Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Acute Coronary Syndrom
Acute Coronary Syndrom
Uploaded by
Wendy MaeOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Acute Coronary Syndrom
Acute Coronary Syndrom
Uploaded by
Wendy MaeCopyright:
Available Formats
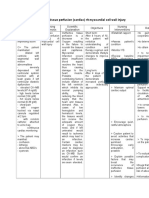
b) Nursing Care Plans
Problem#1: Acute Pain
Cues
S> Masakit ku salu, as verbalized by the pt. O> The patient may manifest: - tachycardia - tachypnea - sleep disturbance - facial grimaces - irritability >The patient manifested: - with oxygen hooked via nasal cannula regulated at 2 lpm with condomcatheter attached to urine bag - continuous cardiac monitoring
Nursing Diagnosis
Acute Pain related to increased lactic acid production secondary to decreased blood and oxygen supply to myocardium
Scientific Explanation
Acute Pain is the prioritized problem because it suggests ischemia which is very fatal. In acute myocardial infarction more commonly known as heart attack, a medical condition that occurs when the blood supply to a part of the heart is interrupted, most commonly due to rupture of a vulnerable plaque. The resulting ischemia or oxygen shortage causes damage and potential death of heart tissue. Because of decreased blood and oxygen supply to myocardium, shifting from aerobic to anaerobic metabolism happens thus there is an increase in lactic
Objectives
Short term: After 4 hours of NI, the patient will report relief of pain.
Nursing Interventions
>Establish rapport >Assess condition >Monitor VS patients
Rationale
>to gain trust and cooperation >to determine s/sx >to obtain baseline data >to determine precipitating factor/s > respirations may be increased as a result of pain and associate anxiety. >observations may/may not be congruent with verbal reports indicating need for further evaluation >to provide non pharmacological measures of relieving pain
Evaluation
Short term: After 4 hours of NI, the patient shall have verbalized methods that provide relief.
Long term: After 2 days of NI, the patient will demonstrate use of relaxation techniques and divertional activities as indicated for individual situation.
>Perform a comprehensive assessment of pain >Assess respirations, BP and heart rate with each episodes of chest pain. >Observe nonverbal cues
Long term: After 2 days of NI, the patient shall have demonstrated use of relaxation techniques and divertional activities as indicated for individual situation.
>Provide comfort measures such as back rub
134
acid production causing irritation to the heart muscle. This mechanism causes a feeling of pain which may activate the sympathetic nervous system thus causing tachypnea and tachycardia as a response. Due to the uncomfortable sensation, the patient may be seen with facial grimaces and irritability.
>Provide adequate rest periods >Maintain bed rest during pain, with position of comfort, maintain relaxing environment to promote calmness. >Prepare for the administration of medications, and monitor response to drug therapy. Notify physician if pain does not abate. >Review ways lessen pain to
>to prevent fatigue and promote relaxation >to reduce oxygen consumption and demand, to reduce competing stimuli and reduces anxiety
>pain control is a priority, as it indicates ischemia
>to wellness >Provide for individualized physical therapy/exercise programs that can be continued by the client when discharged >Discuss with SO(s) ways in which they can assist client and reduce precipitating factors that may cause or increase pain
promote
>promotes active, not passive role
>to wellness
promote
135
>Instruct patient/family in medication effects, side-effects, contraindications and symptoms to report
> to promote knowledge and compliance with therapeutic regimen and to alleviate fear of unknown
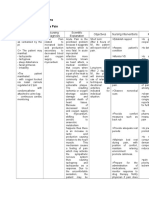
Problem#2: Ineffective airway clearance
Cues
S> The patient may verbalize: - dyspnea O> The patient manifested: - productive cough - fuzziness of the lung markings in both lungs - with oxygen hooked via nasal cannula regulated at 2 lpm with condom catheter attached to urine bag - continuous cardiac monitoring > The patient may manifest: changes in respiratory rate or rhythm
Nursing Diagnosis
Ineffective airway clearance r/t retained tracheobronchial secretions AEB presence of productive cough
Scientific Explanation
Pneumonia is an infectious disease characterized by inflammatory processes affecting the lung parenchyma. The invading organism causes symptoms, in part, by provoking an overly exuberant immune response in the lungs. Mucus production is increased which plugs the airway thus further compromising the airway clearance of the patient. This event may bring about cyanosis. In order to compensate, the patient may breathe
Objectives
Short term: After 4 hours of NI, the patient will demonstrate behaviors to improve or maintain airway patency.
Nursing Interventions
>Establish rapport >Assess condition >Monitor VS >Auscultate sounds breath patients
Rationale
>to gain trust and cooperation >to determine s/sx >to obtain baseline data > to note presence of adventitious breath sounds > use of accessory muscles to breathe indicates and abnormal increase in work of breathing > to identify infectious process and promote timely interventions
Evaluation
Short term: After 4 hours of NI, the patient shall have verbalized methods that provide relief.
Long term: After 4 days of NI, the patient will demonstrate absence/reduction of congestion with breath sounds clear, respirations noiseless and improved oxygen exchange.
>Assess respiratory movements and use of accessory muscles
>Observe for signs and symptoms of infection
Long term: After 2 days of NI, the patient shall have demonstrated use of relaxation techniques and divertional activities as indicated for individual situation.
136
diminished or adventitious breath sounds - cyanosis
rapidly in order to bring in more oxygen thus manifesting changes in respiratory rate or rhythm.
>Monitor chest radiograph reports >Use positioning by placing on a semihigh fowlers position >Elevate head of bed or change position every 2 hours and prn
>to monitor severity of disease
the the
>to facilitate lung expansion > to take advantage of gravity decreasing pressure on the diaphragm and enhancing drainage or ventilation to different lung segments >to aid in mobilization secretions >to secretions the of
>Maintain adequate hydration when possible > Perform nebulization and CPT as indicated >Institute suctioning as needed
loosen
> to clear airway when secretions are blocking the airway > to have patent airway through artificial means >to provide pharmacological management to treat condition
>Use pharyngeal pharyngeal as needed >Administer medication prescribed
nasooroairway
as
137
>Administer analgesics prescribed
as
>to maximize cough when pain is inhibiting effort > to promote continuity of care
>Refer to appropriate support groups
Problem#3: Impaired Gas Exchange
Cues
S> The patient may verbalize: - dyspnea O> The patient manifested: - productive cough - fuzziness of the lung markings in both lungs - with oxygen hooked via nasal cannula regulated at 2 lpm with condom catheter attached to urine bag - continuous cardiac monitoring > The patient may manifest: - confusion - lethargy - abnormal ABGs
Nursing Diagnosis
Impaired Gas Exchange r/t collection of secretions affecting oxygen exchange across alveolar membrane
Scientific Explanation
Pneumonia both affects ventilation and diffusion. An inflammatory reaction can occur in the alveoli, producing exudates that interfere in the diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide. White blood cells, mostly neutrophils, also migrate into the alveoli and fill the normally aircontaining spaces. Areas of the lungs are not adequately ventilated because of secretions and mucosal edemathat cause partial occlusion of the bronchi or alveoli, with a resultant
Objectives
Short term: After 4 hours of NI, the patient will demonstrate behaviors to improve or maintain airway patency.
Nursing Interventions
>Establish rapport >Assess condition >Monitor VS >Auscultate sounds breath patients
Rationale
>to gain trust and cooperation >to determine s/sx >to obtain baseline data >to note presence of adventitious breath sounds >use of accessory muscles to breathe indicates and abnormal increase in work of breathing >to identify infectious process and promote timely interventions
Evaluation
Short term: After 4 hours of NI, the patient shall have demonstrated behaviors to improve or maintain airway patency.
Long term: After 4 days of NI, the patient will demonstrate absence or reduction of congestion with breath sounds clear, respirations noiseless and improved oxygen exchange.
>Assess respiratory movements and use of accessory muscles
>Observe for signs and symptoms of infection
Long term: After 4 days of NI, the patient shall have demonstrated absence or reduction of congestion with breath sounds clear, respirations noiseless and improved oxygen exchange.
138
- cyanosis
decrease in alveolar oxygen tension. An imbalance in oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange may be evident in the patients arterial blood gases. A decrease in oxygen supply may cause confusion and lethargy.
>Monitor chest radiograph reports >Evaluate oximeter determine oxygenation pulse to
>to monitor severity of disease
the the
>to assess respiratory insufficiency >to facilitate lung expansion > to take advantage of gravity decreasing pressure on the diaphragm and enhancing drainage or ventilation to different lung segments >to aid in mobilization secretions the of
>Use positioning by placing on a semihigh fowlers position >Elevate head of bed or change position every 2 hours and prn
>Maintain adequate hydration when possible with precautions on fluid overload >Perform nebulization and CPT as indicated >Institute suctioning as needed
>to secretions
loosen
> to clear airway when secretions are blocking the airway > to have patent airway through
>Use pharyngeal
nasooro-
139
pharyngeal airway as needed >Encourage adequate rest and limit activities to within client tolerance >Administer medication prescribed >Administer analgesics prescribed as
artificial means > helps limit oxygen needs/consumption
>to provide pharmacological management to treat condition >to maximize cough when pain is inhibiting effort > to promote continuity of care
as
>Refer to appropriate support groups
Problem#4: Ineffective tissue perfusion (cardiac) r/t myocardial cell wall injury
Cues
S> The patient may verbalize: - sense of impending doom O> The patient manifested: dilated left ventricle with segmental wall motion abnormalities - severely depressed left ventricular systolic function with
Nursing Diagnosis
Ineffective tissue perfusion (cardiac) r/t myocardial cell wall injury
Scientific Explanation
Ineffective tissue perfusion is a decrease in Oxygen resulting in the failure to nourish the tissues and capillaries. Myocardial Infarction occurs when insufficient blood supply reaches the heart thus causing damage to the heart muscle. Possible
Objectives
Short term: After 4 hours of NI, the patient will verbalize understanding of condition and therapy regimen and demonstrate lifestyle changes to improve circulation.
Nursing Interventions
>Establish rapport >Assess condition >Monitor VS >Review baseline ABGs, electrolytes, BUN/Cr, cardiac enzymes > Assess for patients
Rationale
>to gain trust and cooperation >to determine s/sx >to obtain baseline data > to note degree of impairment/organ involvement > Early detection of
Evaluation
Short term: After 4 hours of NI, the patient shall have demonstrated behaviors to improve or maintain airway patency.
Long term:
Long term: After 4 days of NI,
140
at least grade 3 left ventricular diastolic dysfunction - elevated CKMB levels (47.4 ng/dl) - hgb levels below normal (124 g/dl) - hct levels below normal (0.39 g/dl) - chest pain - with oxygen hooked via nasal cannula regulated at 2 lpm with condom catheter attached to urine bag - continuous cardiac monitoring > The patient may manifest: - confusion - lethargy - abnormal ABGs - cyanosis
contributing factors include dilation of the left ventricle which inhibits its normal pumping ability, thus reducing the blood supply that the heart and tissues demand. Also, in cases of low hemoglobin and hematocrit levels, the tissues would not receive the adequate amount of oxygen they need, and if left untreated would result to ischemia which may lead to an infarction. Certain cardiac markers may be used to diagnose an infarction such as CK-MB. Such would confirm an infarction if levels are seen elevated.
After 4 days of NI, the patient will demonstrate increased perfusion as individually appropriate.
possible causative factors related to temporarily impaired arterial blood flow > Maintain optimal cardiac output
cause facilitates prompt, effective treatment. > This ensures adequate perfusion of vital organs. Support may be required to facilitate peripheral circulation (e.g., elevation of affected limb, antiembolism devices) > to conserve energy and lowers tissue O2 demands > to maximize tissue perfusion
the patient shall have demonstrated absence or reduction of congestion with breath sounds clear, respirations noiseless and improved oxygen exchange. .
