Professional Documents
Culture Documents
sm3 041
Uploaded by
Sadie HnatowOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
sm3 041
Uploaded by
Sadie HnatowCopyright:
Available Formats
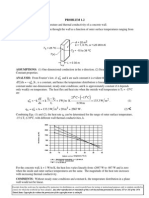
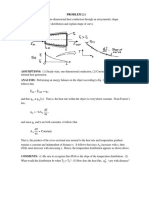
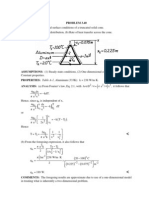
PROBLEM3.
41
KNOWN: Temperature dependence of the thermal conductivity, k.
FIND: Heat flux and form of temperature distribution for a plane wall.
SCHEMATIC:
ASSUMPTIONS: (1) One-dimensional conduction through a plane wall, (2) Steady-state
conditions, (3) No internal heat generation.
ANALYSIS: For the assumed conditions, q
x
and A(x) are constant and Eq. 3.26 gives
( )
( )
( )
1
o
L T
x o
0 T
2 2
x o o 1 o
1
q dx k aT dT
1 a
q k T T T T .
L 2
'' = +
(
'' = +
(
} }
From Fouriers law,
( )
x o
q k aT dT/dx. '' = +
Hence, since the product of (k
o
+aT) and dT/dx) is constant, decreasing T with increasing x
implies,
a > 0: decreasing (k
o
+aT) and increasing |dT/dx| with increasing x
a = 0: k = k
o
=> constant (dT/dx)
a < 0: increasing (k
o
+aT) and decreasing |dT/dx| with increasing x.
The temperature distributions appear as shown in the above sketch.
You might also like
- MODULE 2: Worked-Out ProblemsDocument22 pagesMODULE 2: Worked-Out Problemscaptainhass100% (3)
- Heat Transfer Problem Solutions Involving Generation Rates, Distributions, FluxesDocument18 pagesHeat Transfer Problem Solutions Involving Generation Rates, Distributions, FluxesFuriNo ratings yet
- Problem 1.3: Q DT DX Q KDocument1 pageProblem 1.3: Q DT DX Q Kmojodank12No ratings yet
- sm3 088Document1 pagesm3 088Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm2 040 PDFDocument1 pagesm2 040 PDFNilton MafraNo ratings yet
- sm3 092Document2 pagessm3 092Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- PDE HW Chap 1Document7 pagesPDE HW Chap 1ammar_harbNo ratings yet
- Fouriers Law and Thermal ConductivityDocument20 pagesFouriers Law and Thermal ConductivityvdnsitNo ratings yet
- HMT Unit 1Document33 pagesHMT Unit 1Muthuvel MNo ratings yet
- Heat Loss Through a Concrete Wall as a Function of Outside TemperatureDocument1 pageHeat Loss Through a Concrete Wall as a Function of Outside TemperatureHuma MaqsoodNo ratings yet
- Heat Diffusion EquationDocument8 pagesHeat Diffusion EquationSrikar GhooliNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Problems SolutionsDocument5 pagesHeat Transfer Problems SolutionsEvets EelNo ratings yet
- Chapter2. Conduction HT (Autosaved)Document125 pagesChapter2. Conduction HT (Autosaved)AhmedNo ratings yet
- ProblemDocument20 pagesProblemLucas LentzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Conduction AnalysisDocument16 pagesChapter 2 Conduction AnalysisNurul AsyilahNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Part 1Document40 pagesHeat Transfer Part 1Sunil AnandNo ratings yet
- Computational Modelling of Steady Diffusion Process: Prof. Nilanjan Chakraborty E-MailDocument34 pagesComputational Modelling of Steady Diffusion Process: Prof. Nilanjan Chakraborty E-MailRoberto SacotoNo ratings yet
- Fourier Law: Heat Transfer Rate is Proportional to Temperature DifferenceDocument9 pagesFourier Law: Heat Transfer Rate is Proportional to Temperature DifferenceManu GuptaNo ratings yet
- Transport Introduction1 (B)Document69 pagesTransport Introduction1 (B)Syarifah Anis AqilaNo ratings yet
- Ps1 SolutionsDocument15 pagesPs1 SolutionsSomrita BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass TransferDocument29 pagesHeat and Mass TransferJanardhanaNo ratings yet
- sm5 119Document1 pagesm5 119Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Heat Transfer ModesDocument51 pagesFundamentals of Heat Transfer ModesSandeep MishraNo ratings yet
- sm2 1Document1 pagesm2 1Penny RogersNo ratings yet
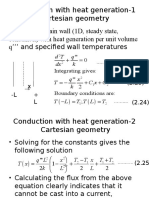
- Conduction With Heat Generation-1 Cartesian GeometryDocument14 pagesConduction With Heat Generation-1 Cartesian GeometryRaja SettiNo ratings yet
- sm2 001Document1 pagesm2 001ahmedNo ratings yet
- Heat Diffusion EquationDocument7 pagesHeat Diffusion EquationGaye KanaltıNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer - Chapter 1Document11 pagesHeat Transfer - Chapter 1lisbon9090No ratings yet
- 1.1 Introduction To ConductionDocument22 pages1.1 Introduction To ConductionAjay YadavNo ratings yet
- PERSAMAAN KONDUKSI PANAS DAN BERBAGAI KASUSDocument25 pagesPERSAMAAN KONDUKSI PANAS DAN BERBAGAI KASUSArdanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 One-Dimensional Diffusion ProblemsDocument7 pagesChapter 2 One-Dimensional Diffusion Problemskelvin felix garciaNo ratings yet
- Steady 1D Heat ConductionDocument19 pagesSteady 1D Heat ConductionEn CsakNo ratings yet
- WRRW DDD: Heat Transfer Unit1Document11 pagesWRRW DDD: Heat Transfer Unit1Manu GuptaNo ratings yet
- Phys 222 Lecture Notes PDFDocument88 pagesPhys 222 Lecture Notes PDFCristian SuárezNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer CH 2 SolutionsDocument77 pagesFundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer CH 2 SolutionsLuke Vazquez100% (5)
