Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ben Paolo C
Uploaded by
Ben Paolo Cecilia RabaraOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ben Paolo C
Uploaded by
Ben Paolo Cecilia RabaraCopyright:
Available Formats
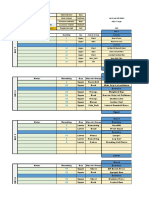
Ben Paolo C. Rabara 1. What is the chemical structure of Caffeine?
3FPharmacy
Empirical Formula: C8H10N4O2 IUPAC Name: 1,3,7-trimethyl-1H-purine-2,6(3H,7H)-dione 3,7-dihydro-1,3,7-trimethyl-1H-purine-2,6-dione
2. Sources of Caffeine Natural: Common sources of caffeine are coffee, tea, soft drinks and energy drinks, and (to a lesser extent) chocolate derived fromcocoa beans. Commercial: Of all the commercial sources of caffeine, guarana paste has the highest concentration of the pure compound, about 4%. Guarana paste is made from the seed of the Paullinia tree, found primarily in Brazil.
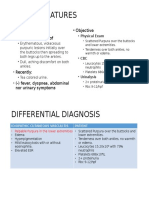
3. Uses of Caffeine? The biggest use of caffeine is as a stimulant. People drink coffee and other drinks with caffeine to stay awake. Doctors sometimes use caffeine as a medicine like for example: headaches and head pain. Caffeine is sometimes given to people after lumber puncture, caffeine was found to relieve hunger so it was used for loss. 4. Mechanism of Action
the effect of caffeine on the vascular endothelium is a greater expression of NO, which has an autocrine effect, acting on the same endothelial cell to increase Ca2+, potentiating the response, and coming out of the endothelial cell to diffuse rapidly to the VSMC in a paracrine fashion. 4. To what 2nd degree metabolic does caffeine belong? Xanthine alkaloid 5. What is sublimation? Sublimation is the process of transformation directly from the solid phase to the gaseous phase without passing through an intermediate liquid phase.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- 4 Day RoutineDocument310 pages4 Day RoutineBen Paolo Cecilia Rabara0% (1)
- CASSEEEDocument6 pagesCASSEEEBen Paolo Cecilia RabaraNo ratings yet
- Pediatric CalculatorDocument3 pagesPediatric CalculatorBen Paolo Cecilia RabaraNo ratings yet
- Training Program For HypertrophyDocument217 pagesTraining Program For HypertrophyBen Paolo Cecilia RabaraNo ratings yet
- CASSEEEDocument6 pagesCASSEEEBen Paolo Cecilia RabaraNo ratings yet
- Diaz V People and Levi Strauss (2013) : FactsDocument1 pageDiaz V People and Levi Strauss (2013) : FactsDiane AngelineNo ratings yet
- Iron Buff 22052019Document201 pagesIron Buff 22052019Ben Paolo Cecilia RabaraNo ratings yet
- Erythematous Lesions PDF-notes 201610271601Document17 pagesErythematous Lesions PDF-notes 201610271601Ben Paolo Cecilia RabaraNo ratings yet
- Peds0813 Motor Vehicle TraumaDocument28 pagesPeds0813 Motor Vehicle TraumaBen Paolo Cecilia RabaraNo ratings yet
- Neonatal HypoglycemiaDocument11 pagesNeonatal HypoglycemiaBen Paolo Cecilia Rabara100% (1)
- Salient Features of The PatientDocument2 pagesSalient Features of The PatientBen Paolo Cecilia RabaraNo ratings yet
- Complete PE CheckList PDFDocument3 pagesComplete PE CheckList PDFBen Paolo Cecilia RabaraNo ratings yet
- PGI Graduation 2019 FinalDocument153 pagesPGI Graduation 2019 FinalBen Paolo Cecilia RabaraNo ratings yet
- Guide To Adulting 101 by Paps MDDocument2 pagesGuide To Adulting 101 by Paps MDBen Paolo Cecilia Rabara0% (1)
- Book OneDocument15 pagesBook OneBen Paolo Cecilia RabaraNo ratings yet
- Erythematous Lesions PDF-notes 201610271601Document17 pagesErythematous Lesions PDF-notes 201610271601Ben Paolo Cecilia RabaraNo ratings yet
- 60 in 60Document10 pages60 in 60Ben Paolo Cecilia RabaraNo ratings yet
- SEO Fast Start:: A Simple, Step by Step System For Better ResultsDocument117 pagesSEO Fast Start:: A Simple, Step by Step System For Better ResultsNeven ErkićNo ratings yet
- Boehringer Ingelheim Leadership RolesDocument1 pageBoehringer Ingelheim Leadership RolesBen Paolo Cecilia RabaraNo ratings yet
- Summary of Encyclical LettersDocument4 pagesSummary of Encyclical LettersBen Paolo Cecilia RabaraNo ratings yet
- Drug Info Inquiry FormDocument1 pageDrug Info Inquiry FormBen Paolo Cecilia RabaraNo ratings yet
- 2MEDICINE8 Thyroid Gland Disorders UERM2015B PDFDocument16 pages2MEDICINE8 Thyroid Gland Disorders UERM2015B PDFBen Paolo Cecilia Rabara100% (1)
- Pharmaceutical Incompatibilities GuideDocument7 pagesPharmaceutical Incompatibilities GuideBen Paolo Cecilia Rabara88% (8)
- SAR of Macrolides, Penicillins, and Other AntibioticsDocument36 pagesSAR of Macrolides, Penicillins, and Other AntibioticsBen Paolo Cecilia RabaraNo ratings yet
- 3 IdiotsDocument1 page3 IdiotsBen Paolo Cecilia RabaraNo ratings yet
- National Children's HospitalDocument9 pagesNational Children's HospitalBen Paolo Cecilia RabaraNo ratings yet
- Ice Cream FitnessDocument54 pagesIce Cream FitnessBen Paolo Cecilia RabaraNo ratings yet
- Alkajohn LoidDocument9 pagesAlkajohn LoidBen Paolo Cecilia RabaraNo ratings yet
- pH Measurement and Buffer Preparation GuideDocument3 pagespH Measurement and Buffer Preparation GuideBen Paolo Cecilia Rabara100% (2)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)