> Encourage quiet, restful atmosphere > Caution patient to avoid activities that increase cardiac workload. Encourage early ambulation, if possible > Explain possible factors that may boost the occurrence of ineffective tissue perfusion > Identify changes r/t systemic or peripheral alterations in circulation >Administer
> To impose awareness on the patient and SO
> To evaluate if further complications will occur >Drugs that improve
141
medications caution
with
perfusion also carry the risk of adverse response >Information necessary for client to make informed choices about remedial risk factors and commitment to lifestyle changes, as appropriate, to prevent complications or manage symptoms when present >Facilitates management of hypertension which is a major risk factor in the damage of blood vessels or organ dysfunction.
>Discuss individual risk factors
>Instruct in blood pressure monitoring at home
Problem#5: Decreased Cardiac Output
Cues
S> the patient may verbalize: - shortness of breath /dyspnea - fatigue - anxiety O> The patient manifested: dilated left ventricle with
Nursing Diagnosis
Decreased cardiac output r/t altered stroke volume
Scientific Explanation
The hypoxic tissue in myocardial infarction within the border zone may become a site for generating arrhythmias. Infracted tissue does not contribute to tension generation during systole, and therefore can alter
Objectives
Short term: After 4 hours of NI, the patient will participate in activities that decrease the workload of the heart such as stress management or therapeutic medication regimen
Nursing Interventions
>Establish rapport >Assess condition >Monitor VS >Monitor ECG for patients
Rationale
> to gain trust and cooperation > to determine signs and symptoms > to obtain baseline data > decrease in
Evaluation
Short term: After 4 hours of NI, the patient shall have participated in activities that decrease the workload of the heart such as stress management or therapeutic
142
segmental wall motion abnormalities - severely depressed left ventricular systolic function with at least grade 3 left ventricular diastolic dysfunction - with oxygen hooked via nasal cannula regulated at 2 lpm with condomcatheter attached to urine bag - continuous cardiac monitoring The patient may manifest: - dysrhythmias - ECG changes - cyanosis - pallor - prolonged capillary refill decreased peripheral pulses - variations in blood pressure readings
ventricular systolic and diastolic function and disrupt electrical activity within the heart. Without improvement, the heart muscles may undergo remodeling such as hypertrophy, losing its normal pumping ability, thus may cause inadequate blood to meet the needs of the bodys tissues. Cardiac output and tissue perfusion are interrelated, thus a decrease in cardiac output may bring about cyanosis, pallor and prolonged capillary refill. There may also be fatigue and shortness of breath as there is not enough oxygen supplied to the tissues.
program
dysrrhythmias, conduction defects and for heart rate
cardiac output may result in changes in cardiac perfusion causing dysrhythmias > to note effectiveness medicines for of
medication regimen program Long term: After 4 days of NI, the patient shall have displayed hemodynamic stability AEB normalization of ECG tracings and blood pressure readings
Long term: After 4 days of NI, the patient will display hemodynamic stability AEB normalization of ECG tracings and blood pressure readings
>Monitor cardiac rhythms continuously >Encourage patient to decrease intake of caffeine, cola and chocolates >Observe skin color, temperature, capillary refill time and diaphoresis
> caffeine is a cardiac stimulant and may adversely affect cardiac function > peripheral vasoconstriction may result in pale, cool, clammy skin, with prolonged capillary refill time due to cardiac dysfunction and decreased cardiac output > to maintain adequate nutrition and fluid balance > to provide adequate oxygenation > to wellness for
>Monitor intake and output and calculate 24 hour fluid balance >Administer supplemental oxygen as indicated >Administer medicines prescribed by physician as the
promote
>Promote adequate
>
to
decrease
143
rest by decreasing stimuli providing quiet environment >Encourage changing positions slowly, dangling legs before standing >Instruct client & family on fluid and diet requirements and restrictions of sodium
oxygen consumption > to prevent occurrence of orthostatic hypotension > restrictions can assist with decrease in fluid retention and hypertension, thereby improving cardiac output > promotes knowledge and compliance with drug regimen
> instruct client and family on medications, side effects, contraindications and signs to report
Problem#6: Risk for Aspiration
Cues
S> O O> the patient manifested: - with productive cough - with presence of crackles on lower lobe of the right lung - with oxygen hooked via nasal cannula regulated at
Nursing Diagnosis
Risk for Aspiration r/t presence of retained secretions
Scientific Explanation
Pneumonai is a serious infection that affects the airsacs with accompanying secretions that may be expectorated. Sudden coughing may mobilize the secretions and may reach the airway which may cause distress to the
Objectives
Short term: After 4 hours of NI, the patient will be free from aspiration AEB having a patent airway
Nursing Interventions
>Establish rapport >Assess condition >Monitor VS > Monitor level of consciousness patients
Rationale
>to gain trust and cooperation >to determine signs and symptoms >to obtain baseline data. > A decreased level of consciousness is a prime risk factor
Evaluation
Short term: After 4 hours of NI, the patient shall be free from aspiration AEB having a patent airway
Long term:
144
2 lpm with condom catheter attached to urine bag - continuous cardiac monitoring >the patient may manifest: - respiratory distress
patients breathing which is fatal. Usually when someone aspirates they cough in an attempt to clear the food or fluid out of their lungs.
After 2 days of NI, the patient will experience no aspiration AEB noiseless respirations and clear breath sounds
for aspiration > Keep suction setup available and use as needed > Notify the physician or other health care provider immediately of noted decrease in cough and/or gag reflexes or difficulty in swallowing >Assist with postural drainage > This is necessary to maintain a patent airway > Early intervention protects the patients airway and prevents aspiration
Long term: After 2 days of NI, the patient shall have experienced no aspiration AEB noiseless respirations and clear breath sounds
>to mobilize thickened secretions which may cause impairment in swallowing >the rested may have difficulty swallowing client less in
>Provide a period prior feeding time
rest to
>Minimize use of sedatives/hypnotics whenever possible. >Provide information on the effect of aspiration on the lungs
>these agents can impair coughing or swallowing >severe coughing and cyanosis associated with eating or drinking or changes in vocal quality after swallowing indicates onset of respiratory symptoms associated with aspiration and requires immediate
145
interventions. >Refer >to promote continuity of care
Problem#7: Anxiety
Cues
S= O O= pt. manifested -with good skin turgor -with pale palpebral conjunctiva -with capillary refill 2 seconds - Cold clammy skin -with oxygen hooked via nasal cannula regulated at 2 lpm -with condom catheter attached to urine bag -continuous cardiac monitoring
Nursing Diagnosis
Anxiety r/t perceived /actual threat of death, pain, possible lifestyle changes by restlessness
Scientific Explanation
Coping with the pain and emotional trauma is difficult. Patient may fear death and or be anxious about immediate environment. Ongoing anxiety (related to concerns about impact of heart attack on future lifestyle, matters left unattended/unresolved and effects of illness on family) may be present in varying degrees for some time and maybe manifested by symptoms of depression such as sleep disturbance and restlessness.
Objectives
Short term: After 3-4 hours of nursing intervention pt will identify healthy ways to deal with and express anxiety.
Nursing Interventions
>Establish rapport >Assess patients condition >Monitor vital signs
Rationale
>To gain trust and cooperation >To monitor physiologic condition >To have baseline data >to help pt. regain control of own behavior
Evaluation
Short term: After 3-4 hours of nursing intervention pt shall have identified healthy ways to deal with and express anxiety.
Long term: After 3 days of nursing intervention pt. will appear relaxed and report anxiety is reduced to a manageable level.
>Observe for verbal/non-verbal signs of anxiety, and stay with the pt. Intervene if pt. displays destructive behavior. >Maintain confident manner (without false reassurance) >Orient pt/SO to routine procedures and expected activities >Provide privacy for pt. and SO.
Long term: >honest explanation can alleviate anxiety >predictability and participation can decrease anxiety >Allows needed time for personal expression of After 3 days of nursing intervention pt. shall have appeared relaxed and reported anxiety is reduced to a manageable level.
Pt. may manifest: -Sleep disturbance -Restlessness -Tachycardia -Tachypnea
146
feelings, may enhance mutual support and promote more adaptive behaviors. >Provide rest periods/uninterrupted sleep, quiet surroundings. >Raise side rails >Emphasize importance of adequate nutritional intake. >Regulate and monitor IV fluid. >Administer medications as ordered > To maintain general good health. >To promote fluid management. >For optimum wellness >Conserves energy and enhances coping abilities. >to provide safety
Problem#8: Fatigue
Cues
S > agad ako napapagod, tulad pag maglalakad at maliligo ako O> The patient manifests: cold clammy skin dry skin weakness
Nursing Diagnosis
Fatigue r/t decrease oxygenation and perfusion 2 pulmonary congestion
Scientific Explanation
Fatigue is an overwhelming sustained sense of exhaustion and decreased capacity for physical and mental work at usual level. Insulin is secreted by beta cells, which are one of four types of cells
Objectives
Short term: After 3 hours of nursing interventions patient will be able to perform ADLs and participate in desired activities at level of ability. Long term:
Nursing Interventions
>Establish rapport
Rationale
>to gain the trust and cooperation of the patient. >to have a general health status of the patient. >to obtain baseline data
Evaluation
Short term: After 3 hours nursing interventions patient shall have performed ADLs and participate in desired activities at level of ability.
>Assess condition
patients
> Monitor vital signs
147
even with simple activities capillary refill < 3 sec. crackles on the right lung field v/s taken and recorded as follows: T=36C, RR=21 cpm, PR=65 bpm, BP=130/80 mmHg.
The patient may manifests: restlessness tachypnea
in the islets of Langerhans in the pancreas, insulin is a storage hormone, when a person eats a meal, insulin secretion increases and move glucose to the blood, into muscle, liver, and fat cells. Due to DM type 2 there is insulin resistance or impaired insulin secretion which results in the inhibition of the transport and metabolism of glucose into energy leading to easy fatigability AEB by pt. weakness even doing activities of daily living.
After 1 day of nursing interventions patient will report improve sense of energy.
> Instruct patient to increase fluid intake up to 8- 10 glasses of water > Instruct to sit instead of standing during activities or shower >Instruct patient to increase intake of vitamin or iron supplementation like juice >Stretch linens >Assist with selfcare needs like keep bed in low position >Stress proper hand washing >Administer as ordered. drugs
> a source of energy and to prevent dehydration > to energy conserve
Long term: After 1 day of nursing interventions patient shall have reported improve sense of energy.
> to promote overall health measures.
>to provide comfort >To energy conserve
>to prevent infection. > for wellness optimum
Problem#9: Risk for Infection
Cues
S> O O> The patient manifested: - productive cough
Nursing Diagnosis
Risk for Infection r/t inadequate primary defenses (decreased ciliary action)
Scientific Explanation
Upper airway characteristics normally prevent potentially infectious particles from
Objectives
Short term: After 2 hours of nursing intervention patient will identify interventions to
Nursing Interventions
>Establish rapport >Assess condition patients
Rationale
>to gain trust and cooperation >to determine s/sx
Evaluation
Short term: After 2 hours of NI, the patient shall have identified
148
- with oxygen hooked via nasal cannula regulated at 2 lpm with condom catheter attached to urine bag continuous cardiac monitoring > The patient may manifest: - fever - chills - DOB - increase in RR, PR - increase in WBC levels and neutrophils
reaching the sterile lower respiratory tract. Pneumonia involves the inflammation of the lung parenchyma which eventually leads to a decreased ciliary action and may further lead to stasis of respiratory secretions the client is at risk for the spread of infection since the continuous production of mucus secretions is a perfect breeding place for microorganisms. And if the body does not cope well the infection may spread to the rest of the body.
prevent/reduce risk/spread of/secondary infection.