- One-Dimensional, Steady-State Conduction With Thermal Energy GenerationDocument35 pagesOne-Dimensional, Steady-State Conduction With Thermal Energy GenerationIvan PonceNo ratings yet
- 1 Semester, A.Y. 2018 - 2019 ME 452 - Heat TransferDocument2 pages1 Semester, A.Y. 2018 - 2019 ME 452 - Heat TransferMark Angelo UyNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer ch2Document26 pagesHeat Transfer ch2Khairul NizamNo ratings yet
- II IIT IRP Physics Worksheet - 13 Q + Soln - Heat Trans & Thermal RadiationDocument13 pagesII IIT IRP Physics Worksheet - 13 Q + Soln - Heat Trans & Thermal RadiationAshwin Kumar100% (1)
- Heat TransgerDocument56 pagesHeat TransgerShusha Shomali67% (3)
- Thermal Analysis of a Hollow Cylindrical SolidDocument8 pagesThermal Analysis of a Hollow Cylindrical SolidchNo ratings yet
- 2 Conduction Tutorial 1Document11 pages2 Conduction Tutorial 1GnazGoragod100% (1)
- sm2 6 PDFDocument1 pagesm2 6 PDFBrain Choirul IchsanNo ratings yet
- sm2 51 PDFDocument2 pagessm2 51 PDFBrain Choirul IchsanNo ratings yet
- Conduction SteadyDocument12 pagesConduction SteadyRafi Mahmoud SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Steady-state heat conduction through an axisymmetric shapeDocument2 pagesSteady-state heat conduction through an axisymmetric shapeJonesHutauruk100% (1)
- مثال فصل 4Document7 pagesمثال فصل 4mohammadNo ratings yet
- sm3 040Document1 pagesm3 040Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- HW#3 - New 01Document2 pagesHW#3 - New 01Gaga852No ratings yet
- Problem 8.3: u p f L 2D Δ = P pV p D 4 u = Δ = Δ &Document14 pagesProblem 8.3: u p f L 2D Δ = P pV p D 4 u = Δ = Δ &Siva PrasadNo ratings yet
- 2D Heat EquationDocument20 pages2D Heat EquationSonakshi SinghNo ratings yet
- Lec. 2 ConductionDocument47 pagesLec. 2 ConductionOsama NoorNo ratings yet
- Thermal Physics Notes New1 PDFDocument21 pagesThermal Physics Notes New1 PDFAryan MauryaNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)From EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)No ratings yet
- Advances in Structure Research by Diffraction Methods: Fortschritte der Strukturforschung mit BeugungsmethodenFrom EverandAdvances in Structure Research by Diffraction Methods: Fortschritte der Strukturforschung mit BeugungsmethodenR. BrillNo ratings yet
- Tables of Coefficients for the Analysis of Triple Angular Correlations of Gamma-Rays from Aligned NucleiFrom EverandTables of Coefficients for the Analysis of Triple Angular Correlations of Gamma-Rays from Aligned NucleiNo ratings yet
- sm9 007Document1 pagesm9 007Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- CH 14Document82 pagesCH 14Sadie Hnatow75% (4)
- sm9 012Document2 pagessm9 012Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- CH 14Document82 pagesCH 14Sadie Hnatow75% (4)
- sm9 011Document1 pagesm9 011Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm9 006Document1 pagesm9 006Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm9 008Document1 pagesm9 008Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm9 010Document1 pagesm9 010Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm9 009Document1 pagesm9 009Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 127Document2 pagessm8 127Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm9 005Document1 pagesm9 005Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm9 004Document1 pagesm9 004Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm9 003Document1 pagesm9 003Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm9 002Document1 pagesm9 002Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 129Document2 pagessm8 129Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm9 001Document1 pagesm9 001Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 128Document1 pagesm8 128Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 118Document1 pagesm8 118Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 126Document1 pagesm8 126Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 123Document1 pagesm8 123Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 124Document2 pagessm8 124Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 125Document1 pagesm8 125Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 120Document1 pagesm8 120Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 121Document1 pagesm8 121Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 119Document1 pagesm8 119Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 117Document3 pagessm8 117Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 122Document3 pagessm8 122Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 116Document2 pagessm8 116Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 114Document2 pagessm8 114Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 115Document3 pagessm8 115Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet