Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ketorolac
Ketorolac
Uploaded by
Jacqueline LimOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ketorolac
Ketorolac
Uploaded by
Jacqueline LimCopyright:
Available Formats
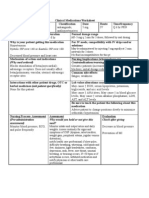
NURS 1566 Clinical Form 3: Clinical Medications Worksheets (You will need to make additional copies of these forms)
Generic Name ketorolac Trade Name Toradol Classification Dose Route Time/frequency nonsteroidal anti30 mg IVP Q 6 hrs PRN inflammatory agents, nonopioid analgesics Duration Normal dosage range 6 hrs or longer 30 mg q 6 hr (not to exceed 120 mg/day)
Peak 1-2 hrs
Onset 10 min
Why is your patient getting this medication Severe back pain
For IV meds, compatibility with IV drips and/or solutions Administration in higher-than-recommended doses does not provide increased effectiveness but may cause increased side effects. Duration of ketorolac therapy, by all routes combined, should not exceed 5 days Use lowest effective dose for shortest period of time. Coadministration with opioid analgesics may have additive analgesic effects and may permit lower opioid doses. Y-Site Compatibility: dexmedetomidine, fentanyl, hydromorphone, morphine, remifentanil, sufentanil Y-Site Incompatibility: azithromycin, fenoldopam Mechanism of action and indications Nursing Implications (what to focus on) (Why med ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactions Inhibits prostaglandin synthesis, producing Concurrent use with aspirin may effectiveness, adverse peripherally mediated analgesia, Also has antipyretic GI effects with aspirin , other NSAIDs , potassium and anti-inflammatory properties. supplements , corticosteroids , or alcohol. Chronic use with acetaminophen may risk of adverse renal reactions, bleeding risk with arnica, chamomile, clove, dong quai, feverfew, garlic, ginger, ginkgo, Panax ginseng. Common side effects Drowsiness, GI BLEEDING, EXFOLIATIVE DERMATITIS, STEVENS-JOHNSON SYNDROME, TOXIC EPIDERMAL NECROLYSIS, anaphylaxis. Interactions with other patient drugs, OTC or Lab value alterations caused by medicine herbal medicines (ask patient specifically) Evaluate liver function tests, especially AST and ALT, adverse GI effects with alcohol. Chronic use with periodically in patients receiving prolonged therapy. May acetaminophen may risk of adverse renal reactions cause levels. May cause prolonged bleeding time that (Tylenol). May effectiveness of antihypertensives may persist for 24-48 hr following discontinuation of (Norvasc, Lopressor). therapy. May cause BUN, serum creatinine, or potassium concentrations. Be sure to teach the patient the following about this medication Instruct patient on how and when to ask for pain medication, Instruct patient to take medication exactly as directed. Take missed doses as soon as remembered if not
almost time for next dose. Do not double doses. May cause drowsiness or dizziness. Advise patient to avoid driving or other activities requiring alertness until response to the medication is known. Caution patient to avoid the concurrent use of alcohol, aspirin, NSAIDs, acetaminophen, or other OTC medications without consulting health care professional. Advise patient to inform health care professional of medication regimen prior to treatment or surgery. Advise patient to consult health care professional if rash, itching, visual disturbances, tinnitus, weight gain, edema, black stools, persistent headache, or influenza-like syndrome (chills, fever, muscle aches, pain) occurs. Nursing Process- Assessment (Pre-administration assessment) Patients who have asthma, aspirininduced allergy, and nasal polyps are at increased risk for developing hypersensitivity reactions. Assess for rhinitis, asthma, and urticaria. Assess pain (note type, location, and intensity) prior to and 1-2 hr following administration. Assessment Why would you hold or not give this med? Occurrence of unwanted or dangerous side effects. Evaluation Check after giving Decrease in severity of pain. Patients who do not respond to one NSAID may respond to another.
