light into eye: Contraction of circular muscles Pupil constricts (less light enters
Iris: (Relaxation of radial muscles) into eye)
Circular muscles Contraction of radial muscles Pupil dilates (more light enters
Radial muscles (Relaxation of circular muscles) into eye)
You might also like
- GEP Worksheets - Diffusion and Osmosis MS RevisedDocument4 pagesGEP Worksheets - Diffusion and Osmosis MS RevisedprameetaNo ratings yet
- Pure Biology TYS Unit 2.5ADocument5 pagesPure Biology TYS Unit 2.5AprameetaNo ratings yet
- GEP Worksheets - Diffusion and Osmosis RevisedDocument10 pagesGEP Worksheets - Diffusion and Osmosis RevisedprameetaNo ratings yet
- GEP Worksheets EnzymesDocument5 pagesGEP Worksheets Enzymesprameeta100% (1)
- GEP Worksheets - Cells and NutrientsDocument7 pagesGEP Worksheets - Cells and Nutrientsprameeta100% (1)
- TYS Unit 2.7Document3 pagesTYS Unit 2.7prameetaNo ratings yet
- MCQ Unit 7 Answers: TYS Unit 7 (Science Biology)Document3 pagesMCQ Unit 7 Answers: TYS Unit 7 (Science Biology)prameetaNo ratings yet
- MCQ Unit 4 Answers: TYS Unit 4 (Science Biology)Document1 pageMCQ Unit 4 Answers: TYS Unit 4 (Science Biology)prameetaNo ratings yet
- Pure Biology TYS Unit 2.5ADocument5 pagesPure Biology TYS Unit 2.5AprameetaNo ratings yet
- MCQ Unit 4 Answers: TYS Unit 4 (Science Biology)Document1 pageMCQ Unit 4 Answers: TYS Unit 4 (Science Biology)prameetaNo ratings yet
- Summary of Effects of AdrenalineDocument1 pageSummary of Effects of Adrenalineprameeta100% (1)
- Concept Map - Transport in Flowering PlantsDocument1 pageConcept Map - Transport in Flowering PlantsprameetaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 Enzymes and DiffOsmoDocument8 pagesLesson 7 Enzymes and DiffOsmoprameetaNo ratings yet
- 09 GEP PLT TPTDocument4 pages09 GEP PLT TPTprameetaNo ratings yet
- 09 SB TYS Unit 10.1Document2 pages09 SB TYS Unit 10.1prameetaNo ratings yet
- Cells Concept MapDocument1 pageCells Concept MapprameetaNo ratings yet
- Repro in Plants Unit 3.1A Tys MCQ: Essay Quesfon 2aiiDocument2 pagesRepro in Plants Unit 3.1A Tys MCQ: Essay Quesfon 2aiiprameeta100% (1)
- 09 Gep SB 2Document3 pages09 Gep SB 2prameeta100% (1)
- Unit 5 Structured Question 1: Nutrition & Transport in Plants Tys Science BiologyDocument4 pagesUnit 5 Structured Question 1: Nutrition & Transport in Plants Tys Science BiologyprameetaNo ratings yet
- 09 Sci GEP 1 EYEDocument4 pages09 Sci GEP 1 EYEprameetaNo ratings yet
- 09 SB Gep1 EYEDocument17 pages09 SB Gep1 EYEprameeta100% (1)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Jadual Seminar 1 0910Document24 pagesJadual Seminar 1 0910ScalperNo ratings yet
- The Logic of Faith Vol. 1Document39 pagesThe Logic of Faith Vol. 1Domenic Marbaniang100% (2)
- IET DAVV 2014 Com2Document12 pagesIET DAVV 2014 Com2jainam dudeNo ratings yet
- ORM-II Theory+exercise+ Answer PDFDocument58 pagesORM-II Theory+exercise+ Answer PDFGOURISH AGRAWALNo ratings yet
- ATRA GM 4L60-4L60E (700R4) Rebuild ProceduresDocument0 pagesATRA GM 4L60-4L60E (700R4) Rebuild ProceduresJuan Manuel Aguero Diaz83% (12)
- Scanner 2000 Microefm Solutions: Making MeasurementDocument6 pagesScanner 2000 Microefm Solutions: Making Measurementesteban casanovaNo ratings yet
- Adverse WeatherDocument13 pagesAdverse WeathermurugeshunivNo ratings yet
- Ch23 Review ProblemsDocument25 pagesCh23 Review ProblemsحمدةالنهديةNo ratings yet
- 253 968 2 SPDocument16 pages253 968 2 SPAlvin MRNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 RevaDocument20 pagesChapter 8 RevaanildhakeNo ratings yet
- Cuda GDBDocument64 pagesCuda GDBVinícius LisboaNo ratings yet
- Mech CVTDocument15 pagesMech CVTsachin guptaNo ratings yet
- Cog Lab - Brain AsymmetryDocument3 pagesCog Lab - Brain AsymmetryMaharshi Majmundar0% (1)
- Process Pumps - Api-610: Single Stage Volute Casing PumpsDocument5 pagesProcess Pumps - Api-610: Single Stage Volute Casing Pumpsmehrzad1373No ratings yet
- Book 1Document6 pagesBook 1Team UnitedNo ratings yet
- Franks 2009Document11 pagesFranks 2009bhanu0% (1)
- TomatoDocument19 pagesTomatoaravind kishanNo ratings yet
- Ch1 - Jigs & FixturesDocument53 pagesCh1 - Jigs & Fixturesttetslm100% (2)
- Experimental Study On Partial Replacement of Fine Aggregate With Quarry Dust and Saw DustDocument13 pagesExperimental Study On Partial Replacement of Fine Aggregate With Quarry Dust and Saw DustPerarasan MNo ratings yet
- Irc 89 PDFDocument49 pagesIrc 89 PDFShashank SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- MNED G12MNEDMockP22017MemoDocument11 pagesMNED G12MNEDMockP22017MemoChey1242No ratings yet
- Fatigue of MaterialsDocument54 pagesFatigue of Materialsc_gaspard0% (1)
- Grade 10: Mathematics Structuring Competencies in A Definitive Budget of WorkDocument2 pagesGrade 10: Mathematics Structuring Competencies in A Definitive Budget of Worksher blasNo ratings yet
- Exam Syllabus For Genius20Document2 pagesExam Syllabus For Genius20Vaishali PandeyNo ratings yet
- Keysight N5193A Online Documentation - PDW DefinitionsDocument3 pagesKeysight N5193A Online Documentation - PDW Definitionssandeep yadavNo ratings yet
- Coal Lab Assignment 2 - v5 - f2019266302Document12 pagesCoal Lab Assignment 2 - v5 - f2019266302Talha ChoudaryNo ratings yet
- UNIT - 1 Formula and ProcedureDocument4 pagesUNIT - 1 Formula and ProcedurevinothNo ratings yet
- Astm G 28 - 97 - Rzi4lvjfraDocument9 pagesAstm G 28 - 97 - Rzi4lvjfraSamuel EduardoNo ratings yet
- Calin o An Informal Introduction To Stochastic Calculus WithDocument331 pagesCalin o An Informal Introduction To Stochastic Calculus Withjldelafuente100% (5)
- Catálogo Greenleaf PDFDocument52 pagesCatálogo Greenleaf PDFAnonymous TqRycNChNo ratings yet