>Monitor VS >Obtain appropriate tissue/fluid specimens
>to obtain baseline data >for observation for culture and sensitivity testing > it is a first line defense against nosocomial infection or cross contamination >for mobilization of respiratory secretions >to limit exposures, thus reduce cross contamination
interventions to prevent/reduce risk/spread of/secondary infection..
Long term: After 4 days of NI, the patient will achieve timely resolution of current infection without complications.
>Stress proper hand washing techniques by all care givers between therapies and client >Encourage coughing &, position change >Monitor clients visitors or caregivers for presence of respiratory illnesses. Offer masks/tissues to client/visitors who are coughing or sneezing >Encourage deep breathing, coughing and frequent position changes
Long term: After 4 days of NI, the patient shall have achieved timely resolution of current infection without complications
>for mobilization of secretions and prevention of aspiration or respiratory infection > Facilitates healing process and enhances natural resistance. >to determine effectiveness of
> Encourage adequate rest balanced with moderate activity. Promote adequate nutritional intake >Administer or monitor medication regimen
149
and note response
clients
therapy and presence of side effects >to correct nor reduce existing risk factors > Delayed recovery or increase in severity of symptoms suggests resistance to antibiotics or secondary infection >to wellness promote
>Administer prophylactic as indicated
antibiotic
> Investigate sudden changes/deterioration in condition, such as increasing chest pain, extra heart sounds, altered sensorium, recurring fever, changes in sputum characteristics >Review individual nutritional needs, appropriate exercise program and need for rest >Emphasize needs for taking antiviral or antibiotics as directed
>Premature discontinuation of treatment when client feels well may result in return of infection and may potentiate drug-resistant strains >to increase awareness of and prevention of aommunicable diseases
>Provide information or involve in appropriate community and national education programs
150
Problem#10: Activity Intolerance
Cues
S> The pt. may verbalize: - exertional dyspnea or discomfort - reports of fatigue or weakness O> the patient manifested: - need for assistance upon movement - limited range of motion - with oxygen hooked via nasal cannula regulated at 2 lpm with condomcatheter attached to urine bag - continuous cardiac monitoring The patient may manifest: tachypnea and increased blood pressure upon performance of activities
Nursing Diagnosis
Activity Intolerance r/t cardiac dysfunction, imbalance in oxygen supply and consumption as evidenced by shortness of breath upon exertion
Scientific Explanation
The underlying mechanism of a heart attack is the destruction of heart muscle cells due to a lack of oxygen. If these cells are not supplied with sufficient oxygen by the coronary arteries to meet their metabolic demands, they die by a process called infarction. The decrease in blood supply may bring about necrosis of the heart muscle which would make it weaker as a pump. As a result, the pumping mechanism of the heart will be ineffective thus giving the individual an insufficient supply of blood, bringing about an inefficient supply of oxygen to the tissues thus
Objectives
Short term: After 4 hours of NI, the patient will use identified techniques to increase activity tolerance.
Nursing Interventions
>Establish rapport >Assess condition >Monitor VS patients
Rationale
>to gain trust and cooperation >to determine signs and symptoms >changes in VS assist with monitoring physiologic responses to increase in activity. >alleviation of factors that are known to create intolerance can assist with development of an activity level program > to help give the patient a feeling of self-worth and wellbeing > to decrease energy expenditure and fatigue
Evaluation
Short term: After 4 hours of NI, the patient shall have used identified techniques to increase activity tolerance.
Long term: After 4 days of NI, the patient will be able to increase and achieve desired activity level, progressively, with no intolerance symptoms noted, such as respiratory compromise.
>Identify causative factors leading to intolerance of activity
>Encourage patient to assist with planning activities, with rest periods as necessary >Instruct patient in energy conservation techniques
Long term: After 4 days of NI, the patient shall have increased and achieved desired activity level, progressively, with no intolerance symptoms noted, such as respiratory compromise
151
- pallor - cyanosis - ischemic changes
ECG
leading to easy fatigability upon simple exertions. If the condition becomes severe, the patient may have inability in performing activities and show changes in vital signs upon performance of activities. Also, there could be changes in the ECG showing signs of ischemia.
>Assist with active or passive ROM exercises >Assist patient with ambulation, as ordered, with progressive increases as patients tolerance permits >Adjust activities according to patients tolerance >Plan care with rest periods between activities >Provide positive atmosphere, while acknowledging difficulty of the situation for the patient >Assist patient with activities and monitor use of assistive devices >Promote comfort measures and provide for relief of pain >Provide referral to other disciplines as indicated
> to maintain joint mobility and muscle tone > to gradually increase the body to compensate for the increase in overload
> to prevent overexertion > to reduce fatigue
> helps to minimize frustration, rechannel activities
> to protect client from injury
> to enhance ability to participate in activities > to develop individually appropriate
152
treatment regimen > Instruct client/SO in monitoring response to activity and recognizing signs and symptoms > may indicate a need in alteration of activities
Problem#11: Self Care Deficit r/t weakness
Cues
S> O> The manifests: patient
Nursing Diagnosis
Self care deficit related to weakness or tiredness.
Scientific Explanation
The nurse may encounter the patient with self care deficit in the hospital. The deficit may be a result of transient limitations, such as those one might experience while recovering from surgery or the result of the progressive deterioration that erodes the individuals ability or willingness to perform the activities required to care for himself. Careful examination of the patients deficit is required in order to be certain that the patient is not failing self-care because of lack of materials with arranging the
Objectives
Short term: After 3 hours of nursing interventions patient will be able to verbalize understanding on the importance of self-care. Long term: After 1 day of nursing interventions patient will safely perform self-care activities.