You might also like
- Seroquel (Quetiapine)Document3 pagesSeroquel (Quetiapine)E100% (1)
- Iron Deficiency Anemia PathoDocument6 pagesIron Deficiency Anemia PathoENo ratings yet
- PDF Human Drug Metabolism Third Edition Michael D Coleman Ebook Full ChapterDocument53 pagesPDF Human Drug Metabolism Third Edition Michael D Coleman Ebook Full Chapterrichard.mcmenamy574100% (2)
- Zosyn (Piperacillin/tazobactram)Document2 pagesZosyn (Piperacillin/tazobactram)E67% (3)
- NeurontinDocument1 pageNeurontinAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Silvadene (Silver Sulfadiazine)Document1 pageSilvadene (Silver Sulfadiazine)ENo ratings yet
- Pedia Drug StudyDocument11 pagesPedia Drug Studyryan50% (2)
- Lopressor (Metoprolol) 100mgDocument2 pagesLopressor (Metoprolol) 100mgAdrianne Bazo100% (2)
- Keppra (Levetiracetam)Document2 pagesKeppra (Levetiracetam)E100% (1)
- Geodon (Ziprasidone)Document2 pagesGeodon (Ziprasidone)ENo ratings yet
- Huma Log Drug CardDocument1 pageHuma Log Drug CardJanet SheldonNo ratings yet
- Lopressor (Metoprolol) IVDocument2 pagesLopressor (Metoprolol) IVAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Avapro (Irbesartan)Document2 pagesAvapro (Irbesartan)ENo ratings yet
- Neurontin (Gabapentin)Document1 pageNeurontin (Gabapentin)E100% (3)
- Lamictal (Lamotrigine)Document1 pageLamictal (Lamotrigine)E100% (1)
- Drug Card ToradolDocument2 pagesDrug Card ToradolAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Medication Administration NCLEX Questions: Terms in This SetDocument8 pagesMedication Administration NCLEX Questions: Terms in This SetAivan Karl Ambagan100% (1)
- Percocet Drug CardDocument1 pagePercocet Drug CardSheri490100% (4)
- Prozac (Fluoxetine) 40mgDocument1 pageProzac (Fluoxetine) 40mgENo ratings yet
- Prozac (Fluoxetine) 40mgDocument1 pageProzac (Fluoxetine) 40mgENo ratings yet
- Drug Card BenadrylDocument1 pageDrug Card BenadrylAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Morphine (Astramorph)Document1 pageMorphine (Astramorph)Adrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceuticals CalculationsDocument9 pagesPharmaceuticals CalculationsAnamNo ratings yet
- Synthroid (Levothyroxine)Document2 pagesSynthroid (Levothyroxine)E100% (2)
- Mercury Drug Corp. vs. de LeonDocument3 pagesMercury Drug Corp. vs. de LeonFairyssa Bianca Sagot100% (1)
- DispensingDocument30 pagesDispensingNamanamana100% (1)
- Supply Chain Management of Getz PharmaDocument11 pagesSupply Chain Management of Getz PharmaBilalYounus67% (3)
- Neuropathic Pain SlidesDocument28 pagesNeuropathic Pain SlidesAndrias Oz100% (1)
- AtroventDocument1 pageAtroventSheri490100% (1)
- Drug Card Tricyclic DepressantsDocument2 pagesDrug Card Tricyclic DepressantsAaLona RobinsonNo ratings yet
- DiflucanDocument1 pageDiflucanSheri490No ratings yet
- Levaquin Drug CardDocument1 pageLevaquin Drug CardSheri490100% (1)
- Ciprofloxacin CiproDocument1 pageCiprofloxacin CiproKristi WrayNo ratings yet
- TrazodoneDocument20 pagesTrazodoneAjay MehtaNo ratings yet
- Ketorolac AHFSDocument17 pagesKetorolac AHFSRIRINo ratings yet
- ClindamycinDocument3 pagesClindamycinShaira TanNo ratings yet
- Drug DigoxinDocument1 pageDrug DigoxinSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Plavix (Clopidogrel)Document1 pagePlavix (Clopidogrel)E50% (2)
- Lanoxin (Digoxin)Document3 pagesLanoxin (Digoxin)E100% (5)
- Salbuterol Generic NameDocument4 pagesSalbuterol Generic NamejunieNo ratings yet
- Daptomycin (Cubicin)Document1 pageDaptomycin (Cubicin)Adrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Med CardsDocument4 pagesMed CardsSonia FernandesNo ratings yet
- PrevacidDocument1 pagePrevacidAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Drug CardDocument2 pagesDrug CardHannahNo ratings yet
- CholestyramineDocument1 pageCholestyramineKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- EzetimibeDocument3 pagesEzetimibeapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Drug OmeprazoleDocument1 pageDrug OmeprazoleSrkocherNo ratings yet
