Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Simple Staining
Simple Staining
Uploaded by
vyastrupti1Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Simple Staining
Simple Staining
Uploaded by
vyastrupti1Copyright:
Available Formats
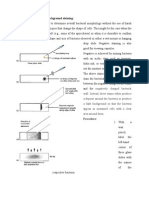
SIMPLE STAINING (NEGATIVE STAINING) INTRODUTION Negative staining is type of simple staining and is so called because the dye
dose not stain the cell instead it imparts contrasting background, thereby making the organism visible. NEGATIVE STAINING METHOD PRINCIPLE Negative staining use acidic dyes like nigrosine, eosin or congo red. Acidic dyes have negatively charged chromogen, which will not bind (react) with bacterial cells because of the similar acidic (negative) charge on the surface of bacterial cell. The stein does not stein the bacteria because of ionic repulsion. Therefore cells are unstained and can be easily visualized against the background. Practical applications of negative staining are 1. Natural shape and size of the cell is not distorted because the heat fixation is not required during the staining. 2. It is possible to observe those bacteria, which are difficult to stein, such as spirochetes. Requirements 1.Young cultures of Escherichia coli , Bacillus subtilis &Stapyloccocus aureus. 3. Nigrosine staining solution (10%). Procedure 1.plase a small drop of nigrosine at the end of slide. For cultures on solid media, add a loopful of distilled water and emulsify a small amount of the culture in the nigrosine water drop. For broth cultures, mix a loopful of the culture into the drop of nigrosine. Do not spread the drop or let dry. 2. Using the end edge of another slide, spread the drop out to produce a smear varying from opaque black to gray. The angle of spreading slide will determine the thickness of the smear. 4. Let the smear air dry, and examine, (do not heat fix the slide).
Results Organisms are observed as transparent objects against the dark background.
You might also like
- Staining TechniquesDocument10 pagesStaining TechniquesJohn Emmanuel TayagNo ratings yet
- StainingDocument60 pagesStainingved.g007No ratings yet
- StainigDocument38 pagesStainigyuppie_raj2175No ratings yet
- Principles and Types of StainingDocument42 pagesPrinciples and Types of StainingMthandeni KhumaloNo ratings yet
- Stains & Staining: Faculty: Dr. Rakesh ShardaDocument34 pagesStains & Staining: Faculty: Dr. Rakesh ShardaQueen Lycka P. Serioza100% (1)
- Dyes and StainsDocument49 pagesDyes and StainsBilal Mumtaz AwanNo ratings yet
- Staining Techniques in Microbiology.Document9 pagesStaining Techniques in Microbiology.rajendraprasadreddyNo ratings yet
- 4 Microbiology Lab Report Practical 3 PDFDocument10 pages4 Microbiology Lab Report Practical 3 PDFNurul IzzahNo ratings yet
- LAB 2-M 265: Bacterial Staining Simple Staining ProceduresDocument16 pagesLAB 2-M 265: Bacterial Staining Simple Staining ProceduresHiba Abu-jumahNo ratings yet
- Negative or Indirect, or Background StainingDocument3 pagesNegative or Indirect, or Background Stainingsrinu.pidNo ratings yet
- Chap4Demonstration of Microorganisms - SJSPDocument133 pagesChap4Demonstration of Microorganisms - SJSPMaryangel RivalesNo ratings yet
- Staining and Mounting - Ms. HubillaDocument47 pagesStaining and Mounting - Ms. HubillaMaria Karina FerrerasNo ratings yet
- Staining MethodsDocument8 pagesStaining MethodsMd Arshad100% (1)
- MicroPara Worksheet 5Document7 pagesMicroPara Worksheet 5Enguio Irish JeanNo ratings yet
- StainingDocument5 pagesStainingyuppie_raj2175No ratings yet
- BI103 Practical 2 HandoutDocument5 pagesBI103 Practical 2 HandoutStephane FongNo ratings yet
- Stains NileDocument37 pagesStains NileNUBWA MEDUGUNo ratings yet
- Microbiology 2Document11 pagesMicrobiology 2POWER KINGNo ratings yet
- Exp#5 Gram StainingDocument4 pagesExp#5 Gram StainingbahadiroztenNo ratings yet
- Staining TechniquesDocument19 pagesStaining TechniquesSwayamprakash PatelNo ratings yet
- Cell Staining: The Simple StainDocument4 pagesCell Staining: The Simple StainAitlas KhanNo ratings yet
- Micro.... Staining TechniquesDocument74 pagesMicro.... Staining TechniquesArslan AzizNo ratings yet
- Assignment Gram Stain.111Document6 pagesAssignment Gram Stain.111premium Shopping centreNo ratings yet
- Gram Staining StainingDocument3 pagesGram Staining StainingSister RislyNo ratings yet
- Staining Reaction 16-11-2016-1Document61 pagesStaining Reaction 16-11-2016-1sameera ruffaiNo ratings yet
- Simple StainingDocument20 pagesSimple StainingjantskieNo ratings yet
- LAB 2: Staining and Streaking: Series of Stains and Chemical Reagents To Increase Contrast and Reveal Information AboutDocument10 pagesLAB 2: Staining and Streaking: Series of Stains and Chemical Reagents To Increase Contrast and Reveal Information AboutrabkaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 MicrobiologyDocument5 pagesExperiment 4 MicrobiologyFrancis TagnongNo ratings yet
- Staining Techniques in MicrobiologyDocument74 pagesStaining Techniques in MicrobiologyLenard MerlinNo ratings yet
- Gram Staining of BacteriaDocument3 pagesGram Staining of Bacteriadavid5king-3119No ratings yet
- Microbial Staining - Principles and Methods Microbial Staining - Principles and MethodsDocument33 pagesMicrobial Staining - Principles and Methods Microbial Staining - Principles and MethodsSELVI ANo ratings yet
- Report On Gram Staining 1Document7 pagesReport On Gram Staining 1Abena FlourishingNo ratings yet
- Microbiology ExperimentDocument9 pagesMicrobiology Experiment门门No ratings yet
- Laboratory 2 - Staining TechniquesDocument7 pagesLaboratory 2 - Staining TechniquesLuzzuvannaNo ratings yet
- Staining NotesDocument5 pagesStaining NotesSwetha RameshNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise 6 SIMPLE STAININGDocument5 pagesLab Exercise 6 SIMPLE STAININGArianne Jans MunarNo ratings yet
- COURSE MLSC 417 Staining in BacteriologyDocument38 pagesCOURSE MLSC 417 Staining in Bacteriologyالمركز الطبي الحديثNo ratings yet
- Methylene Blue-Methylene Blue Stain Is A General Biological Stain Used To Highlight Parts of AnimalDocument2 pagesMethylene Blue-Methylene Blue Stain Is A General Biological Stain Used To Highlight Parts of AnimalleonorNo ratings yet
- Cell Differentiation by GramDocument4 pagesCell Differentiation by GramSherry Anne Ynciong PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Experiment #6 Galinato, Jewel R. BSN 1ADocument11 pagesExperiment #6 Galinato, Jewel R. BSN 1AJyzleen SelmaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity Revil Angelica MDocument16 pagesLaboratory Activity Revil Angelica MAngelica Malacay RevilNo ratings yet
- Gram StainingDocument3 pagesGram Stainingmike peterNo ratings yet
- MONIS, Clemcy Pearl A. (Bacterial Simple Stain Procedure)Document3 pagesMONIS, Clemcy Pearl A. (Bacterial Simple Stain Procedure)Clemcy Pearl MonisNo ratings yet
- LAB 4 Simple Stain 2nd 2020-2021Document17 pagesLAB 4 Simple Stain 2nd 2020-2021Deena Hajj QasemNo ratings yet
- Gram Stain Procedure and Additional Information - Practical 1Document6 pagesGram Stain Procedure and Additional Information - Practical 1kamvajavasNo ratings yet
- Gram StainingDocument2 pagesGram StainingJospes_No ratings yet
- Isolation and Characterization TechniquesDocument28 pagesIsolation and Characterization TechniquesAsad ButtNo ratings yet
- Exercise 7Document3 pagesExercise 7Merve Nur GülerNo ratings yet
- Negative StainDocument2 pagesNegative StainChockalingam MeenakshisundaramNo ratings yet
- Stains and Staining Lab3 and 4Document43 pagesStains and Staining Lab3 and 4Abdurraouf SaidNo ratings yet
- Protocol For: Gram StainingDocument19 pagesProtocol For: Gram StainingmourighoshNo ratings yet
- Negative Staining: Course: MCB 103 Lab Section: 1 Name: Noor-E-Khadiza Shama ID: 1921168 Date: 18/02/20Document3 pagesNegative Staining: Course: MCB 103 Lab Section: 1 Name: Noor-E-Khadiza Shama ID: 1921168 Date: 18/02/20ShamaNo ratings yet
- Fixation and Staining ppt1Document31 pagesFixation and Staining ppt1markwillazNo ratings yet
- Staining Technique in MicrobiologyDocument38 pagesStaining Technique in Microbiologypriya dixitNo ratings yet
- Microbio Prac Write Up 2Document7 pagesMicrobio Prac Write Up 2TADIWANASHE TINONETSANANo ratings yet
- GLENDADocument3 pagesGLENDAKojo PappoeNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1 Microscopic Visualization of Bacteria Differential and Structural StainingDocument6 pagesWorksheet 1 Microscopic Visualization of Bacteria Differential and Structural StainingKyra ErniNo ratings yet
- Capsule Staining Notes SimpleDocument2 pagesCapsule Staining Notes Simplesairam diagnostics kosgiNo ratings yet
- Sterilization: Fundamental Principles of Bacteriology - A J SalleDocument9 pagesSterilization: Fundamental Principles of Bacteriology - A J Sallevyastrupti1No ratings yet
- Spirochete StainingDocument2 pagesSpirochete Stainingvyastrupti175% (4)
- AlcoholDocument3 pagesAlcoholvyastrupti1No ratings yet
- Practical ImmunoelectrophoresisDocument3 pagesPractical Immunoelectrophoresisvyastrupti150% (2)
- Practical Dot ElisaDocument3 pagesPractical Dot Elisavyastrupti1100% (1)