Nursing Interventions
>Establish rapport
Rationale
>to gain the trust and cooperation of the patient. >to have a general health status of the patient. >to obtain baseline data > to encourage and build on successes
Evaluation
Short term: After 3 hours nursing interventions patient shall have verbalized the importance of selfcare.
cold clammy skin good skin turgor capillary refill < 3 sec. irritability weakness when taking a bath easy fatigability even only doing ADLs
>Assess condition
patients
> Monitor vital signs >Assist with necessary adaptations to accomplish ADLs > Arrange for assistive devices as necessary (seat/grab bars) >Instruct patient to increase fluid intake up to 8- 10 glasses of water >Encourage food choices reflecting
> to prevent injury
Long term: After 1 day of nursing interventions patient shall have performed safely self-care activities.
The patient manifests:
may
> to prevent dehydration and a source of energy > to increase energy
restlessness
153
environment to suit the patients physical limitations.
individual likes and abilities that meet nutritional needs >Stretch linens >Stress proper hand washing >Instructed patient to perform good hygiene >Administer as ordered. drugs >to provide comfort >to prevent infection. >To relieve patient and provide comfort > for wellness optimum
154
You might also like
- Learning Plan Nursing PregradDocument3 pagesLearning Plan Nursing Pregradapi-25180064033% (3)
- Nursing Diagnosis Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument11 pagesNursing Diagnosis Diabetic Ketoacidosismonisha50% (4)
- Acute Coronary Syndrome NCP 02Document6 pagesAcute Coronary Syndrome NCP 02AgronaSlaughterNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary Syndrome NCP 01Document5 pagesAcute Coronary Syndrome NCP 01AgronaSlaughter0% (1)
- Coronary Artery Disease Care PlanDocument2 pagesCoronary Artery Disease Care PlanDanelle Harrison, RN100% (2)
- Controlling Microbial Growth in VitroDocument65 pagesControlling Microbial Growth in VitroCarl Elexer Cuyugan Ano100% (16)
- NCP - Ineffective Airway Clearance R/T Retained Secretions 2° BPNDocument1 pageNCP - Ineffective Airway Clearance R/T Retained Secretions 2° BPNCarl Elexer Cuyugan Ano100% (2)
- NCP - Ineffective Airway Clearance R/T Retained Secretions 2° BPNDocument1 pageNCP - Ineffective Airway Clearance R/T Retained Secretions 2° BPNCarl Elexer Cuyugan Ano100% (2)
- Healthcare - Nursing Care Plan - Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument4 pagesHealthcare - Nursing Care Plan - Decreased Cardiac OutputBenjamin CañalitaNo ratings yet
- NCP. Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument5 pagesNCP. Decreased Cardiac OutputJillian AmponinNo ratings yet
- Care Plan Unstable AnginaDocument4 pagesCare Plan Unstable Anginaالغزال الذهبي50% (6)
- NCP AnginaDocument3 pagesNCP AnginaShie LA100% (1)
- NURSING CARE PLAN For Myocardial InfarctionDocument16 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN For Myocardial InfarctionFreisanChenMandumotan100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For A Patient With Pleural EffusionDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For A Patient With Pleural Effusionmac042250% (4)
- Myocarditis NCP 2Document8 pagesMyocarditis NCP 2astro_aaron117375% (4)
- Buergers Disease NCPDocument5 pagesBuergers Disease NCPNikko Dela Cruz100% (2)
- Activity Intolerance Related To Decrease Blood FlowDocument3 pagesActivity Intolerance Related To Decrease Blood FlowDarkCeades100% (3)
- SAMPLE NCP For Angina PectorisDocument3 pagesSAMPLE NCP For Angina Pectorisseanne_may100% (4)
- NCP (Icu)Document2 pagesNCP (Icu)jessie_nuñez_263% (8)
- Family Case Analysis 2Document98 pagesFamily Case Analysis 2Carl Elexer Cuyugan Ano50% (2)
- PainDocument44 pagesPainCarl Elexer Cuyugan Ano100% (4)
- NCP - Risk For Impaired Skin Integrity R/T Dry Skin and Behaviors That May Lead To Skin Integrity Impairment AEB Scratching of ScabsDocument1 pageNCP - Risk For Impaired Skin Integrity R/T Dry Skin and Behaviors That May Lead To Skin Integrity Impairment AEB Scratching of ScabsCarl Elexer Cuyugan Ano100% (4)
- Seminar InsightsDocument2 pagesSeminar InsightsMark Lorenzo Torres67% (6)
- NCP For Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument3 pagesNCP For Acute Coronary Syndromesarahtot75% (4)
- NCP For SVTDocument6 pagesNCP For SVTRen VillenaNo ratings yet
- NCP For AnginaDocument5 pagesNCP For Anginacarizza_bernas100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument7 pagesNursing Care PlanGem Ma100% (7)
- NCP FVDDocument2 pagesNCP FVDMarlon AnryNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationChristine LebicoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For A Patient With Pleural EffusionDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For A Patient With Pleural EffusionTrixie Anne GamotinNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPElbert Vierneza100% (2)
- Nanda NCP BasedDocument14 pagesNanda NCP Baseddeliejoyce100% (1)
- NCP - Excess Fluid Volume (Aortic Stenosis)Document3 pagesNCP - Excess Fluid Volume (Aortic Stenosis)Daniel Vergara Arce100% (3)
- NCP Impaired Gas Exhange CHEST INJURYDocument4 pagesNCP Impaired Gas Exhange CHEST INJURYMa. Elaine Carla Tating100% (2)
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument2 pagesDecreased Cardiac OutputEdrianne J.100% (2)
- NCP 1Document1 pageNCP 1hsiriaNo ratings yet
- Dka NCPDocument3 pagesDka NCPMaryjoy Gabriellee De La CruzNo ratings yet
- NCP Heart BlockDocument3 pagesNCP Heart BlockEköw Santiago Javier33% (3)
- NCP Pleural EffusionDocument3 pagesNCP Pleural EffusionEli Xma100% (1)