- CarafateDocument1 pageCarafateAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Drug PrilosecDocument1 pageDrug PrilosecSrkocher100% (1)
- MorphineDocument1 pageMorphineCassie100% (3)
- Er-Drug StudyDocument41 pagesEr-Drug Studyrc_lacampuinganyahooNo ratings yet
- Aerovent, Apovent Atronase, Ipraxa, Ipvent Rhinovent, Rinatecrinovagos, Atrovent, Atrovent HfaDocument4 pagesAerovent, Apovent Atronase, Ipraxa, Ipvent Rhinovent, Rinatecrinovagos, Atrovent, Atrovent HfaGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Stimulates Peripheral Glucose Uptake, Inhibits Hepatic Glucose Production, Inhibits Lipolysis and Proteolysis, Regulating Glucose MetabolismDocument4 pagesStimulates Peripheral Glucose Uptake, Inhibits Hepatic Glucose Production, Inhibits Lipolysis and Proteolysis, Regulating Glucose MetabolismKey CelestinoNo ratings yet
- Ceftriaxone RocephinDocument1 pageCeftriaxone RocephinENo ratings yet
- FiberCon (Polycarbophil)Document1 pageFiberCon (Polycarbophil)ENo ratings yet
- FoscarnetDocument2 pagesFoscarnetTandri JuliantoNo ratings yet
- Coreg (Carvedilol)Document3 pagesCoreg (Carvedilol)ENo ratings yet
- LevaquinDocument1 pageLevaquinKatie McPeek100% (1)
- Grapefruit Juice and Drug Interactions - 0717Document2 pagesGrapefruit Juice and Drug Interactions - 0717Asri YaniNo ratings yet
- ATI DRUG TABLES Module4 Respiratory Expectorants Guaifenesin 1Document1 pageATI DRUG TABLES Module4 Respiratory Expectorants Guaifenesin 1noeyeshaveseenNo ratings yet
- RamiprilDocument3 pagesRamiprilapi-3797941No ratings yet
- AtivanDocument1 pageAtivanSheri490No ratings yet
- DigoxinDocument1 pageDigoxinSheri490100% (2)
- LantusDocument1 pageLantusCassie100% (4)
- Pregabalin An Anticonvulsant DrugDocument2 pagesPregabalin An Anticonvulsant DrugmeimeiliuNo ratings yet
- Methocarbamol (Robaxin)Document1 pageMethocarbamol (Robaxin)ENo ratings yet
- Metformin, Glucophage, Glucophage XR, Glumetza, Fortamet, RiometDocument5 pagesMetformin, Glucophage, Glucophage XR, Glumetza, Fortamet, RiometAgronaSlaughterNo ratings yet
- ToradolDocument2 pagesToradolAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- KetorolacDocument2 pagesKetorolacJacqueline LimNo ratings yet
- New Singulair MontelukastDocument1 pageNew Singulair MontelukastCassie100% (2)
- TylenolDocument1 pageTylenolCassieNo ratings yet
- NURS 1566 Clinical Form 3: Clinical Medications WorksheetsDocument1 pageNURS 1566 Clinical Form 3: Clinical Medications WorksheetsCassieNo ratings yet
- ZofranDocument1 pageZofranKatie McPeek0% (1)
- NURS 2516 Clinical Medications Worksheets: Nursing Process-AssessmentDocument1 pageNURS 2516 Clinical Medications Worksheets: Nursing Process-AssessmentAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- CymbaltaDocument2 pagesCymbaltaENo ratings yet
- Prinivil LisinoprilDocument3 pagesPrinivil LisinoprilENo ratings yet
- Pepcid IV FamotidineDocument2 pagesPepcid IV FamotidineAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- CymbaltaDocument2 pagesCymbaltaAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Congestive Heart Failure-ABDocument3 pagesCongestive Heart Failure-ABENo ratings yet
- Pyelonephritis 1 Running Head: PYELONEPHRITISDocument4 pagesPyelonephritis 1 Running Head: PYELONEPHRITISENo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Short PathoDocument2 pagesPneumonia Short PathoENo ratings yet
- Hyperparathyroidism PathoDocument2 pagesHyperparathyroidism PathoENo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart FailureDocument4 pagesCongestive Heart FailureENo ratings yet
- Influenza B PathoDocument4 pagesInfluenza B PathoENo ratings yet
- Pancreatitis Short PathoDocument2 pagesPancreatitis Short PathoENo ratings yet
- Hyponatremic Dehydration PathoDocument4 pagesHyponatremic Dehydration PathoENo ratings yet
- Campral (Acamprosate Calcium)Document1 pageCampral (Acamprosate Calcium)E100% (1)
- Acute Pancreatitis PathoDocument5 pagesAcute Pancreatitis PathoENo ratings yet
- Theragran (Multiple Vitamins)Document3 pagesTheragran (Multiple Vitamins)ENo ratings yet
- Buspar (Buspirone)Document1 pageBuspar (Buspirone)ENo ratings yet
- Clinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsDocument1 pageClinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsENo ratings yet
- FiberCon (Polycarbophil)Document1 pageFiberCon (Polycarbophil)ENo ratings yet
- Ecotrin (ASA 81mg)Document3 pagesEcotrin (ASA 81mg)E100% (1)
- Florinef (Fludrocortisone)Document3 pagesFlorinef (Fludrocortisone)E100% (1)
- ZofranDocument1 pageZofranKatie McPeek0% (1)
- Lexapro (Escitalopram Oxalate)Document2 pagesLexapro (Escitalopram Oxalate)ENo ratings yet
- Zocor (Simvastatin)Document3 pagesZocor (Simvastatin)E100% (1)
- Solu-Cortef (Hydrocortisone)Document3 pagesSolu-Cortef (Hydrocortisone)E100% (2)
- Duration of Intravenous N-Acetylcysteine in Acetaminophen PoisoningDocument19 pagesDuration of Intravenous N-Acetylcysteine in Acetaminophen Poisoninghinam27No ratings yet
- Medicine Prescriptions JavaDocument6 pagesMedicine Prescriptions Javaapi-636650239No ratings yet
- ASHP Cold Chain Management Resource Guide 1Document12 pagesASHP Cold Chain Management Resource Guide 1Grupo Logístico El SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Dosage Calculations Dosage CalculationsDocument25 pagesDosage Calculations Dosage CalculationsJay Clarrise Enteria ErlanoNo ratings yet
- IQ4I Research & Consultancy Published A New Report On "Biologics Outsourcing Global Market - Forecast To 2028Document9 pagesIQ4I Research & Consultancy Published A New Report On "Biologics Outsourcing Global Market - Forecast To 2028VinayNo ratings yet
- DK ResumeDocument5 pagesDK ResumeMandar NaikNo ratings yet
- List of Drugs For FinalsDocument3 pagesList of Drugs For FinalsLena EmataNo ratings yet
- Prescribe With Confidence. GenoScribe Live Software by Emgenex Is Integrating Pharmacogenetic Testing With Medication Risk Management SoftwareDocument3 pagesPrescribe With Confidence. GenoScribe Live Software by Emgenex Is Integrating Pharmacogenetic Testing With Medication Risk Management SoftwarePR.comNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Environmental Microbiology Data From Cleanroom SamplesDocument5 pagesAnalysis of Environmental Microbiology Data From Cleanroom SamplesFran141985No ratings yet
- Isocretic and Gradient EllusionDocument3 pagesIsocretic and Gradient EllusionNazmul Islam AbirNo ratings yet
- Special LipidsDocument24 pagesSpecial LipidsAshraf ShaikhNo ratings yet
- IPSF Statement:member State Mechanism On SubstandardDocument1 pageIPSF Statement:member State Mechanism On SubstandardInternational Pharmaceutical Students' Federation (IPSF)No ratings yet
- Prescription: Aneri Desai Department of PharmaceuticsDocument31 pagesPrescription: Aneri Desai Department of Pharmaceuticsaneri desaiNo ratings yet
- uk-spc-nexium-DRESS-update-GI 21 0009aDocument17 pagesuk-spc-nexium-DRESS-update-GI 21 0009aDeisy ClerkeNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0378517323003551 MainDocument12 pages1 s2.0 S0378517323003551 MainMiy AichNo ratings yet
- Integrated Treatment of Schizophrenia: Il Trattamento Integrato Della SchizofreniaDocument26 pagesIntegrated Treatment of Schizophrenia: Il Trattamento Integrato Della SchizofreniaArya DibyoNo ratings yet
- Formulation and Evaluation of Langsat Lansium Domesticum Corr Peel Ethanol Extracts Lotion As Anti Mosquito RepellentDocument10 pagesFormulation and Evaluation of Langsat Lansium Domesticum Corr Peel Ethanol Extracts Lotion As Anti Mosquito RepellentNurul Rizky VannyNo ratings yet
- Orig 1 S 000 Clin Pharm RDocument220 pagesOrig 1 S 000 Clin Pharm RAnonymous P2vzA4rwNo ratings yet
- Quimica de MXDocument800 pagesQuimica de MXkimerax100% (2)
- Anti Ulcerant StatDocument3 pagesAnti Ulcerant StatHumayera KabirNo ratings yet
- Compilation of Community Procedures On Inspections and Exchange of InformationDocument7 pagesCompilation of Community Procedures On Inspections and Exchange of InformationedsonleviNo ratings yet
- Medication AdministrationDocument8 pagesMedication AdministrationMarku LeeNo ratings yet