- Lung Cancer (Nursing Care)Document5 pagesLung Cancer (Nursing Care)heiyuNo ratings yet
- NCP Inffective Tissue PerfusionDocument3 pagesNCP Inffective Tissue PerfusionPaul Cubacub0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan (NCP) For A Patient With Angina PectorisDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan (NCP) For A Patient With Angina PectorisKian Herrera100% (1)
- CP Intestinal Obstruction Nursing Care PlanDocument7 pagesCP Intestinal Obstruction Nursing Care PlanShiella Heart MalanaNo ratings yet
- Myocardial InfarctionDocument5 pagesMyocardial InfarctionDharline Abbygale Garvida AgullanaNo ratings yet
- Risk For Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument3 pagesRisk For Decreased Cardiac OutputSid Artemis FriasNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument7 pagesNCPChris Denver BancaleNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument7 pagesNCPJo Chiko FlorendoNo ratings yet
- Uti NCPDocument1 pageUti NCPAngelique Vinoya100% (2)
- Decrease Cardiac OutputDocument6 pagesDecrease Cardiac OutputGerardeanne ReposarNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPRachel PerandoNo ratings yet
- NCP - Risk For Infection - DMDocument3 pagesNCP - Risk For Infection - DMcessi18100% (1)
- NURSING CARE PLAN Decreased Cardiac Output FnaDocument2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN Decreased Cardiac Output FnaAce Dioso Tubasco100% (1)
- NCP For CTTDocument1 pageNCP For CTTJen Rhae LimNo ratings yet
- NCP For Mi PainDocument2 pagesNCP For Mi PainKahMallariNo ratings yet
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument2 pagesDecreased Cardiac OutputDheza Rodis Santos0% (1)
- NCPDocument15 pagesNCPCamille PinedaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective DataDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Subjective DataAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN - Myocardial Infarction Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN - Myocardial Infarction Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationsweethoney220% (1)
- NCP AneurysmDocument4 pagesNCP AneurysmJanielle Christine Monsalud100% (1)
- NCP For CHF 3 Activity IntoleranceDocument2 pagesNCP For CHF 3 Activity IntoleranceAngelyn ArdinesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 1 DiagDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan 1 Diagguysornngam100% (1)
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationsDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationsAjay SupanNo ratings yet
- NCP Cad ElectiveDocument1 pageNCP Cad ElectivejoegeNo ratings yet
- Data Nursing Diagnos IS Scientific Backgrou ND Goal/Objective Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesData Nursing Diagnos IS Scientific Backgrou ND Goal/Objective Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDienizs LabiniNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Tissue Perfusion Related To Decrease Hemoglobin Concentration in The BloodDocument2 pagesIneffective Tissue Perfusion Related To Decrease Hemoglobin Concentration in The BloodKit Alizon BarredoNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute PainDocument3 pagesNCP Acute PainNathalie kate petallarNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objective Interventions Rationale Expected Outcome Short Term: Short TermDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objective Interventions Rationale Expected Outcome Short Term: Short TermGensen Cu RoxasNo ratings yet
- NCP 1: Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion Related To Interruption of Blood Flow Secondary To Cerebrovascular AccidentDocument14 pagesNCP 1: Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion Related To Interruption of Blood Flow Secondary To Cerebrovascular AccidentKyle Jingco100% (2)
- B. Pathophysiology A) Schematic Diagram (Book - Based) : Wasting Blood Glucose LevelDocument2 pagesB. Pathophysiology A) Schematic Diagram (Book - Based) : Wasting Blood Glucose LevelCarl Elexer Cuyugan Ano50% (2)
- Hydatidiform Mole Study GuideDocument4 pagesHydatidiform Mole Study GuideCarl Elexer Cuyugan AnoNo ratings yet
- "Acute Coronary Syndrome Non ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction, Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes Mellitus Type 2, and Community Acquired Pneumonia" IntroDocument6 pages"Acute Coronary Syndrome Non ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction, Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes Mellitus Type 2, and Community Acquired Pneumonia" IntroCarl Elexer Cuyugan AnoNo ratings yet
- CarlncmDocument2 pagesCarlncmCarl Elexer Cuyugan AnoNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Pregnancy Study GuideDocument5 pagesEctopic Pregnancy Study GuideCarl Elexer Cuyugan Ano100% (1)
- Diversity of Microorganisms 2Document71 pagesDiversity of Microorganisms 2Carl Elexer Cuyugan Ano100% (4)
- Nurse0710 PampangaDocument135 pagesNurse0710 PampangaproffsgNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Sepsis (Sepsis Neonatorum) Medical Management Not Included...Document29 pagesNeonatal Sepsis (Sepsis Neonatorum) Medical Management Not Included...Carl Elexer Cuyugan Ano100% (3)
- Traumatic Brain Injuries Study GuideDocument18 pagesTraumatic Brain Injuries Study GuideCarl Elexer Cuyugan Ano100% (1)
- Iii. Patient and His Illness A. Review of Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument13 pagesIii. Patient and His Illness A. Review of Anatomy and PhysiologyCarl Elexer Cuyugan AnoNo ratings yet
- "Acute Coronary Syndrome Non ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction, Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes Mellitus Type 2, and Community Acquired Pneumonia" Client Centered PathophysiologyDocument3 pages"Acute Coronary Syndrome Non ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction, Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes Mellitus Type 2, and Community Acquired Pneumonia" Client Centered PathophysiologyCarl Elexer Cuyugan Ano50% (2)
- Shapes and Arrangements of BacteriaDocument22 pagesShapes and Arrangements of BacteriaCarl Elexer Cuyugan Ano100% (3)
- Microbial Physiology and Genetics Part 1Document43 pagesMicrobial Physiology and Genetics Part 1Carl Elexer Cuyugan Ano100% (7)
- Hypertension Study GuideDocument4 pagesHypertension Study GuideCarl Elexer Cuyugan AnoNo ratings yet
- Craniotomy Surgical Case ReportDocument58 pagesCraniotomy Surgical Case ReportCarl Elexer Cuyugan Ano100% (9)
- Principles of Antimicrobial Therapy Part 1Document83 pagesPrinciples of Antimicrobial Therapy Part 1Carl Elexer Cuyugan Ano100% (1)
- Diversity of Microorganisms 1 - AcellularDocument39 pagesDiversity of Microorganisms 1 - AcellularCarl Elexer Cuyugan Ano100% (1)
- Diversity of Microorganisms 1 - ProkaryoticDocument45 pagesDiversity of Microorganisms 1 - ProkaryoticCarl Elexer Cuyugan Ano100% (6)
- The Metabolic and Endocrine Systems NotesDocument9 pagesThe Metabolic and Endocrine Systems NotesCarl Elexer Cuyugan Ano100% (2)
- Cell Structure and TaxonomyDocument50 pagesCell Structure and TaxonomyCarl Elexer Cuyugan AnoNo ratings yet
- Basic Drug Computations Part 1Document8 pagesBasic Drug Computations Part 1Carl Elexer Cuyugan Ano100% (4)
- Gastrointestinal Tract System NotesDocument8 pagesGastrointestinal Tract System NotesCarl Elexer Cuyugan Ano100% (1)
- Complications of Intravenous TherapyDocument37 pagesComplications of Intravenous TherapyCarl Elexer Cuyugan Ano100% (3)
- Basic Computations 2 IV & IVFDocument37 pagesBasic Computations 2 IV & IVFCarl Elexer Cuyugan Ano100% (5)
- The Contemporary Relational Supervisor 2Nd Edition Robert Ernest Lee Thorana Strever Nelson Online Ebook Texxtbook Full Chapter PDFDocument69 pagesThe Contemporary Relational Supervisor 2Nd Edition Robert Ernest Lee Thorana Strever Nelson Online Ebook Texxtbook Full Chapter PDFwilliam.roper672100% (6)
- Ch. 2 - Questions Flashcards by Brian Weldon - BrainscapeDocument10 pagesCh. 2 - Questions Flashcards by Brian Weldon - BrainscapeKay MendozaNo ratings yet
- Mental Health & Psychiatric NursingDocument617 pagesMental Health & Psychiatric NursingEVERYTHING TvNo ratings yet
- Week 7 ExamDocument5 pagesWeek 7 ExamKevin NyasogoNo ratings yet
- Safety Leadership NewDocument35 pagesSafety Leadership NewdhabriNo ratings yet
- Catalogo BlueSAODocument132 pagesCatalogo BlueSAOJuan CeballosNo ratings yet
- 21.0 - Permit To Work Systems v3.0 English (Full Permission)Document18 pages21.0 - Permit To Work Systems v3.0 English (Full Permission)Amal JagadiNo ratings yet
- NODocument8 pagesNOAbu Abbas AiyubNo ratings yet
- Новий Microsoft Word DocumentDocument3 pagesНовий Microsoft Word Documentwood swordNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cleft Lip and Palate: Prof. Adetokunbo Adebola Aminu Kano TH / Bayero University, Kano, NigeriaDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Cleft Lip and Palate: Prof. Adetokunbo Adebola Aminu Kano TH / Bayero University, Kano, NigeriaYuan MarcelitaNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia PPT NewDocument22 pagesPneumonia PPT NewOsuri MapitigamaNo ratings yet
- Redondo, I., Russell, C. y Bernal, J. (2018)Document9 pagesRedondo, I., Russell, C. y Bernal, J. (2018)Marcos EspindolaNo ratings yet
- Classicaland Operant Conditioning ANSWERSDocument3 pagesClassicaland Operant Conditioning ANSWERSNeurotic AlienNo ratings yet
- Instruction ManualDocument46 pagesInstruction ManualNaufrago WilliesNo ratings yet
- Ayusante CatalogueDocument12 pagesAyusante CatalogueAnkit Modi0% (1)
- Mood DisordersDocument25 pagesMood DisordersRence IremedioNo ratings yet
- Ielts Speaking 1 - Topic Food and HealthDocument1 pageIelts Speaking 1 - Topic Food and HealthDuyen TranNo ratings yet
- Articulo en Ingles de ErgonomiaDocument4 pagesArticulo en Ingles de ErgonomiaNohora Alexandra PINZON PLAZASNo ratings yet
- 01/25/2021 - Ernst & Young BC LTC COVID-19 Response ReviewDocument28 pages01/25/2021 - Ernst & Young BC LTC COVID-19 Response ReviewThe Vancouver SunNo ratings yet
- NURS 682 Care Coordination and Role of The Advanced Practice NurseDocument9 pagesNURS 682 Care Coordination and Role of The Advanced Practice NurseParya VNo ratings yet
- Deparmental ListDocument39 pagesDeparmental ListLiaquat RaniaNo ratings yet
- Tarot BookDocument64 pagesTarot BookK BhauNo ratings yet
- Contactos Bioseguridad Covid19Document10 pagesContactos Bioseguridad Covid19Aldo Ezequilla RamirezNo ratings yet
- Cl_XII_Summer_vacation_HW(Eng_Core)[1]Document6 pagesCl_XII_Summer_vacation_HW(Eng_Core)[1]kuntalsaikia82No ratings yet
- AACN BSN Essentials PaperDocument9 pagesAACN BSN Essentials PaperSikany S EmmanNo ratings yet
- CITATION Ann12 /L 17417Document3 pagesCITATION Ann12 /L 17417The seriNo ratings yet
- 5th Engineers Responsibility and SafetyDocument49 pages5th Engineers Responsibility and SafetyayanNo ratings yet
- April 9, 2021 Strathmore TimesDocument12 pagesApril 9, 2021 Strathmore TimesStrathmore TimesNo ratings yet














































































































![Cl_XII_Summer_vacation_HW(Eng_Core)[1]](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/738917279/149x198/034399bf94/1717437509?v=1)



